Difference Between Alternative Medicine and Quackery
The word “alternative medicine” refers to medical interventions that take the place of conventional, or mainstream, therapy. It is also known as “integrative” or “complementary” medicine by some people. In the US, almost half of adult user’s report using complementary or alternative medicine.
The commercial marketing of fictitious and unverified health plans is known as quackery. It has its roots in market customs, where commercialism trumps expertise in the promotion of complementary and alternative medicine.

Alternative medicine
Conventional medical care is replaced with alternative medicine. One such involves treating cancer with a particular diet rather than oncologist-prescribed cancer medications. For the most part, less study has been done on alternative medicine.

Quackery
It’s a health fraud that advertises deceptive goods and services with unverified, unproven quality or effects.
Similarity
Both are ways of medical treatment
Difference between alternative medicine and quackery
Principle of practice
Alternative medicine
Often referred to as complementary or integrative medicine, alternative medicine encompasses a variety of medical procedures and therapies that are employed in addition to or instead of traditional medical treatments. These methods have their roots in conventional or antiquated therapeutic techniques and are frequently supported by theories or other types of evidence, even though they might not adhere to the same exacting criteria as mainstream medicine.
Quackery
Contrarily, quackery is the practice and promotion of dubious or unproven medical procedures or goods that have either been refuted by the scientific and medical communities or lack scientific legitimacy. Quackery usually entails the use of false or unsupported claims to take advantage of the weak for personal benefit.
Credibility in science
Alternative medicine
A few techniques used in alternative medicine have been examined scientifically and may have some benefit in specific circumstances. When these procedures are backed by proof of their efficacy and safety, they might be included into standard medical care. Acupuncture, herbal medicine, and chiropractic adjustments are a few examples.
Quackery
Quackery is usually based on mystical or pseudoscientific ideas and lacks scientific validity. Miracle cures may be promised by quack therapies, but they never provide reliable proof for their claims. Quack medicine includes, among other things, unscientific treatments, supernatural talismans, and miracle cures.
Regulation & Licensing
Alternative medicine
In certain jurisdictions, a number of alternative medicine practices and practitioners may be subject to licensing and regulation. Usually, this entails establishing guidelines for instruction, practice, and moral behavior. Healthcare providers, such as naturopathic physicians and acupuncturists, occasionally work in regulated fields.
Quackery
Quackery is frequently linked to unregistered and unregulated people and goods that could endanger the public’s health. These kinds of actions may be dishonest and in certain circumstances unlawful.
Ethical considerations
Alternative medicine
Complementary treatment is intended to enhance patients’ well-being by ethical practitioners of alternative medicine. They frequently uphold the highest ethical standards of practice and promote candid conversation with traditional healthcare practitioners.
Quackery
Quacks frequently take advantage of weak patients because they are motivated by money. Their actions raise ethical concerns because they could mislead patients, jeopardize their health, and erode public confidence in medical institutions.
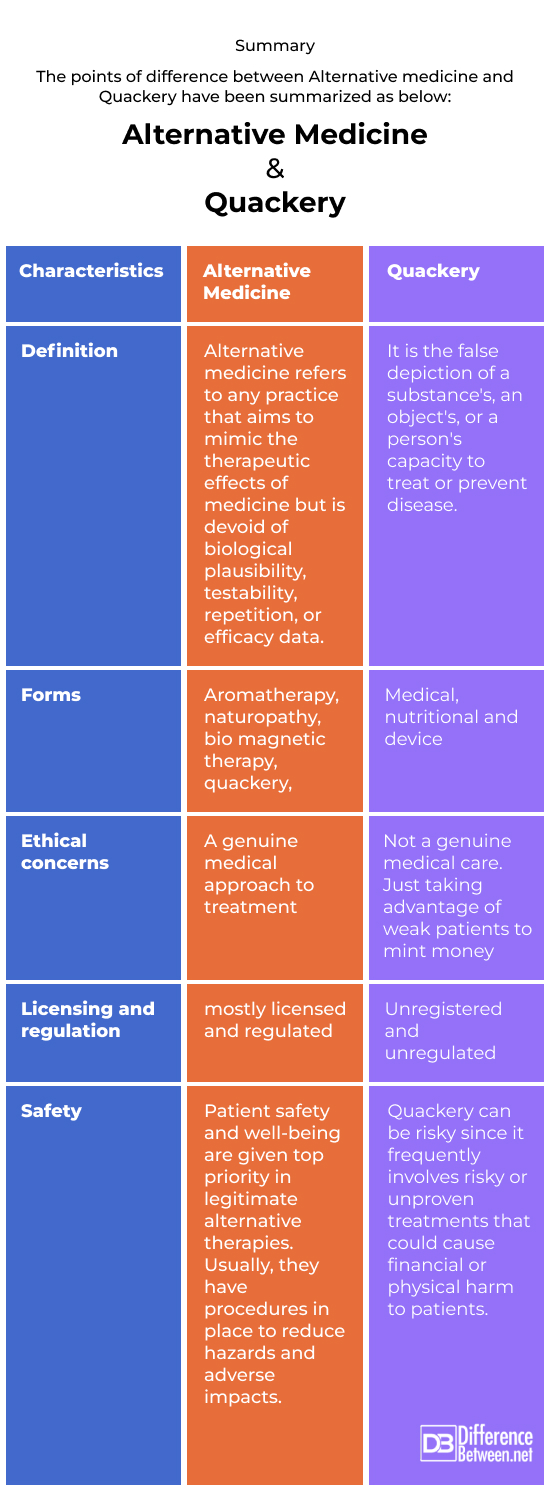
Summary
The points of difference between Alternative medicine and Quackery have been summarized as below:
FAQ:
What is the difference between medicine and alternative medicine?
Complementary medicine refers to treatments that are used in addition to mainstream western (or allopathic) medicine, whereas alternative medicine is used in substitute of conventional medicine.
What is alternative quackery?
The commercial marketing of fictitious and unverified health plans is known as quackery. It has its roots in market customs, where commercialism trumps expertise in the promotion of complementary and alternative medicine. Most commonly, quackery refers to the selling of the “cure-alls” mentioned previously.
What is the difference between alternative medicine and modern medicine?
While conventional and alternative medicine focus primarily on the medical elements of sickness, they also take into account the patient’s social, psychological, and spiritual well-being. This is something that contemporary medicine frequently overlooks.
What is the difference between quack and quackery?
Quackery: Quacks and charlatans are notorious for feigning to possess knowledge and abilities that they do not, particularly in the medical area. To earn financial gain, the quack usually makes grandiose claims about their ability to heal ailments.
What is an example of quackery?
One example is homoeopathy, which propagates the notion that ingesting a chemical that generates the same symptoms as the illness will treat it and that smaller doses of medication are more beneficial than bigger ones. It is marketed as a treatment for a wide range of ailments, but there isn’t any solid scientific proof to support it.
What are the 5 major types of alternative medicine?
- whole healthcare systems.
- body-mind methods.
- biologically oriented methods.
- body-based and manipulative therapy.
- energetic medicine.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Allen, R. W. (2014). From Quackery to Control: Perceptions of Complementary and Alternative Medicine from Users with Mental Health Disorders (Doctoral dissertation, East Tennessee State University).
[1]Han, D. W., & Hwang, J. H. (2010). A Critical Review on Complementary and Alternative Medicine/Pseudo-medicine/Quackery: Implication on Health Policy. The Korean Society of Law and Medicine, 11(2), 113-145.
[2]Winnick, T. A. (2005). From quackery to “complementary” medicine: The American medical profession confronts alternative therapies. Social Problems, 52(1), 38-61.
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADFcx6P058-quackery/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAD2EYm_TZM-alternative-medicine-vs-traditional-medicine-concept-/
