Difference Between Typhoid and Paratyphoid
Typhoid and Paratyphoid, febrile infections of systemic organs and the bloodstream are caused by bacteria Salmonella Typhi and S. Paratyphi. They are characterized by prolonged fever and GIT disturbances.

What is Typhoid?
Definition
Typhoid, Also known as Enteric Fever or Travellers’ fever, is a bacterial infection of the Gastrointestinal Tract which is caused by poor sanitation and unhygienic practices.
Pathophysiology
- Highly Contagious
- Can spread through stool, and urine of the infected person
- When a person suffering from Typhoid cooks food without washing hands, the infection spreads to the person consuming that food.
- Incubation period is 1-2 weeks
- Bacteria enter the intestines after the initial incubation period, penetrate into the bloodstream, and later invade the spleen, liver, and bone marrow, spreading throughout the organs of the body.
Prevalence
- More prevalent in the Indian Subcontinent, Africa, and countries with poor sanitation systems.
- According to a study, about ~26 Million cases are reported annually and reported deaths are around 216,510.
- Persists as a Community Health Problem in underdeveloped countries.
Causative organism
A bacterium known as Salmonella Typhi. (Related to the bacterium causing Food poisoning)
Signs and Symptoms
- Persistent fever that intensifies every day
- Abdominal pain
- Maculopapular rashes, “rose spots”
- Extremely Fatigued body
- Headaches and body aches
- No appetite
- Intermittent cough
- Constipation or Diarrhea
- Hepatomegaly and Splenomegaly
Diagnosis
- Blood Complete Profile
- Blood Culture and Sensitivity
- Abdominal Ultrasound
Treatment
Prompt Treatment is needed to prevent complications like intestinal bleeding and hemorrhaging.
An Antibiotic Course of 1-2 weeks is advised.
More severe cases might need hospital admission and intravenous antibiotics administration.
Preventive vaccination is also available that is given to travelers before traveling to countries with a prevalence of the disease.
Prognosis
Although it is 100% curable by Antibiotics, but chances of reinfection are always there.
A person with low immunity or unhygienic practices can have a relapse of the disease after 2-3 weeks and can even become a silent carrier of the disease.

What is Paratyphoid
Definition
Paratyphoid is an enteric febrile infection caused by any one of the variants of Salmonella paratyphi and can affect the bloodstream and systemic organs.
Pathophysiology
- Highly contagious
- Spreads through stool, urine, and unhygienic practices
- Can spread through food cooked by carrier
- Incubation period about 10 days
- Not only humans, but some domestic animals are also carriers.
- Pathophysiology is similar to typhoid fever.
Prevalence
- 5.4 million cases are reported annually
- Prevalent in third-world countries with poor sanitation systems.
- Travellers’ vaccine for S. Paratyphi is mandatory before traveling to these countries.
Causative Organism
Three serotypes of Salmonella Paratyphi are responsible for paratyphoid.
- S. Paratyphi A
- S. Paratyphi B
- S. Paratyphi C
Signs and Symptoms
- Gradual onset of fever
- Persistent headache
- Lethargy and fatigue
- Poor appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea/ vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea
- “Rose spots” (maculopapular rash)
- Hepatosplenomegaly
Diagnosis
- Blood Culture and Sensitivity
- Blood Complete Picture
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Stool test
- Urine culture
Treatment
Antibiotics (Oral and IV) for 1-2 weeks
Hospital Admission
Rehydration
Prognosis
Usually recovery is complete after timely administration of antibiotics and rehydration therapy.
Difference between Typhoid and Paratyphoid
Definition
Typhoid and paratyphoid are bacterial febrile infections caused by different sets of causative organisms but with the same pathophysiology.
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology is the same for both typhoid and paratyphoid; bacteria enter the intestines and penetrate the bloodstream and later bone marrow, spleen, and liver. However, humans are the only carriers of typhoid while paratyphoid can be found in both humans and domestic animals.
Causative organism
Typhoid is caused by the bacteria Salmonella Typhi while paratyphoid is caused by any one of the three serotypes of Salmonella Paratyphi.
Symptoms
Both typhoid and paratyphoid present the same symptoms. However, the severity of symptoms of typhoid is much more intense as compared to paratyphoid.
Prevalence
Typhoid is more prevalent as compared to paratyphoid, with ~26 million annual cases of typhoid and ~5.6 million annual reported cases of paratyphoid.
Treatment
Treatment is the same after the onset of the disease. However, typhoid is preventable by vaccine shot while there is no vaccine for paratyphoid yet.
Table Comparing Typhoid and Paratyphoid
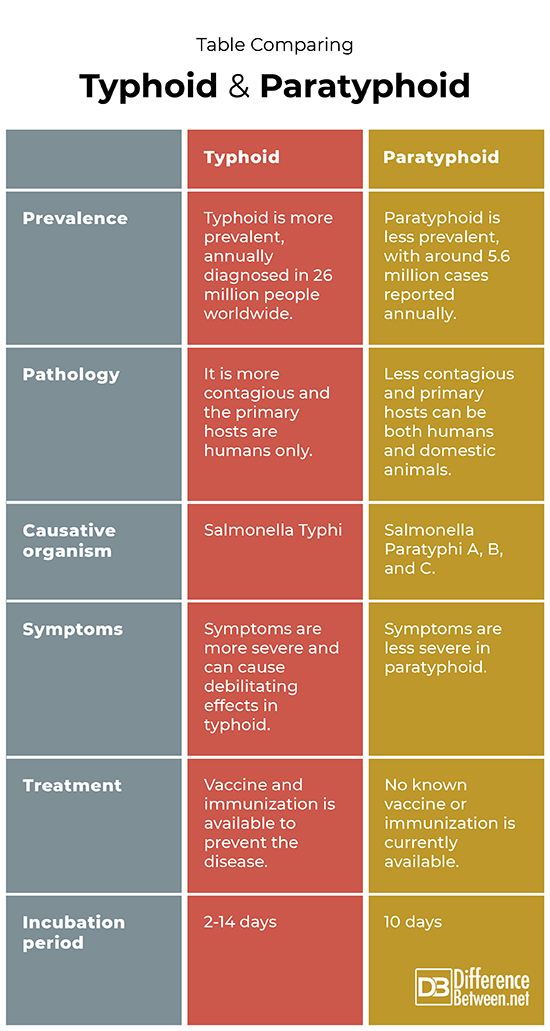
Summary of Typhoid and Paratyphoid
- Typhoid and paratyphoid are febrile, enteric infections caused by bacteria, affecting systemic organs and the bloodstream.
- Annually, 26 million cases of typhoid are reported while 5.6 million cases of paratyphoid are reported.
- Symptoms of typhoid are more severe and have intense effects on the body while symptoms of paratyphoid are less severe and have less deteriorating effects on the patient.
- Typhoid is caused by the bacteria known as Salmonella Typhi while paratyphoid is caused by different serotypes of Salmonella Paratyphi.
- Incubation period of typhoid infection is between 2-14 days while paratyphoid can show symptoms within 10 days of exposure.
- Vaccination against Typhoid causing bacteria is available and it can be prevented while no vaccine is yet available for paratyphoid.
- Typhoid is carried by humans only while paratyphoid can be carried by both humans and domestic animals.
FAQs
What is typhoid or paratyphoid?
Typhoid and paratyphoid are enteric infections caused by bacteria and present with fever, abdominal pain, and other symptoms.
What is the difference between Salmonella typhi and typhoid?
Salmonella Typhi is the bacterium that is the causative organism of the infection typhoid.
What is the difference between enteric fever and typhoid fever?
Typhoid fever is also known as enteric fever so they are the same.
What are the symptoms of paratyphoid?
Paratyphoid and typhoid have similar symptoms like abdominal pain, fever, headache, body aches, fatigue, nausea, poor appetite, and hepato-splenomegaly.
What is typhoid called today?
Typhoid is also called Enteric Fever or Travelers fever.
Is Para typhoid contagious?
Paratyphoid is contagious and can be spread through the food cooked by an infected cook.
- Difference Between Cystocele and Rectocele - September 8, 2023
- Comparison Between DHEA and DHEA Sulfate - September 1, 2023
- Difference Between Osteoporosis and Osteopenia - June 14, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. (n.d.). Paratyphoid fever. Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved February 1, 2023, from https://www.britannica.com/science/paratyphoid-fever https://www.britannica.com/science/paratyphoid-fever
[1]Bennet, J. E., & Douglas. (2020). Paratyphoid fever. Paratyphoid Fever - an overview | Science Direct Topics. Retrieved February 1, 2023, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/paratyphoid-fever
[2]Abdel Wahab MF; Haseeb AN; Hamdy HS; Awadalla YA; (n.d.). Comparative study between Paratyphoid A and typhoid fever cases. The Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association. Retrieved February 1, 2023, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17214195/
