Difference Between VQ Scan and CTA
With the advent of technological evolution in the medical industry, the field of nuclear medicine has evolved significantly in the last couple of years. In particular, computer tomography angiography (CTA) and ventilation-perfusion (VQ) scan have come into their own as important diagnostic tools in routine clinical practice. But, which one’s better?

What is a VQ Scan?
A ventilation/perfusion scan, commonly called a VQ scan is a medical imaging technique that uses small amount of a radioactive substance called a tracer to obtain images of a bodily organ in order to diagnose or rule out a pulmonary embolism. It is basically a scan of the lungs; hence the name ventilation (V) and perfusion (Q) scan. It measures air flow using a ventilation scan and blood flow using a perfusion scan, in your lungs. It uses nuclear radiology to detect any blood clot in the lungs and if left untreated, the blood clots can be fatal.
A VQ scan mainly involves two scans that are usually done one after the other. It is one procedure but there are two tests involved; one is to measure how well air flows through your lungs and the other scan shows where the blood is flowing through the lungs. The ventilation part evaluates airflow going in and out of the lungs, and the perfusion part evaluates the blood flow to the lungs. This test is performed in the nuclear medicine area of the radiology department.
What is CTA?
Computer tomography angiography, or CT angiography, is the most common diagnostic test performed by doctors to test a pulmonary embolism, which is a blood clot in the lungs or the pulmonary arteries leading from the heart into the lungs. CTA is a non-invasive procedure that uses a powerful X-Ray machine to take high-quality images of your heart and its blood vessels. If something shows on the scans, the doctor may further prescribe treatments to monitor the clot over time. It plays an important role in the evaluation and management of acute pulmonary embolism.
The test combines a CT scan with a special dye injection that produces images of blood vessels and tissues in a body part. The injection is administered through an IV in your arm. CT is a preferred first-line imaging test used in the evaluation of any suspected acute PE. If chest radiographs are abnormal, a VQ scan is likely to be non-diagnostic, so in this case, a CTA would be a preferred diagnostic strategy.
Difference between VQ Scan and CTA
Overview
– Ventilation-Perfusion (VQ) scanning and Computer Tomography Angiography (CTA) are two of the most common imaging tests used in the clinical setting to diagnose acute pulmonary embolism (PE). VQ scan measures the circulation of air and blood flow within the lungs. The word ‘Q’ is used to describe blood flow in physiology. The CT pulmonary angiogram works similarly to the coronary angiogram but focuses on the pulmonary arteries instead of the coronary arteries. CTA is a non-invasive procedure that uses a powerful X-Ray machine to take high-quality images of the heart and its blood vessels.
Procedure
– The VQ scan is a two-step procedure. The first test requires you to inhale a radioisotope tracer that’s mixed with oxygen through a mouthpiece and then you just lay flat on the scanner bed and the machine starts taking images. The second scan requires you to be injected with a radioactive tracer via an IV and then the tracer travels through your blood and into the lungs. In both the scans, the images will show which areas of your lungs aren’t getting enough blood.
The CT angiogram looks for blood clots in the lungs and employs a CT scan combined with a special dye injection that produces images of blood vessels and tissues in a body part. The injection is administered through an IV in your arm and the images are taken when the iodine contrast passes through the pulmonary arteries and throughout the lungs.
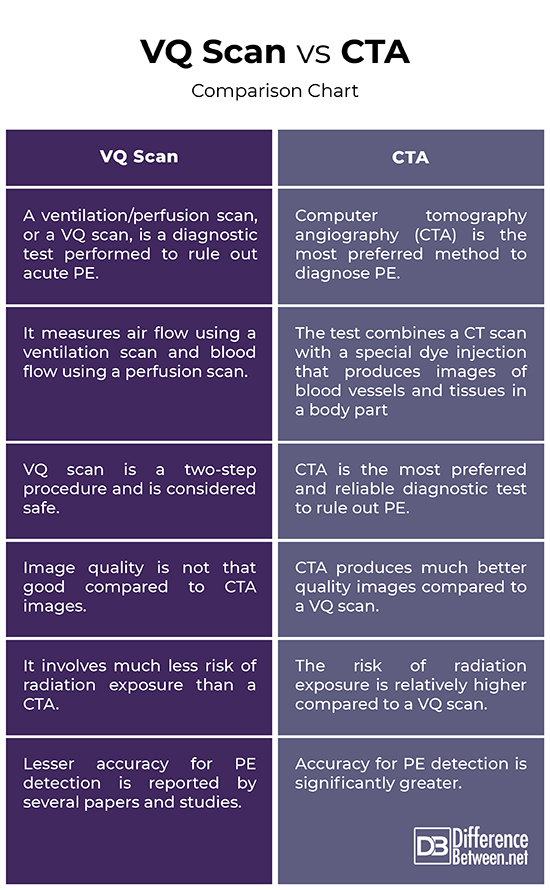
VQ Scan vs. CTA: Comparison Chart
Summary
Both CTA and VQ scanning are two of the most common diagnostic methods to test an acute pulmonary embolism in patients. CTA, however, produces better quality images and is considered a more reliable and preferred diagnostic tool for PE detection. Even accuracy for PE detection is significantly greater in CTAs compared to VQ scanning. However, the risk of radiation exposure is significantly lower in a VQ scan compared to CT angiography. VQ is also more sensitive than CTA.
What is the difference between a VQ scan and CTPA?
A VQ scan is a two-step procedure that uses a ventilation scan to measure airflow and a perfusion scan to measure blood flow, in order to diagnose acute PE. CTPA, on the other hand, is the most preferred and reliable diagnostic tool to rule out suspected PE. CTPA takes images of blood vessels running from the heart to the lungs.
When would you use a VQ scan?
VQ scan is a nuclear radiology test to look for or rule out blood clots in your lungs. There are two tests involved; one is to measure how well air flows through your lungs and the other scan shows where the blood is flowing through the lungs.
What is another name for VQ scan?
VQ scan is also called a ventilation-perfusion scan, or ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy. It is a diagnostic method to detect any evidence of blood clots in lungs.
What type of test is a VQ scan?
VQ scan is a diagnostic test that measures airflow (ventilation) and blood flow (perfusion) in the lungs. The test looks for any evidence of blood clots in the lungs to rule out pulmonary embolism.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Geibel, A., et al. Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Challenge for Hemostasiology. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2012. Print
[1]Brant, William E. and Clyde A. Helms. Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology. Pennsylvania, United States: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2012. Print
[2]Konstantinides, Stavros V. Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2007. Print
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEEcv-8xAE-ventilation-perfusion-scan/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEdhyrTUQs-hand-holding-mouse-with-blur-computed-tomography-angiography-coronay-cta-coronary-background-/
