Difference Between BYOD, CYOD, COPE and COBO
With flexibility in the workplace and technological advancement, businesses have started to think about their employees when deciding how to handle provisioning of mobile devices. Generally, there are four main approaches to what level of freedom the employees can have while using mobile devices at their workplace for work purposes: bring your own device (BYOD), choose your own device (CYOD), company owned business only (COBO), and company owned personally enabled (COPE).

What is BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)?
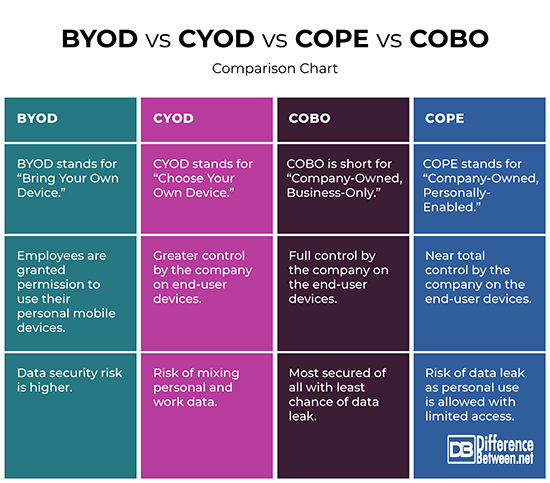
BYOD is a fairly common device ownership and management model that almost every organization implements. In this model, employees are granted permission to use their personal mobile devices to connect to their organizational networks. BYOD simply refers to the use of personal devices for work purposes. This model is popular among small to medium businesses, largely because of the cost-saving measures. However, large business organizations are also exploring it as an option because this reduces the technology overhead and expenditures associated with lost or stolen devices. This is a common practice where employees are encouraged to use their personal devices for work-related activities.

What is CYOD (Choose Your Own Device)?
CYOD is yet another mobile device management program that allows employees access to a limited choice of devices that are approved for the business work and meet the criteria for the management. Employees are offered a suite of choices but the company retains control over security, reliability, and durability. This means company maintains a list of pre-approved mobile devices and do not have to deal with the variability, yet employees have some degree of flexibility and privacy. Employees can buy this device at full or partial expense borne by the company, and use it for both personal and work use.

What is COPE (Company-Owned, Personally-Enabled)?
Under the COPE business model, employees get company-provided devices as per company’s policy, though employees may use the devices for their personal uses as well. COPE model is mostly focused on smartphones because nobody wants to carry two smartphones to work. So, companies provide smartphones primarily for work related requirements, but employees can use the smartphone for basic functionalities like call, message, or personal applications with some controls on flexibility and usage. Such devices are fully administered and managed by the company, and the users have restricted access to installing or using apps that are not authorized by the company.

What is COBO (Company-Owned, Business-Only)?
COBO stands at the opposite side of the spectrum. Under this model, the devices are property of the company and are used exclusively for business purposes. The devices are procured, provisioned, secured, and monitored by the company. The devices are strictly business-only, restricting users from accessing any applications for personal use. The company chooses and pays for the devices and then put their most restrictive security policies in place. This simply means the company issues the employee a device and holds ownership and maintenance of the device. Such devices are fully administered and managed by the company, and users have limited access to add/modify the applications.
Difference between BYOD, CYOD, COPE, and COBO
Control
– BYOD is a common device management model wherein employees are encouraged to use their personal devices for work-related activities. CYOD means employees are offered a suite of choices but the company retains control over security, reliability, and durability of the devices. Under the COPE model, employees get company-provided devices as per company’s policy, though employees may use the devices for their personal uses as well. Under the COBO model, the devices are property of the company and are used exclusively for business purposes.
Security
– Data security risk in BYOD is relatively more as data exchange between business and personal applications cannot be restricted. The risk is slightly lower in CYOD than BYOD, but there is also potential risk of mixing personal and work-related data, and could result in data leak. In COPE, employees may use the devices for their personal use as well, so risk of mixing personal and work data is there. COBO, on the other hand, is the most secured of all with least chance of data leak as the devices are full administered and managed by the company.
BYOD vs. CYOD vs. COPE vs. COBO: Comparison Chart
Summary
Whether you decide to implement the BYOD, CYOD, COBO, or COPE model, all the models point to one thing – increased productivity for mobile employees. Choosing the right device management model is the key to successful enterprise mobility and secured business environment. The one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work all the time and business organizations have to incorporate a mix of two or more models within their environment to achieve maximum productivity. Besides, each model has its own set of pros and cons. COBO is the most secured of them all though.
What is COBO calling?
COBO refers to devices that are strictly used for work related uses and remain the property of the company. Employees are not allowed to use such devices for personal use.
What does COPE stand for in security Plus?
COPE stands for “Corporate-Owned, Personally-Enabled,” which means the organization procures and maintains the devices and then use them as both personal and corporate devices.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Sachowski, Jason. Digital Forensics and Investigations: People, Process, and Technologies to Defend the Enterprise. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2018. Print
[1]Polkowski, Zdzislaw, et al. Data Science in Engineering and Management: Applications, New Developments, and Future Trends. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2018. Print
