Difference Between Table Salt And Sea Salt
Introduction
Salt: a simple compound, a kitchen staple, and a marvel of nature. Its presence is ubiquitous in our daily lives, yet its varieties, specifically table salt and sea salt, offer distinct flavors, textures, and health implications. Understanding these differences is not just a matter of culinary curiosity but also one of nutritional significance.

What is Table Salt?
Definition and Production Process
Table salt, scientifically known as sodium chloride, is more than just a kitchen staple; it’s a culinary chameleon. Its journey from the earth to our tables is a fascinating one. Originating from underground salt deposits left by ancient bodies of water, it is mined through extensive processes. Once extracted, it undergoes rigorous purification to remove natural impurities. The result is those fine, consistent granules we’re all familiar with. Unlike its sea-sourced counterpart, table salt often receives additional treatment – anti-caking agents are introduced to prevent clumping, and iodine is frequently added for its health benefits, a practice dating back to the early 20th century to prevent iodine deficiency disorders.
Common Uses of Table Salt
- Culinary Versatility:
- Ideal for precise measurements in cooking due to its fine, uniform grains.
- A staple for baking, where consistency in ingredient proportions is crucial.
- Food Preservation:
- Essential in curing meats and pickling vegetables due to its moisture-extracting properties.
- Helps in extending the shelf life of various foods.
- Beyond the Kitchen:
- Popular in household cleaning, acting as a gentle abrasive and a natural deodorizer.
- Used in gardening to control weeds and pests.
- Accessibility and Affordability:
- Widely available and cost-effective, making it a common choice for various uses.
Health Implications of Table Salt
- Essential for Bodily Functions:
- Crucial for nerve transmission and muscle contraction.
- An indispensable component of our daily diet.
- Risks of Excessive Consumption:
- High sodium intake can lead to hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases due to excessive sodium.
- Moderation is Key:
- Growing awareness of the need for moderate salt consumption.
- Balancing sodium intake is important for overall health.
- Iodine Fortification:
- Added iodine helps prevent thyroid disorders.
- Careful consideration is needed in regions with sufficient dietary iodine.

What is Sea Salt?
Definition and Production Process
Sea salt originates from a simple yet elegant process where seawater is channeled into large ponds. Exposed to the sun and wind, the water gradually evaporates, leaving behind sparkling salt crystals. This method, often performed with minimal human intervention, preserves the natural essence of the ocean. In certain regions, sea salt harvesting remains an artisanal tradition, where it’s collected manually, maintaining centuries-old techniques. The minimal processing of sea salt not only retains its unique mineral content but also embeds it with the character of its marine source, offering a taste that’s as rich in flavor as it is in history.
Common Uses of Sea Salt
- Elevating Culinary Creations: Its unique mineral content and flavor profile make it a chef’s favorite for seasoning and finishing dishes.
- Versatility in the Kitchen: From grilling meats to topping chocolates and caramels, sea salt enhances a variety of dishes.
- Innovative in Mixology: Its ability to add a new dimension to cocktails makes it a trendy ingredient in modern mixology.
Varieties and Flavors
- A Spectrum of Choices: Each harvesting location offers a unique variety, like the delicate Hawaiian red alaea salt or the smoky flavor of smoked sea salt.
- Taste the Difference: These varieties bring not just different textures but also a range of flavors – from subtly sweet to intensely saline – adding depth to culinary creations.
Health Implications of Sea Salt
- Trace Elements: The additional minerals, such as magnesium and potassium, can contribute to a balanced diet.
- Sodium Content Awareness: Despite its natural sourcing, it’s important to monitor intake as it still contains high levels of sodium.
- Balancing Dietary Needs: For individuals with specific health considerations, like low iodine levels, integrating sea salt into their diet should be done thoughtfully, often in conjunction with other iodine-rich foods.
Possible Similarities Between Table Salt and Sea Salt:
- Basic Composition: Both table salt and sea salt primarily consist of sodium chloride, making them chemically similar at their core.
- Culinary Essentials: Each plays a crucial role in cooking and food seasoning, enhancing flavors in a wide array of dishes.
- Preservation Properties: Historically, both have been used for preserving food, leveraging their ability to inhibit the growth of bacteria.
- Nutritional Role: In terms of basic nutritional value, particularly their sodium content, they are quite similar, contributing to daily dietary sodium intake.
- Solubility: Both dissolve easily in water, a property that makes them versatile in various culinary processes, from cooking to baking.
Differences Between Table Salt and Sea Salt
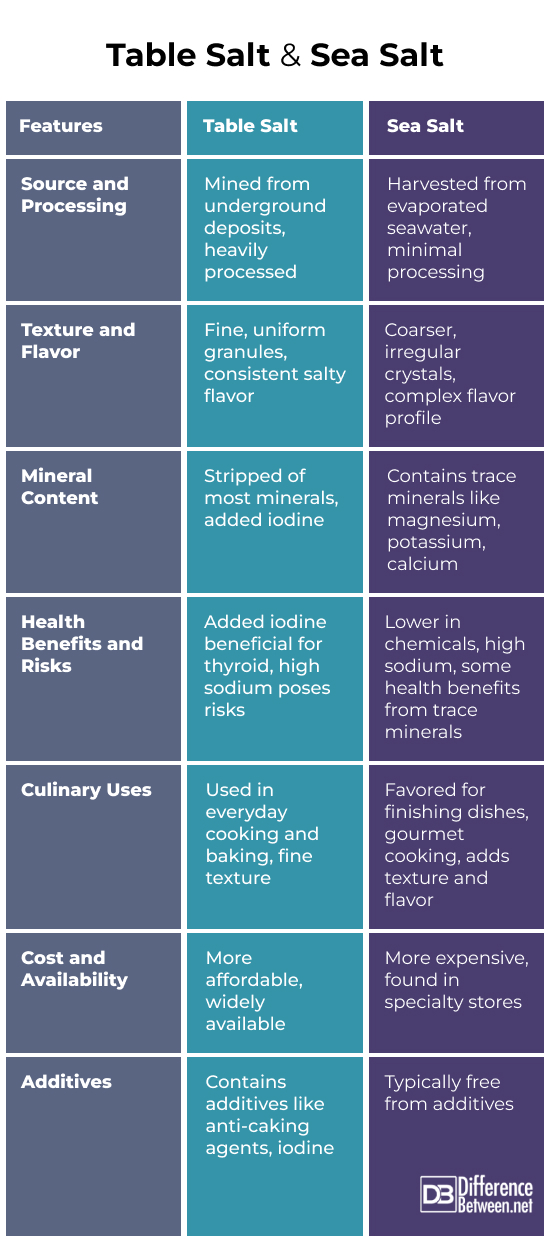
- Source and Journey:
- Table Salt: Mined from underground deposits, refined for purity.
- Sea Salt: Produced by evaporating seawater, retaining natural elements.
- Texture and Flavor:
- Table Salt: Fine and uniform, offering a consistent, reliable taste.
- Sea Salt: Coarse, irregular crystals, with a varied and nuanced flavor palette.
- Mineral Content:
- Table Salt: Primarily sodium chloride with added iodine.
- Sea Salt: Contains trace minerals like magnesium and potassium, enhancing flavor and character.
- Health Implications:
- Table Salt: Essential but to be consumed in moderation due to high sodium; iodine is beneficial for thyroid health.
- Sea Salt: High in sodium, but includes beneficial trace elements; consumption should still be moderated.
- Culinary Roles:
- Table Salt: A versatile choice for everyday cooking and baking, known for precision and consistency.
- Sea Salt: Ideal for gourmet cooking and finishing, adding texture and bursts of flavor.
- Accessibility and Affordability:
- Table Salt: Widely available and budget-friendly.
- Sea Salt: Generally more expensive and found in specialty stores.
- Nature vs Nurture – Additives:
- Table Salt: Often contains additives for practicality, such as anti-caking agents.
- Sea Salt: Typically additive-free, maintaining a more natural state.
Table Salt Vs Sea Salt
FAQs
Is sea salt better than table salt?
No, not always. Both have a salt concentration that is comparable. Preference is determined by flavor, texture, and personal health concerns.
Which salt is healthiest?
No salt is “healthiest.” Sea salt has trace minerals; iodized table salt provides iodine. Balance and moderation are key.
Is sea salt better than table salt for high blood pressure?
Neither is better. Both contain similar levels of sodium, which is the primary concern in high blood pressure management.
Can you substitute table salt for sea salt?
Yes, but adjust quantities. Table salt is finer, so use less if substituting for coarse sea salt.
Is sea salt actually healthier?
Sea salt has minor additional minerals but is not significantly healthier than table salt, as sodium content is similar.
Which salt is best for cooking?
Depends on the recipe. Table salt is best for precise measurements and even flavor, while sea salt is great for finishing and texture.
What can I use if I don’t have sea salt?
Use table salt or kosher salt as substitutes, keeping in mind differences in crystal size and flavor intensity.
Why do recipes call for sea salt?
For its distinct texture and the subtle flavor differences it brings, especially in finishing dishes.
Should you use sea salt to cook?
Sea salt can be used in cooking, especially for its texture and flavor, but it’s not a necessity; personal preference and recipe requirements should guide your choice.
- Difference Between Suicide and Euthanasia - May 22, 2024
- Difference Between Vitamin D and Vitamin D3 - May 21, 2024
- Difference Between Running Shoes and Walking Shoes - April 30, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
7 Comments
Trackbacks
Leave a Response
References :
[0](1) Durack, E., Alonso-Gomez, M., & Wilkinson, M. G. (2008). Salt: a review of its role in food science and public health. Current Nutrition & Food Science, 4(4), 290-297.
[1](2) Davidson, A., Jaine, T., Davidson, J., Saberi, H., & Vannithone, S. (2006). The Oxford Companion to Food (pp. 706-708). Oxford University Press.
[2](3) Durack, E., Alonso-Gomez, M., & Wilkinson, M. G. (2008). Salt: a review of its role in food science and public health. Current Nutrition & Food Science, 4(4), 290-297.
[3](4) Bloch, M. R. (1976). Salt in human history. Interdisciplinary science reviews, 1(4), 336-352.
[4](5) Davidson, A., Jaine, T., Davidson, J., Saberi, H., & Vannithone, S. (2006). The Oxford Companion to Food (pp. 706-708). Oxford University Press.
[5](6) Durack, E., Alonso-Gomez, M., & Wilkinson, M. G. (2008). Salt: a review of its role in food science and public health. Current Nutrition & Food Science, 4(4), 290-297.
[6]Davidson, A., Jaine, T., Davidson, J., Saberi, H., & Vannithone, S. (2006). The Oxford Companion to Food (pp. 706-708). Oxford University Press.
[7]Durack, E., Alonso-Gomez, M., & Wilkinson, M. G. (2008). Salt: a review of its role in food science and public health. Current Nutrition & Food Science, 4(4), 290-297.
[8]Bloch, M. R. (1976). Salt in human history. Interdisciplinary science reviews, 1(4), 336-352.
[9]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADaEnqV2uY-crystals-of-shallow-salt-in-a-scoop-spoon-on-a-dark-gray-table-background-for-advertising-salt-table-salty-salted-food-/
[10]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADAPD8ikDU-sea-salt/

Please make a correction in your point no.5 in Summary.
Yours writing is:
5. Sea salt is growing in popularity as a health alternative to sea salt, though it is more expensive than the former.
Correction is:
5. Table Salt is growing in popularity as a health alternative to sea salt, though it is more expensive than the former.
Actually, it SHOULD read:
“5. Sea salt is growing in popularity as a healthy alternative to table salt, though it is more expensive than the latter.”
THAT would be accurate. 🙂
Boom! Lol. Yes i believe she/he transposed the two salts.
You really should rewrite #5 in the summary. It makes NO sense as it currently reads!
It SHOULD read like this:
“5. Sea salt is growing in popularity as a healthy alternative to table salt, though it is more expensive than the latter.”
PLEASE edit it. Also, you made the same mistake in the paragraph where that line originally shows up. You are basically saying the opposite of what you mean, as the word “former” there would refer to sea salt the MORE expensive variety, rather than table salt, the LATTER, which actually IS the cheaper variety.
As well, on the line right before the summary, you have: “…a living salt teaming with…” In this phrase, the word “teaming” should be “teeming,” as in “full of.” That word generally has the connotation of something living, so it fits, I suppose. If you keep the word “teaming,” you need to add the word “up”, as in “teaming up with.” That would make more sense.
I find it absurd and annoying that this has been up since November 2009 and it still hasn’t been edited. *sigh* You even had someone pointing out that #5 wasn’t correct, although that suggestion wasn’t the correct way to write it, either. These edit suggestions ARE correct.
How do I start a salt production?
Much ado about anon ! .
SEA SALT IS :
TASTIER,
HEALTHIER
period