Difference Between Granulomatous and Non-Granulomatous
Granulomatous refers to inflammatory responses where granulomas are formed. Non-granulomatous responses are inflammation without the formation of granulomas.

What is Granulomatous?
Definition:
Granulomatous is a term used to describe a type of inflammation, where nodules (granulomas) made up of epithelioid histiocytes are formed.
Types of granulomatous conditions:
Certain illnesses can be granulomatous, for instance: Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), necrotising sarcoidal granulomatosis, granulomatous uveitis, and Wegener’s granulomatosis. Wegener’s granulomatosis is a type of vasculitis. In other words, it involves inflammation in the blood vessels. Today, you may see it also referred to as granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
Symptoms and onset:
The symptoms vary somewhat depending on the exact type of granulomatous condition. In the case of CGD, symptoms include pain in the chest, swollen lymph nodes, fever, a runny nose, and skin rash. Symptoms of granulomatous uveitis include blurry vision and some minor eye pain. Granulomatous inflammatory responses tend to begin slower than is the case for non-granulomatous responses.
Cell types:
Cells that are found in granulomatous inflammation include multinucleated giant cells, and also macrophages, mononuclear cells, and epithelioid cells. The cells come together to form the nodular structures known as granulomas.
Diagnosis:
The diagnosis is based on the results of blood tests and imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs. Imaging tests may be helpful in seeing the granulomas that are formed during the inflammatory response. Special tests can indicate exactly what type of granulomatous illness you have. For instance, CGD is diagnosed when phagocytes in a blood sample react in a specific way to hydrogen peroxide.
What is non-granulomatous?
Definition:
This is an aggressive inflammatory reaction to an antigen, but the response does not result in granuloma formation.
Types of non-granulomatous conditions:
There are some non-granulomatous illnesses that occur in people. Examples include non-granulomatous rosacea, non-granulomatous interstitial lung disease, and non-granulomatous uveitis. Acute suppurative non-granulomatous inflammation is a type of reaction that often happens after a bacterial infection.
Symptoms and onset:
Non-granulomatous illnesses tend to begin suddenly and quickly, but there are exceptions to this rule. The symptoms of the non-granulomatous condition will vary depending on the type of illness being caused. In the case of non-granulomatous uveitis, symptoms are eye pain and tearing up of the eye. In non-granulomatous interstitial lung disease, patients experience a dry cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. In non-granulomatous rosacea, the skin is affected.
Cell types:
In non-granulomatous conditions the cells that are most abundant are the polymorphonuclear leukocytes and plasma cells.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of non-granulomatous infections can be done with blood tests like complete blood cell counts and imaging tests.
Difference between Granulomatous and Non-granulomatous?
Definition
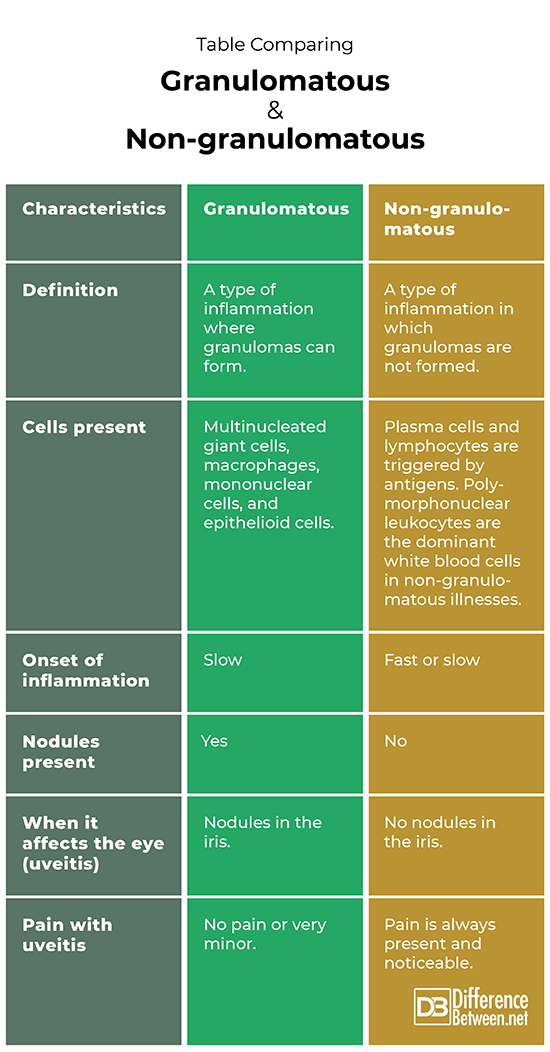
Granulomatous refers to inflammatory conditions where granulomas are formed. Non-granulomatous refers to inflammatory conditions where granulomas are not formed.
Cells present.
Multinucleated giant cells, macrophages, mononuclear cells, and epithelioid cells are present in granulomatous inflammation. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes are the dominant white blood cells in non-granulomatous illnesses, but you can also find plasma cells and lymphocytes.
Onset of inflammation
Inflammation usually begins slowly with granulomatous illnesses. Inflammation most often happens fast with non-granulomatous illnesses, but some are slower.
Nodules present
In the case of granulomatous illnesses, nodules are present in the affected tissue. In the case of non-granulomatous illnesses, nodules are absent from the affected tissue.
When it affects the eye (uveitis)
Nodules occur in the iris if the eye has a granulomatous inflammation. Nodules do not occur in the iris if the eye has a non-granulomatous inflammation.
Pain with uveitis
Granulomatous uveitis causes little to no pain in the eye. Non-granulomatous uveitis always causes eye pain.
Table comparing Granulomatous and Non-granulomatous
Summary of Granulomatous Vs. Non-granulomatous
- Granulomatous and non-granulomatous both refer to some type of inflammatory response in the body.
- A granulomatous response is when granulomas are likely to be produced from inflammation.
- A non-granulomatous response is when there is a particularly aggressive immune system response to an antigen.
FAQ
What is the difference between granulomatous and non-granulomatous inflammation?
Granulomatous inflammation is different because granulomas are created in the process of the inflammatory reaction.
What is the meaning of granulomatous?
Granulomatous means a tendency to form granulomas.
What is the difference between granulomatous KP and non-granulomatous?
In both cases, precipitates are formed on the eye but with granulomatous keratic precipitates (KP), these are large and yellow. In non-granulomatous KP, precipitates are white and small.
What is non-granulomatous disease?
This is a type of disease where granulomas are not formed; these illnesses tend to result from an aggressive reaction to some antigen that the immune system reacts to.
What is meant by granulomatous inflammation?
This is an inflammatory condition where specific immune cells accumulate and together the cells can, and often do, form granulomas (nodules). This is a particular response of the immune system in which granulomas are created in the course of the reactions occurring.
What is non granulomatous chronic inflammation?
This is a slowly developing inflammatory response involving leucocytes but not involving granuloma production.
What is an example of granulomatous inflammation?
Granulomatous uveitis is one example of granulomatous inflammation, in which there is inflammation that involves the eye.
What does granulomatous reaction mean?
A granulomatous reaction is the process whereby inflammatory cells come together and form a nodular structure. This nodular structure is referred to as a granuloma.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Elnahry, Ayman G., and Gehad A. Elnahry. "Granulomatous uveitis." StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
[1]James, D. Geraint. "A clinicopathological classification of granulomatous disorders." Postgraduate Medical Journal 76.898 (2000): 457-465.
[2]Rosenzweig, S. D. "Inflammatory manifestations in chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)." Journal of Clinical Immunology 28.Suppl 1 (2008): 67-72.
