Difference Between Neuromodulation and Neurostimulation
Neuromodulation is defined as modification of nerve function. Neurostimulation is defined as stimulation of nerves.

What is Neuromodulation?
Definition:
Neuromodulation is a method in which nerve function is altered in some way to bring about a therapeutic response.
Uses:
Neuromodulation can be used to help people with pain but it is also used to help epileptics and people with various neuromuscular dysfunction. Chronic pain sufferers may also benefit from neuromodulation methods.
Methods:
There is more than one way in which neuromodulation can take place. In the case of neuromodulation, nerve impulses (also called action potentials) can be triggered or inhibited. Nerves can be stimulated using neurostimulator devices such as electrodes. Chemicals can be used to alter nerve impulses. Examples of neuromodulation drugs include anti-seizure medications like carbamezapine and gabapentin.
Advantages:
The method of neuromodulation can help treat pain in patients where conventional methods have failed. Some of the medications such as carbamezapine treat severe nerve pain and act as an anti-convulsant.
Disadvantages:
There are potential risks to different types of neuromodulation methods, including adverse reactions where drugs are used. Medications that are used as neuromodulators may have unpleasant or even dangerous side effects. In some cases, a rare skin reaction called Stevens-Johnsons syndrome can occur resulting in a painful rash. More dangerous allergic reactions can occur so patients need to be monitored carefully. There is a risk of infection and bleeding with invasive methods.

What is Neurostimulation?
Definition:
Neurostimulation is the method in which nerves are stimulated using some type of device.
Uses:
The uses of neurostimulation include treating patients who have Parkinson’s disease or epilepsy. It can even be used to treat tinnitus, incontinence, and some types of chronic pain.
Methods:
Direct brain stimulation is one type of neurostimulation in which electrodes are implanted into the brain via temporary holes drilled in the skull, and used to trigger nerve impulses. In Parkinson’s disease the most common method is by neural stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) of the brain. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is a non-invasive way of treating chronic pain, particularly muscle pain. It involves placing electrodes on the skin. The machine then releases small electrical impulses.
Advantages:
Neurostimulation is helpful for some people in treating pain or movement problems. It can help to stimulate nerves of people struggling with peripheral nerve problems, and it helps treat inflamed spinal meninges.
Disadvantages:
Neurostimulation does not work to relieve pain in all cases. For instance, spinal cord pain is not alleviated for all patients who undergo neurostimulation. With deep brain stimulation there is a risk of infection associated with the procedure. Spinal cord stimulation has a small risk of complications such as hemorrhage or blood clots.
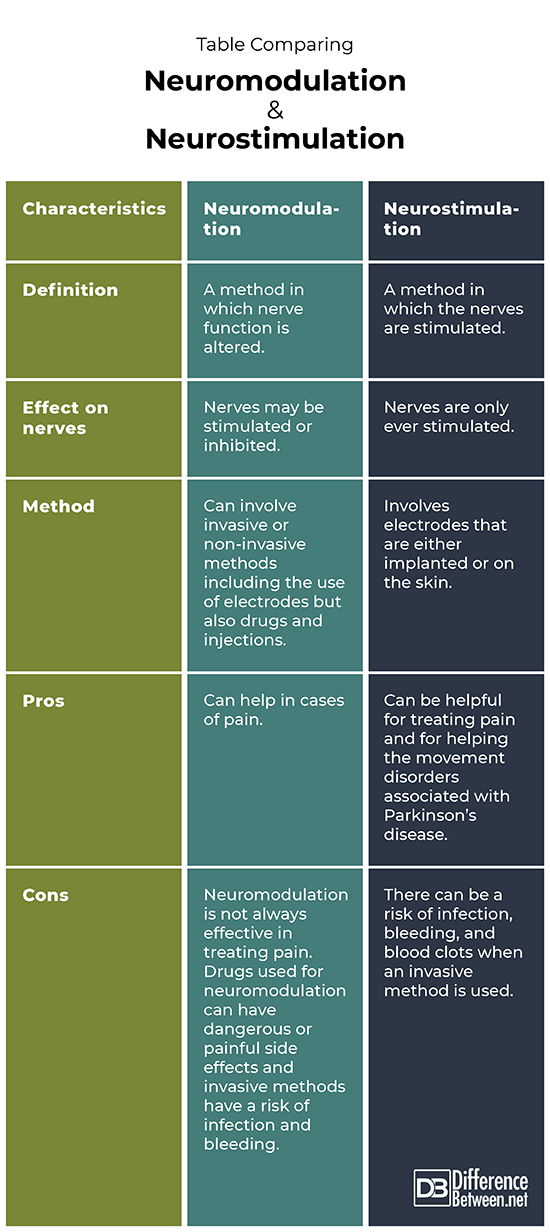
Difference between Neuromodulation and Neurostimulation
Definition
Neuromodulation isa method in which nerve function is altered. Neurostimulation is a method in which the nerves are stimulated.
Effect on nerves
In the case of neuromodulation, nerves can be stimulated or even inhibited. In the case of neurostimulation, nerves are only ever stimulated and not inhibited.
Method
Neuromodulation methods can involve the use of electrodes, other devices, and also drugs. Neurostimulation methods always involve the use of electrodes that may be implanted or placed on the skin.
Pros
The benefit of neuromodulation is that it can be very helpful in treating pain and abnormal electrical activity. The benefit of neurostimulation is that it can treat pain and also help with movement disorders by stimulating the nerves.
Cons
The drawback of neuromodulation is that it doesn’t always work for treating pain and there can be bad side effects where drugs are used, as well as a risk of infection and bleeding. The drawback of neurostimulation is there is a risk of infection, bleeding, and clots when invasive procedures are done.
Table comparing Neuromodulation and Neurostimulation
Summary of Neuromodulation and Neurostimulation
- Neuromodulation is a term used to describe a method in which nerve function is modified.
- Neurostimulation is one type of neuromodulation in which nerve function is stimulated by means of devices.
- Both neuromodulation and neurostimulation can help some patients who have chronic pain.
FAQ
What is a neuromodulation device?
A neuromodulation device is an electronic device such as electrodes, which can be used to modify the nerve stimulus.
What are some examples of neuromodulation?
Spinal cord stimulation and the use of anti-convulsant medications are examples of neuromodulation.
How does neuromodulation work for tinnitus?
In some cases, neuromodulation in the form of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), has assisted patients with tinnitus, but the result is not permanent. The way tDCS works is a low frequency current is passed between two electrodes that are placed on the head. The idea is to alter the brain activity in the temporal lobe, which is where the problem of tinnitus occurs.
What is a neurostimulator used for?
A neurostimulator is a device used to trigger nerve activity.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Luan, Song, et al. "Neuromodulation: present and emerging methods." Frontiers in neuroengineering 7 (2014): 27.
[1]Peter, Nicole, and Tobias Kleinjung. "Neuromodulation for tinnitus treatment: an overview of invasive and non-invasive techniques." Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B 20.2 (2019): 116-130.
[2]Swann, Nicole, et al. "Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus alters the cortical profile of response inhibition in the beta frequency band: a scalp EEG study in Parkinson's disease." Journal of Neuroscience 31.15 (2011): 5721-5729.
