Difference Between Somatic and Visceral
Somatic is a general term referring to parts of the body like the bones, skin, and musculoskeletal system. Visceral is a term that is used for referring to internal organs and the vascular system.
What is Somatic?
Definition:
Somatic refers to structures of the body like the skeletal muscles, bones, joints, and skin.
Innervation:
Nerves of the somatic nervous system are those that control the contraction of skeletal muscles, and are, thus, under conscious control. The somatic nervous system also includes both neurons that are sensory and neurons that are motor in function. In other words, information is both transported to the central nervous system (CNS) from sensory receptors, and away from the CNS to effectors (glands and muscles).
Reflexes:
Somatic reflexes are those actions that occur in the skeletal muscles. A good example is the patellar reflex, when your leg kicks up in response to the doctor tapping your knee. The somatic reflexes are trigged because somatic sensory receptors are activated.
Pain:
With somatic pain it is usually quite easy to establish what is injured. For instance, an inflamed joint will often swell and appear red while if you break a particular bone on an extremity, you will not be able to move that extremity. Somatic pain can be very painful. Somatic pain can be in the superficial tissues but also deeper in structures like bones.
What is Visceral?
Definition:
Visceral refers to the internal organs of the body, including the vascular system (blood vessels).
Innervation:
The visceral nerves are those of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which bring about involuntary actions in the internal organs.
Reflexes:
Visceral reflexes involve actions of the internal organs. Such examples include sneezing, coughing, dilation of the pupil, vomiting, and swallowing.
Pain:
In the case of visceral pain, it is not so easy to find out what is inflamed or injured. The organ that is affected may also have referred pain, so for instance, gallstones can also be felt as pain in the shoulder even though the gallbladder is not there. Visceral pain can be as bad as somatic pain, or worse depending on the problem. Visceral pain can be due to inflammation, infection, or obstruction of an organ or duct.
Difference between Somatic and Visceral?
Definition
Somatic is word used to refer to structures of the skin, joints, bones, and skeletal muscles. Visceral is a word used to refer to the internal organs.
Innervation
The somatic nervous system, is that which controls skeletal muscles. The visceral nervous system is also called the autonomic nervous system, and it controls the functioning of internal organs.
Reflex
Somatic reflexes are those involving the skeletal muscles. Visceral reflexes are those involving the internal organs.
Nerves
Somatic nerves control conscious (voluntary) actions such as moving your arms and legs. Visceral nerves control unconscious (involuntary) actions of internal organs and structures.
Pain sensation
Somatic pain is often easier when it comes to establishing where the pain is originating from. This is not the case always with visceral pain. Visceral pain is often more difficult because it is deep in the body and it is not always clear as to exactly which organ is affected.
Examples of pain
Examples of somatic pain include broken bones, pulled muscles, the pain of arthritis, and cuts. Examples of visceral pain are those associated with conditions such as endometriosis, gallstones, kidney stones, irritable bowel syndrome, vasculitis, and angina
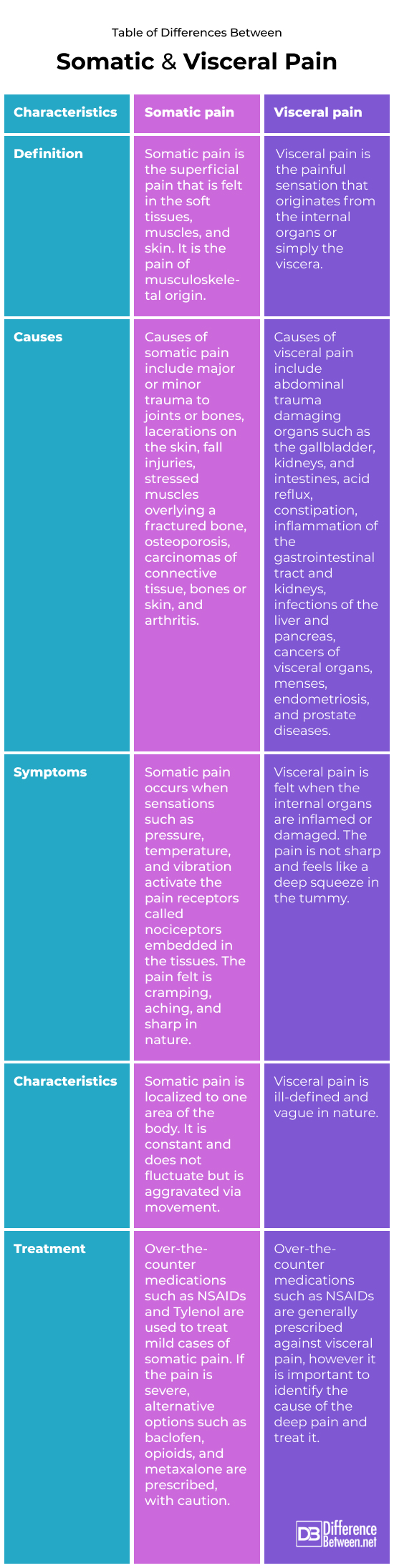
Table comparing Somatic and Visceral
Summary of Somatic Vs. Visceral
- Somatic and visceral are two terms that are used to refer to different parts of the body.
- Somatic refers to the muscles, skin, and bones.
- Visceral refers to internal organs such as the heart, gallbladder, liver, stomach, and so on.
FAQ
What are somatic and visceral structures?
Somatic structures include the skin, skeletal muscles, and bones. Visceral structures include the blood vessels and internal organs.
What is somatic vs. visceral pain examples?
An example of somatic pain is a pulled muscle or broken bone. An example of visceral pain is that of kidney stones. Both types of pain can be excruciatingly painful.
What is an example of a somatic pain?
The pain you feel from cutting yourself or breaking a bone are examples of somatic pain.
Is skin somatic or visceral?
Skin is considered part of the somatic system. It contains several sensory structures that detect information and send signals to the brain.
What organs are somatic?
Bones, skeletal muscles, and skin are all somatic structures.
Is taste visceral or somatic?
Taste involves visceral nerves. It is part of the visceral afferent system.
Is bone pain somatic or visceral?
Bone pain is somatic not visceral.
What are the three types of somatic reflexes?
The three types of somatic reflex are the withdrawal reflex, stretch reflex, and the inverse stretch reflex.
Is somatic visceral or neuropathic?
Somatic pain is neuropathic not visceral.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Collett, Beverly. "Visceral pain: the importance of pain management services." British Journal of Pain 7.1 (2013): 6-7.
[1]Grundy, Luke, Andelain Erickson, and Stuart M. Brierley. "Visceral pain." Annual review of physiology 81 (2019): 261-284.
[2]Woolf, C. J. "Somatic pain--pathogenesis and prevention." British Journal of Anaesthesia 75.2 (1995): 169-176.
