Difference Between Subdural Hematoma and Stroke
Subdural hematoma is a type of intracranial hemorrhage that occurs when blood leaks out from a ruptured vessel in the subdural space. Stroke is a life-threatening medical emergency due to a sudden compromise in the blood supply of the brain. The blood vessels are either obstructed or there is bleeding in the brain in a stroke.
What is a subdural hematoma?
Definition: Subdural hematoma is the bleeding that occurs in the space below the dura mater, which is one of the three protective meninges of the brain. Subdural hematoma is not a bleed that occurs in the brain tissue, instead, it is the bleeding that occurs within the skull.
Causes and risk factors: Head injury is the main cause of subdural hematoma. There is evidence of brain atrophy in older people and even minor head trauma in the elderly makes them prone to develop subdural hematomas. Alcoholics and patients on anticoagulant medications are also at a higher risk of developing subdural hemorrhage.
Types: Acute, subacute and chronic are the three types of subdural hematomas. In acute subdural hematoma, symptoms appear right after the surgery, within minutes or hours. Subacute hematoma takes days to weeks whereas chronic hematoma takes weeks to months for the symptoms to appear.
Symptoms: Subdural hematoma is a type of traumatic brain injury. The symptoms of subdural hematoma can occur immediately after the bleed or may take weeks or months to become evident, as in its chronic variant. Signs and symptoms of subdural hematoma include a persistent headache, nausea, vomiting, slurred speech, confusion, dizziness, weakness of one side of the body, visual disturbances, and difficulty in walking. If the bleeding persists, the symptoms can get worse and can include paralysis, seizures, and coma.
Diagnosis: Thorough medical history and physical and neurological exam are essential to diagnose subdural hematomas. Healthcare professionals enquire about the details of the head injury such as how and when it occurred, the symptoms patient had immediately after injury, the consciousness level of the patient, and drug history. Computed tomography (CT) scan is the diagnostic imaging modality. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be needed.
Treatment: Hematomas which are small and have few symptoms might need no surgery. Bed rest and medications can cure such bleeds. Larger subdural hematomas are treated by decompression surgery.
Complications: Complications of subdural hematomas include brain herniation, increased risk of further bleeding, seizures after surgery, coma, and death.

What is a stroke?
Definition: A stroke is a medical emergency in which the brain tissue is not getting its blood supply adequately. The blood vessels in the brain are either blocked or there is a spilling of blood in the cranial tissue due to the rupture of a vessel.
Causes and risk factors: Two types of strokes are hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures. Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain is blocked. Risk factors for developing stroke include uncontrolled high blood pressure, anticoagulant use, aneurysms in blood vessels, smoking, and hypercholesterolemia.
Symptoms: Symptoms of stroke include difficulty in speaking, paresthesia of the face, arm, or leg, trouble walking, blurring of vision, and a sudden severe headache. Attention needs to be paid if any of these symptoms present in a patient and urgent hospital admission becomes necessary.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis of stroke is made by neurological exam and radiological tests such as CT scan and MRI, which show the exact size and location of the bleed.
Treatment: Thrombolytic drugs and thrombectomy are used to treat ischemic strokes. Blood pressure medications and therapies to reduce bleeding are used in hemorrhagic strokes. Sometimes, surgery becomes necessary to salvage the brain tissue from death. If the neurological deficits prevail after the stroke, physiotherapy becomes necessary to recover.
Complications: Permanent disabilities are the main complication of stroke. These include paralysis of one part of the body, weakness of muscles, difficulty in talking, and swallowing, and inability to void. Depression is also a complication that follows after physical compromise.
Difference between subdural hematoma and stroke
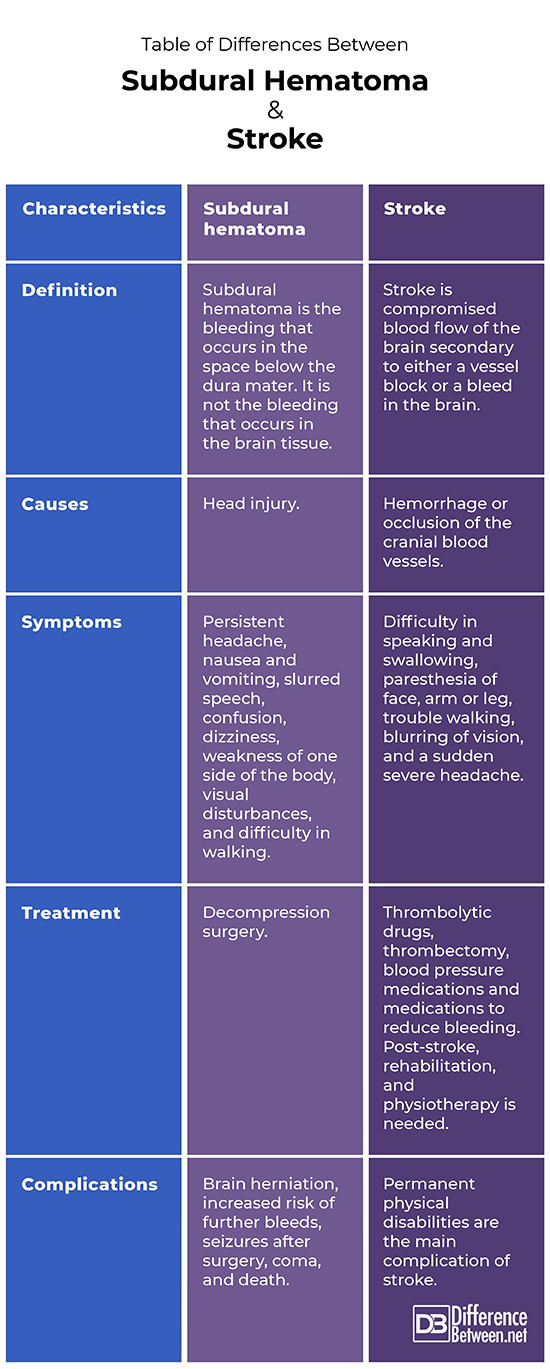
- Definition: Subdural hematoma is the bleeding that occurs in the space below the dura mater. It is not the bleeding that occurs in the brain tissue. A stroke is compromised blood flow of the brain secondary to either a vessel block or a bleed in the brain.
- Causes and risk factors: Head injury is the main cause of subdural hematoma. Risk factors of subdural hemorrhage include elderly patients, alcoholics, and those on anticoagulants. Causes of stroke include hemorrhage and occlusion of the cranial blood vessels. Risk factors for developing stroke include uncontrolled high blood pressure, anticoagulant use, aneurysms in blood vessels, smoking, and hypercholesterolemia.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of subdural hematoma include a persistent headache, nausea, vomiting, slurred speech, confusion, dizziness, weakness of one side of the body, visual disturbances, and difficulty in walking. Symptoms of stroke include difficulty in speaking and swallowing, paresthesia of the face, arm, or leg, trouble walking, blurring of vision, and a sudden severe headache.
- Diagnosis: Subdural hematoma is diagnosed by history, examination, and on CT scan findings. CT and MRI scans are needed to diagnose a stroke as well.
- Treatment: Larger subdural hematomas are treated by decompression surgery. Thrombolytic drugs, thrombectomy, blood pressure medications, and medications to reduce bleeding are used to treat stroke. Post-stroke, rehabilitation, and physiotherapy are needed.
- Complications: Complications of subdural hematomas include brain herniation, increased risk of further bleeding, seizures after surgery, coma, and death. Permanent physical disabilities are the main complication of stroke.
Table of differences between subdural hematoma and stroke
FAQs:
What are the five warning signs of stroke?
Five warning signs of stroke are sudden numbness in the face, arm or leg, sudden confusion or trouble speaking, sudden visual disturbance, sudden loss of balance or trouble walking and sudden, severe headache.
What happens to a person when they have a stroke?
As the blood supply to the brain is affected the person may have symptoms such as difficulty in speaking and swallowing, paresthesia of face, arm or leg, trouble walking, blurring of vision, and a sudden severe headache.
Can subdural bleeding mimic a stroke?
Yes, it can have the same symptoms as stroke.
Is a brain hematoma a stroke?
Yes, it is a type of hemorrhagic stroke.
Is there a difference between bleed on the brain and a stroke?
No, these are the same.
What happens to the brain after a subdural hematoma?
Brain tissue is compromised after the hematoma, and it can result in lifelong physical compromise.
What is the survival rate of a subdural hematoma?
If operated timely, the functional survival rates can be as high as 65%.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Byrne, Paul, and John Bartlett. "Chronic subdural haematoma." British journal of neurosurgery 5.5 (1991): 459-460.
[1]ABODERIN, ISABELLA, and GRAHAM VENABLES. "Stroke management in Europe." Journal of Internal Medicine 240.4 (1996): 173-180.
[2]Phipps, Michael S., and Carolyn A. Cronin. "Management of acute ischemic stroke." Bmj 368 (2020).
