Difference Between Lecithin and Choline
Both lecithin and choline are essential for health. They may be found in foods and may be taken as supplements. Specifically, lecithin contains choline. Their distinctions are discussed below.

What is Lecithin?
Lecithin is a group of fatty substances vital for proper biological function in animals and plants. It is found in the tissues of the body and is naturally occurring in many kinds of foods like eggs, sunflower seeds, sea food, green vegetables, legumes, red meat, and animal fat. One of its main components, phosphatidylcholine (PC), has been reported to have health benefits. Most lecithin supplements are made from soybeans and there have been no well-documented interactions with certain drugs or conditions. Hence, they are generally recognized as safe; as a general rule, the dosage should not exceed 5,000 mg per day. They are available in various forms such as tablets, capsules, soft gels, powder, liquid, and paste (Leonard, 2017; Christiansen, 2021).
The uses/benefits of lecithin include the following (Watson, 2017; Christiansen, 2021):
- Emulsifier and Extends Shelf Life
A commercial form of lecithin is used in food preparations, cosmetics, and medications.
- Treat certain health conditions
Lecithin supplements may be taken to treat digestive problems (by improving intestinal mucus) and high cholesterol (by increasing good HDL cholesterol and lowering bad HDL cholesterol). Lecithin has been promoted to treat issues related to the gallbladder, heart, liver, skin, and mental health (i.e., bipolar disorder and anxiety). Lecithin supplements have also been claimed to improve sleep patterns, alleviate stress, reduce inflammation, and enhance athletic performance. They may also prevent clogged milk ducts of breast-feeding mothers; increase immune function by increasing white blood cells; and may improve memory and brain development.
The possible side effects of lecithin supplements may include diarrhea, nausea, increased salivation, abdominal pain, decreased appetite, and abdominal bloating. Certain individuals may also have allergic reactions; however, this rarely happens even in people with soy allergies. Also, since there is only limited research on lecithin safety, children should not yet take lecithin supplements (Christiansen, 2021).

What is Choline?
Choline is an essential nutrient that supports different bodily functions (i.e., metabolism and cell growth) and overall health. It is needed by all animal and plant cells for structural integrity. This recently discovered nutrient has only been acknowledged as a required nutrient by the Institute of Medicine in 1998 (Brown, 2018).
It is made by the body and is naturally occurring in some foods such as proteins (i.e., beef, soybeans, poultry, and fish), vegetables (i.e., broccoli, potatoes, and mushrooms), whole grains (i.e., rice, whole wheat bread, and quinoa), and nuts. However, many people are not meeting the recommended intake. Some multivitamins and supplements also contain choline in the form of lecithin (Eske, 2019).
The health benefits of choline include the following (Eske, 2019; Brown, 2018):
- Cell Maintenance and DNA Synthesis
Choline affects gene expression, cell messaging, and makes fats that make up cellular membranes.
- Metabolism
Choline is helpful in fat metabolism and is required for making a substance which removes cholesterol from the liver.
- Supports Heart, Liver, and Lung Function
Choline is being converted into a neurotransmitter that facilitates breathing and heart rate. Choline supplementation has also been shown to improve lung function and reduce fatty liver disease symptoms.
- Improves Memory and Cognition
Choline is a vital nutrient for brain development.
- Reduces the Risk of Pregnancy Complications
It has been reported to reduce preeclampsia markers.
Too much choline consumption may cause adverse effects such as sweating, hypotension, vomiting, excessive salivation, liver toxicity, and fishy body odor. The daily upper intake levels for choline are based on age (National Institutes of Health, 2021):
1-8 years old- 1g
9-13 years old- 2g
14-18 years old- 3g
19 and above – 3.5g
Difference between Lecithin and Choline
Definition
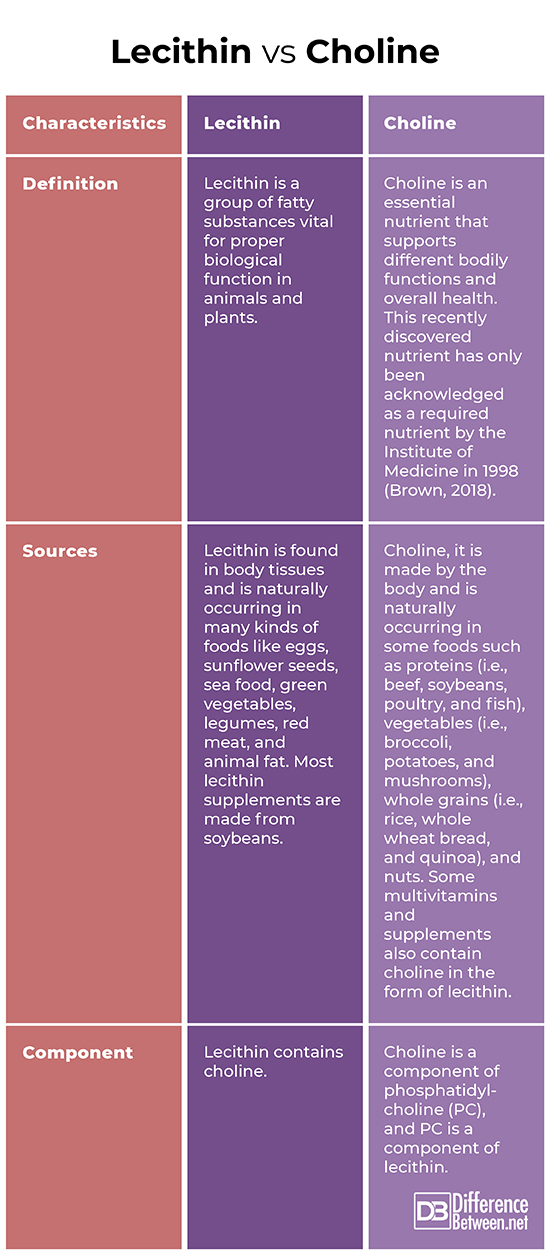
Lecithin is a group of fatty substances vital for proper biological function in animals and plants. One of its main components, phosphatidylcholine (PC), has been reported to have health benefits (Leonard, 2017). In comparison, choline is an essential nutrient that supports different bodily functions (i.e., metabolism and cell growth) and overall health. It is needed by all animal and plant cells for structural integrity. This recently discovered nutrient has only been acknowledged as a required nutrient by the Institute of Medicine in 1998 (Brown, 2018).
Sources
Lecithin is found in body tissues and is naturally occurring in many kinds of foods like eggs, sunflower seeds, sea food, green vegetables, legumes, red meat, and animal fat. Most lecithin supplements are made from soybeans. As for choline, it is made by the body and is naturally occurring in some foods such as proteins (i.e., beef, soybeans, poultry, and fish), vegetables (i.e., broccoli, potatoes, and mushrooms), whole grains (i.e., rice, whole wheat bread, and quinoa), and nuts. Some multivitamins and supplements also contain choline in the form of lecithin.
Component
Lecithin contains choline. Specifically, choline is a component of phosphatidylcholine (PC), and PC is a component of lecithin.
Lecithin vs Choline
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is choline and lecithin the same thing?
They are closely related but they are not the same thing. In our diet, lecithin is the primary source of choline (WebMD, 2022).
Is sunflower lecithin the same as choline?
Sunflower lecithin is rich in essential fatty acids like choline. Some multivitamins and supplements also contain choline in the form of lecithin.
Is choline and inositol the same as lecithin?
Lecithin consists of choline, inositol, linoleic acid, and phosphorus among others. Hence, choline and inositol are components of lecithin.
What percentage of lecithin is choline?
One of the main components of lecithin is phosphatidylcholine and it contains about 13% choline by weight (Zeisel, 2015).
Summary
- Both lecithin and choline are nutrients essential for health and may be found in foods and may be taken as supplements.
- Lecithin contains choline.
- Lecithin supplements are generally recognized as safe; as a general rule, the dosage should not exceed 5,000 mg per day.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]National Institutes of Health. (2021) Choline. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Choline-Consumer/
[1]WebMd. (2022). Lecithin. https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-966/lecithin#:~:text=Reviews%20(44)-,Overview,similar%20to%20the%20B%20vitamins.
[2]Zeisel, S. (2015). Choline. Linus Pauling Institute. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/other-nutrients/choline
