Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians
Although used interchangeably, reptiles and amphibians are two separate classes of animals that are distinct in their characteristics. Reptiles are cold-blooded animals that have water-proof scales on their skins and have the ability to crawl and lay eggs on the ground. Amphibians are cold-blooded animals that have a dual capability to live on both land and water. They have water permeable, moist skin and their larval and adult forms are different in appearance.

What are reptiles?
Definition:
Reptiles are cold-blooded animals that have water-proof scales on their skins, and have an ability to crawl and lay eggs on the ground.
Origin and number of species:
The origin of reptiles dates back to as old as 315 million years. 6500 species of reptiles have been identified so far.
Habitat:
Reptiles are terrestrial animals. Most of them cannot survive underwater, however, a few exceptions are crocodiles, turtles, and alligators.
Respiration:
Reptiles rely on their lungs for respiration.
Skin:
Reptiles have a water-impermeable skin cover that has a layer of scales. Some reptiles have hard shells as well.
Fertilization:
Reptiles replicate by internal fertilization.
Eggs:
The eggs laid by reptiles have a rubbery, often leathery outer covering and are laid on land.

What are amphibians?
Definition:
Amphibians are cold-blooded animals that have a dual capability to live on both land and water. They have water permeable, moist skin and their larval and adult forms are different in appearance.
Origin and number of species:
The origin of amphibians dates back to as old as 370 million years and there are about 5500 species of amphibians present worldwide.
Habitat:
Amphibians in their larval stage persist and thrive underwater, however they transition their habitat to land once they grow up and in their adult forms.
Respiration:
Amphibians use gills in their larval stages for breathing, however they develop and use lungs in their adult versions for breathing.
Skin:
Amphibians have wet, water-permeable skin that has a bulk of mucus and poison glands all over it.
Fertilization:
Amphibians replicate by external fertilization.
Eggs:
Amphibians discharge their eggs in the water and are jellylike, and see-through in appearance.
Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians
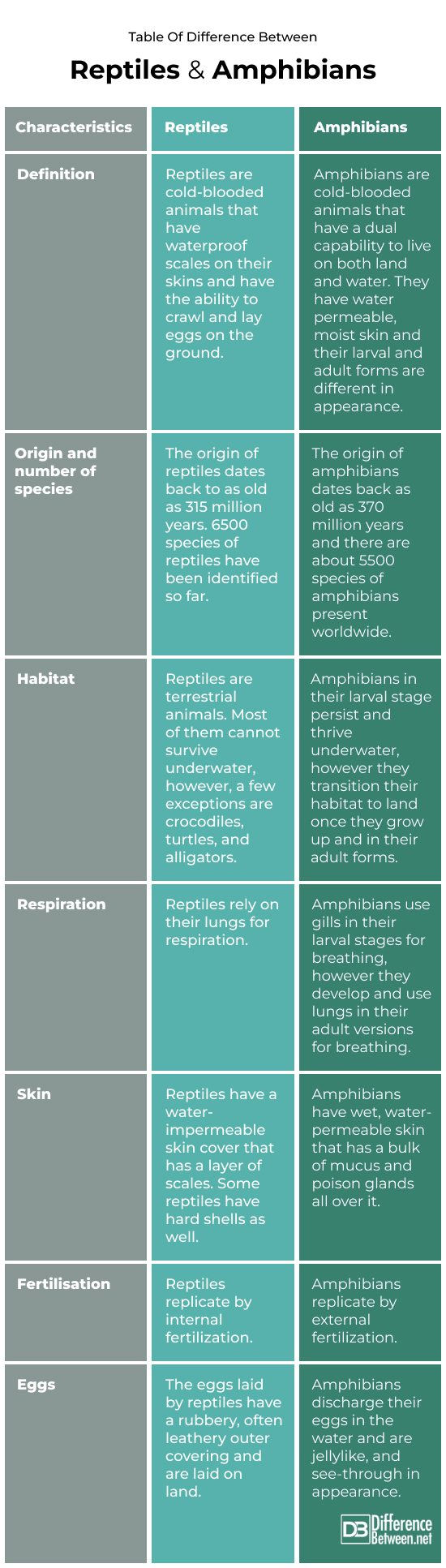
Definition:
Reptiles are cold-blooded animals that have water-proof scales on their skins and have the ability to crawl and lay eggs on the ground. Amphibians are cold-blooded animals that have a dual capability to live on both land and water. They have water permeable, moist skin and their larval and adult forms are different in appearance.
Origin and number of species:
The origin of reptiles dates back to as old as 315 million years. 6500 species of reptiles have been identified so far. The origin of amphibians dates back as old as 370 million years and there are about 5500 species of amphibians present worldwide.
Habitat:
Reptiles are terrestrial animals. Most of them cannot survive underwater, however, a few exceptions are crocodiles, turtles, and alligators.
Amphibians in their larval stage persist and thrive underwater, however they transition their habitat to land once they grow up and in their adult forms.
Respiration:
Reptiles rely on their lungs for respiration.
Amphibians use gills in their larval stages for breathing, however they develop and use lungs in their adult versions for breathing.
Skin:
Reptiles have a water-impermeable skin cover that has a layer of scales. Some reptiles have hard shells as well.
Amphibians have wet, water-permeable skin that has a bulk of mucus and poison glands all over it.
Fertilization:
Reptiles replicate by internal fertilization. Amphibians replicate by external fertilization.
Eggs:
The eggs laid by reptiles have a rubbery, often leathery outer covering and are laid on land. Amphibians discharge their eggs in the water and are jellylike, and see-through in appearance.
Table of Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians
FAQs
What is the difference between mammals, reptiles, and amphibians?
Mammals are warm-blooded animals that give birth to live babies. Reptiles are cold-blooded animals that have water-proof scales on their skins and have the ability to crawl and lay eggs on the ground. Amphibians are cold-blooded animals that have a dual capability to live on both land and water.
How are ancient amphibians and reptiles different?
Reptiles are cold-blooded animals that have water-proof scales on their skins and have the ability to crawl and lay eggs on the ground. Amphibians are cold-blooded animals that have a dual capability to live on both land and water.
What are the 10 characteristics of amphibians?
Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrate animals that have a dual capability to live on both land and water. They perform external fertilization and have primitive lungs. They have water permeable, moist skin and their larval and adult forms are different in appearance. Amphibians discharge their eggs in the water and are jellylike, and see-through in appearance.
What are the 5 differences between mammals and reptiles?
Mammals are warm-blooded animals that give birth to live babies. They are covered with hair or fur. They can regulate body temperature. They have a four-chambered heart Reptiles are cold-blooded animals that have water-proof scales on their skins, can crawl and lay eggs on the ground, and cannot regulate their body temperature. They have a three-chambered heart.
What changed from amphibians to reptiles?
The presence of limbs and lungs differentiates reptiles from ancient amphibians.
Is An Axolotl an Amphibian?
Yes.
Why were amphibians replaced by reptiles?
Reptiles were able to adapt on dry land, unlike amphibians.
Is Turtle an amphibian?
No, it is a reptile.
Is A Gecko an amphibian?
It is a reptile.
What is the word for both reptiles and amphibians?
Herptiles.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
2 Comments
Trackbacks
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Wake, David B., and Michelle S. Koo. "Amphibians." Current Biology 28.21 (2018): R1237-R1241.
[1]Duellman, William E., and Linda Trueb. Biology of amphibians. JHU press, 1994.
[2]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEP1wOo8YQ/
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADB9ScspC4-bullfrog/

“Ultimately they lose their tales…”?
Does that mean they have no stories to tell their grand-tadpoles?