Difference Between Zoonotic and Human to Human Transmission
There are several modes of disease transmission, and each of them affects the human body differently. It can be plenty of work to study all of them at once, but for the purpose of this piece, we’ll review two of the most common ways infections can get into the human body – zoonotic and human-to-human transmission. To break down the essential information, we will examine the meaning, possible similarities, and differences between zoonotic and human-to-human disease transmission.

What is Zoonotic Transmission?
Zoonotic disease transmission, also Zoonosis, refers to illnesses transmitted from animals to humans. The truth is that animals don’t have an intensive hygiene program like humans. So, their bodies are covered with harmful germs, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and even fungi. When these germs are brought into contact with the human body, they cause different diseases. You should note that zoonotic diseases may be mild or severe in the human body. Furthermore, these diseases are not restricted to any region or continent.
One scary fact about zoonotic transmission is that it’s a prominent source of human illness. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 61% of all human diseases have a zoonotic origin. Also, 75% of newly discovered diseases originate from contact with animals. Common examples of zoonotic diseases include rabies, dengue fever, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, dengue fever, malaria, salmonella infection, e.coli infection, anthrax, brucellosis, etc.
What is Human-to-Human Transmission?
Human-to-human transmission refers to illnesses that humans spread. While this isn’t a popular mode of disease transmission, it can take various forms. Human-to-human diseases can be spread through skin contact, sweat, saliva, etc. These illnesses may also be mild or severe depending on the microorganism attacking the body and the affected body part.
It’s worth noting that the contagiousness of a human-to-human disease varies considerably. There are instances where superspreaders transmit certain diseases. Without any preventive measures, these superspreaders can infect an average of 200 people.
Possible Similarities Between Zoonotic and Human-to-Human Transmission
No doubt, zoonotic and human-to-human transmission involve how diseases are spread from one person to another. Each mode of transmission is distinct, but there are a few similarities between them. Here’s a list of them:
- Pathogenic adaptation: The pathogens in zoonotic and human-to-human transmission are socially adapted to infect and spread among the human population. Often, these pathogens mutate or change their behavior to survive.
- Risk factors: The risk factors of zoonotic and human-to-human transmission diseases are similar. These risk factors include close contact with the infected individuals, poor hygiene, and exposure to contaminated food and water.
- Preventive measures: Both zoonotic and human-to-human disease transmission can be prevented using vaccination, public health interventions, and quarantine.
Difference Between Zoonotic and Human-to-Human Transmission
When you look closely at zoonotic and human-to-human transmission diseases, they have a similar effect on the human body. They attack internal body organs and weaken the immune system. However, the main distinction between both illnesses relates to their transmission mode.
Zoonotic diseases can only be spread from contact with the infected animal. This means that if someone suffers from zoonosis, they can’t transfer it to another person unless the disease mutates. If another person will suffer from the same condition, they must have come into contact with the animal carrying the disease pathogen. On the other hand, human-to-human transmission illnesses are spread from one person to another. More often than not, the spreader will be responsible for infecting other people who would later become spreaders themselves.
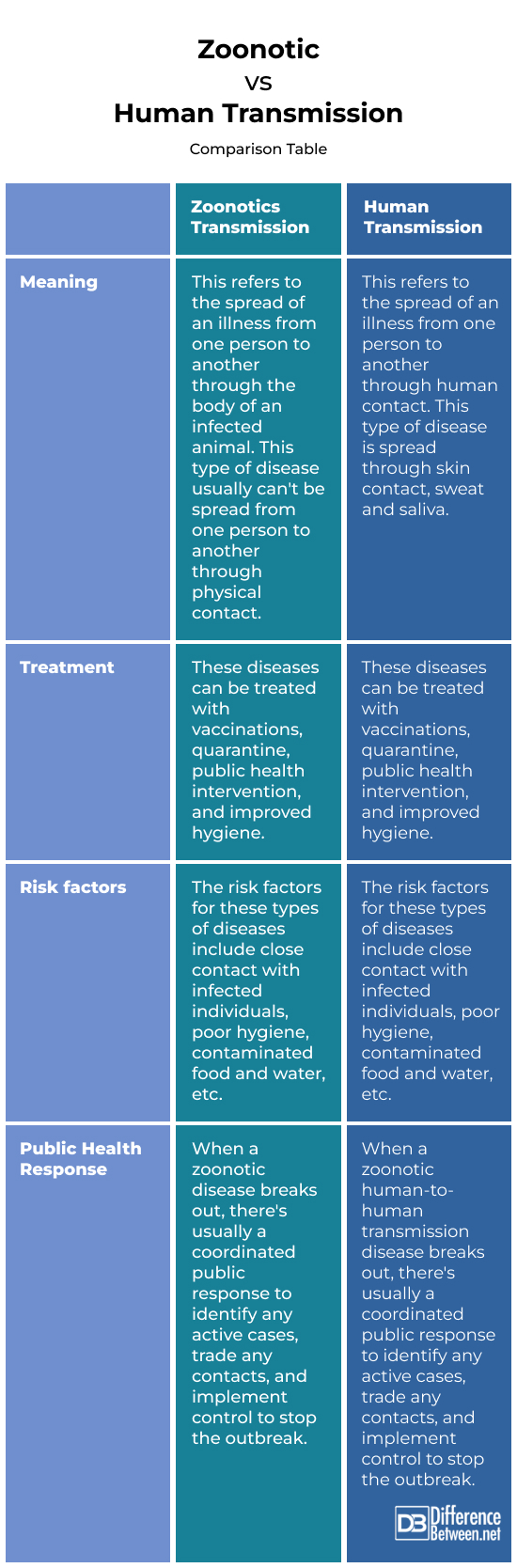
Zoonotic vs Human Transmission: Comparison Table
Summary
To create effective disease prevention and control measures, it’s crucial to understand the differences between zoonotic and human-to-human transmission. Zoonotic diseases are spread from contact with animals while human-to-human transmission relies on close interpersonal contact. By addressing both zoonotic and human-to-human transmission pathways it is essential for building resilient health systems and ensuring the well-being of communities worldwide.
FAQs
Can zoonotic diseases be transmitted from humans to humans?
In most cases, zoonotic diseases can’t be transmitted between humans. However, in some cases it may adapt to human-to-human transmission under certain conditions, leading to outbreaks or even pandemics
What is human to human transmission called?
Human-to-human transmission is also known as an epidemiologic vector. It’s also referred to as interpersonal transmission or person-to-person transmission.
What is the meaning of zoonotic transmission?
Zoonotic transmission is a term used to describe the spread of diseases from person to another through an animal.
What is the difference between zoonotic and vector transmission?
Zoonotic transmission involves the transfer of diseases by contact with infected animals, while vector transmission refers to the spread of diseases through small arthropods.
What is an example of a human to human disease transmission?
Ebola virus and Coronavirus are examples of human to human disease transmission.
What does zoonotic mean?
Can a disease be both zoonotic and vector-borne?
Yes, a disease can be both zoonotic and vector-borne. In fact, many zoonotic diseases are transmitted to humans through vectors, such as mosquitoes or ticks.
Was coronavirus zoonotic?
Yes, the coronavirus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, known as SARS-CoV-2, is believed to be of zoonotic origin. It is thought to have originated in bats and may have been transmitted to humans through an intermediate host, possibly a species of animal sold at a seafood market in Wuhan, China.
Is rabies zoonotic or vector-borne?
Rabies is a good example of a zoonotic transmission disease.
- Difference Between Space Colonization and Space Habitats - May 13, 2024
- Difference Between Space Junk and Operational Satellites - May 9, 2024
- Difference Between Vector-Borne and Airborne Diseases - May 7, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
References :
[0]Nolen, L. D., Osadebe, L., Katomba, J., Likofata, J., Mukadi, D., Monroe, B., Doty, J., Hughes, C. M., Kabamba, J., Malekani, J., Bomponda, P. L., Lokota, J. I., Balilo, M. P., Likafi, T., Lushima, R. S., Ilunga, B. K., Nkawa, F., Pukuta, E., Karhemere, S., & Tamfum, J.-J. M. (2016). Extended Human-to-Human Transmission during a Monkeypox Outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 22(6), 1014–1021. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2206.150579
[1]Nolen, L. D., Osadebe, L., Katomba, J., Likofata, J., Mukadi, D., Monroe, B., Doty, J., Hughes, C. M., Kabamba, J., Malekani, J., Bomponda, P. L., Lokota, J. I., Balilo, M. P., Likafi, T., Lushima, R. S., Ilunga, B. K., Nkawa, F., Pukuta, E., Karhemere, S., & Tamfum, J.-J. M. (2016). Extended Human-to-Human Transmission during a Monkeypox Outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 22(6), 1014–1021. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2206.150579
[2]Rahman, Md. T., Sobur, Md. A., Islam, Md. S., Ievy, S., Hossain, Md. J., El Zowalaty, M. E., Rahman, A. T., & Ashour, H. M. (2020). Zoonotic Diseases: Etiology, Impact, and Control. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091405
[3]Minnesota Department of Health. (2022, October 11). Zoonotic diseases: Disease transmitted from animals to humans - minnesota dept. of health. State.mn.us. https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/animal/zoo/index.html
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADCOHMgHow-zoonotic-disease-colorful-word-with-stethoscope/
[5]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADq3hdHA1Y-f019-1970/
