Difference Between Pemphigus Foliaceus and Vulgaris
Pemphigus foliaceus is an uncommon autoimmune condition that causes tender itchy blisters on the scalp, face, and trunk. Pemphigus vulgaris is an uncommon autoimmune condition that causes tender blisters on mucosal membranes like the mouth, genitalia, and eyes.
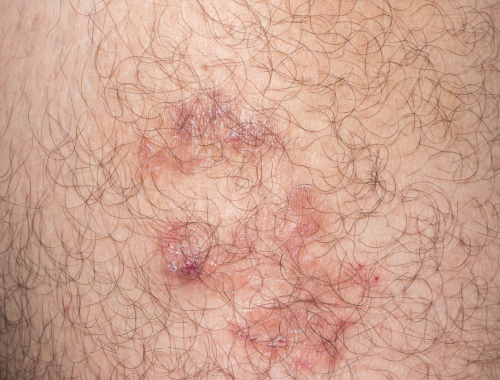
What is pemphigus foliaceus?
Definition:
Pemphigus foliaceus is an uncommon autoimmune condition that causes tender itchy blisters on the scalp, face, and trunk.
Causes:
Causes of pemphigus foliaceus include genetic factors like the presence of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) gene and environmental factors. It is an autoimmune disease in which the immune cells are acting against the adhesion sites of the epidermal cells. Pemphigus foliaceus flare can occur secondary to drugs like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, enalapril and penicillamine, UV exposure, and insect bite.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of pemphigus foliaceus include small fluid-filled blisters on skin, that are prone to rupture. These turn into patches that are scaly and crusty and cause itchiness and pain.
Diagnosis:
History and physical examination of the blisters are important to diagnose pemphigus foliaceus. Skin biopsy and blood tests are also needed to accurately identify the pathology.
Treatment:
Treatment for pemphigus foliaceus includes avoidance of the medicines causing symptoms, using steroids as creams or oral tablets, and taking immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and methotrexate.
What is pemphigus vulgaris?
Definition:
Pemphigus vulgaris is an uncommon autoimmune condition that causes tender blisters on mucosal membranes like the mouth, genitalia, and eyes.
Causes:
Pemphigus vulgaris occurs due to antibodies acting against the proteins in the skin. The exact cause of the condition is not known. Medicines like penicillamine and ACE inhibitors are also known to trigger pemphigus vulgaris.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of pemphigus vulgaris are painful blisters in the mucosal membranes of the mouth and genitalia. There is crusting and peeling at the blistering zone.
Diagnosis:
Examination of the skin blisters will be essential to diagnose pemphigus vulgaris. A positive Nikolsky’s sign is an indicator of the condition, where the skin breaks down with wiping. A biopsy of the blister will confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment:
Medications used to treat pemphigus vulgaris include high-dose corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants like azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, methotrexate, and rituximab. Blisters are treated with numbing lotions, soothing creams, and damp dressing.
Difference between pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris
Definition:
Pemphigus foliaceus is an uncommon autoimmune condition that causes tender itchy blisters on the scalp, face, and trunk. Pemphigus vulgaris is an uncommon autoimmune condition that causes tender blisters on mucosal membranes like the mouth, genitalia, and eyes.
Causes:
Causes of pemphigus foliaceus include genetic factors like the presence of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) gene and environmental factors. It is an autoimmune disease in which the immune cells are acting against the adhesion sites of the epidermal cells. Pemphigus foliaceus flare can occur secondary to drugs like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, enalapril and penicillamine, UV exposure, and insect bite. Pemphigus vulgaris occurs due to antibodies acting against the proteins in the skin. The exact cause of the condition is not known. Medicines like penicillamine and ACE inhibitors are also known to trigger pemphigus vulgaris.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of pemphigus foliaceus include small fluid-filled blisters on skin, that are prone to rupture. These turn into patches that are scaly and crusty and cause itchiness and pain.
Symptoms of pemphigus vulgaris are painful blisters in the mucosal membranes of the mouth and genitalia. There is crusting and peeling at the blistering zone.
Diagnosis:
History and physical examination of the blisters are important to diagnose pemphigus foliaceus. Skin biopsy and blood tests are also needed to accurately identify the pathology. Examination of the skin blisters will be essential to diagnose pemphigus vulgaris. A positive Nikolsky’s sign is an indicator of the condition, where the skin breaks down with wiping. A biopsy of the blister will confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment:
Treatment for pemphigus foliaceus includes avoidance of the medicines causing symptoms, using steroids as creams or oral tablets, and taking immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and methotrexate. Medications used to treat pemphigus vulgaris include high-dose corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants like azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, methotrexate, and rituximab. Blisters are treated with numbing lotions, soothing creams, and damp dressing.
Table of differences between pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris

FAQs
Can pemphigus foliaceus turn into pemphigus vulgaris?
Yes
What is pemphigus foliaceus erythematosus and vulgaris?
Pemphigus foliaceus is an uncommon autoimmune condition that causes tender itchy blisters on the scalp, face, and trunk. Pemphigus vulgaris is an uncommon autoimmune condition that causes tender blisters on mucosal membranes like the mouth, genitalia, and eyes.
Are pemphigus and pemphigus vulgaris the same?
Pemphigus vulgaris is a subtype of the broad category of skin disorder that is pemphigus.
How can you tell the difference between pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid?
Blisters in pemphigus vulgaris are flaccid and rupture easily whereas in bullous pemphigoid these blisters are tense and firm.
What is Pemphigus foliaceus also called?
It is also called fogo selvagem.
Is pemphigus foliaceus fatal?
It is not life-threatening.
What triggers pemphigus foliaceus?
Pemphigus foliaceus flare can occur secondary to drugs like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, enalapril and penicillamine, UV exposure, and insect bite.
How do you get rid of pemphigus foliaceus?
Treatment for pemphigus foliaceus includes avoidance of the medicines causing symptoms, using steroids as creams or oral tablets, and taking immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and methotrexate.
What is the most common cause of death in pemphigus?
Respiratory infections and cardiovascular disease.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Porro, Adriana Maria, Camila Arai Seque, and Maria Carolina Corsi Ferreira. "Pemphigus vulgaris." Anais brasileiros de dermatologia 94 (2019): 264-278.
[1]Harman, K. E., S. Albert, and M. M. Black. "Guidelines for the management of pemphigus vulgaris." British Journal of Dermatology 149.5 (2003): 926-937.
[2]Martin, Linda K., et al. "Interventions for pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus." Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1 (2009).
