Difference Between Gallstones and Kidney Stones Pain
Gallstones pain is felt in the upper right side of the abdomen where the liver and gallbladder is located. Kidney stones pain is concentrated in the back and flank region but can travel as the stone passes.

What is Gallstones Pain?
Definition:
Gallstone pain is severe and occurs in the upper right part of the abdomen and often extends into the upper back between the shoulder blades.
Symptoms:
The pain of gallstones worsens if a stone blocks the common bile duct. The pain worsens rapidly when this happens, with tenderness extending into the back between the shoulder blades. Additional symptoms can include nausea and vomiting and fever if the gallbladder becomes infected. Jaundice can occur due to the flow of bile being blocked by the stone.
Reasons for gallstones:
Gallstones occur most often in women, possibly due to hormones. Sudden changes in weight and a diet of junk food that is high in fat also seem to be related to the problem.
How gallstones is diagnosed:
The location and type of pain can make a doctor suspect gallstones. An ultrasound exam can also show a shrunken gallbladder with one or more gallstones present.
Treatment options:
The best way to treat gallstones is to take out the gallbladder which is best done during laparoscopic surgery.
Complications of gallstones:
Untreated gallstones can result in bile blockages and infections and sometimes gallstones also cause problems with the functioning of the pancreas.

What is Kidney Stones Pain?
Definition:
Kidney stone pain is excruciating, beginning suddenly in the back and flank region.
Symptoms:
The pain of a kidney stone is severe and moves through the body as the stone moves. This means that the pain often travels from the back region down the side towards the bladder. Vomiting is another common symptom of a kidney stone. An inability to urinate may also occur with kidney stones.
Reasons for kidney stones:
Kidney stones may form because of an unhealthy diet which contains too much oxalate, excess vitamin C, and can happen if a person is dehydrated or has hypercalcemia.
How kidney stones is diagnosed:
The clinical symptoms, particularly the severity and location of pain, can indicate a kidney stone. In addition, urinalysis often indicates hematuria (blood in the urine). Imaging tests like CT scans can also be done.
Treatment options:
Kidney stones can be broken up by a method called shock wave lithotripsy, which uses shock waves to break up the kidney stones. This method does not work for all situations though and sometimes the stones need to be removed endoscopically.
Complications of kidney stones:
Kidney stones can block the passage of urine and result in swelling in the ureter, infections in the kidney, and renal damage. A dangerous complication is infection leading to blood-poisoning.
Difference between Gallstones and Kidney stones pain?
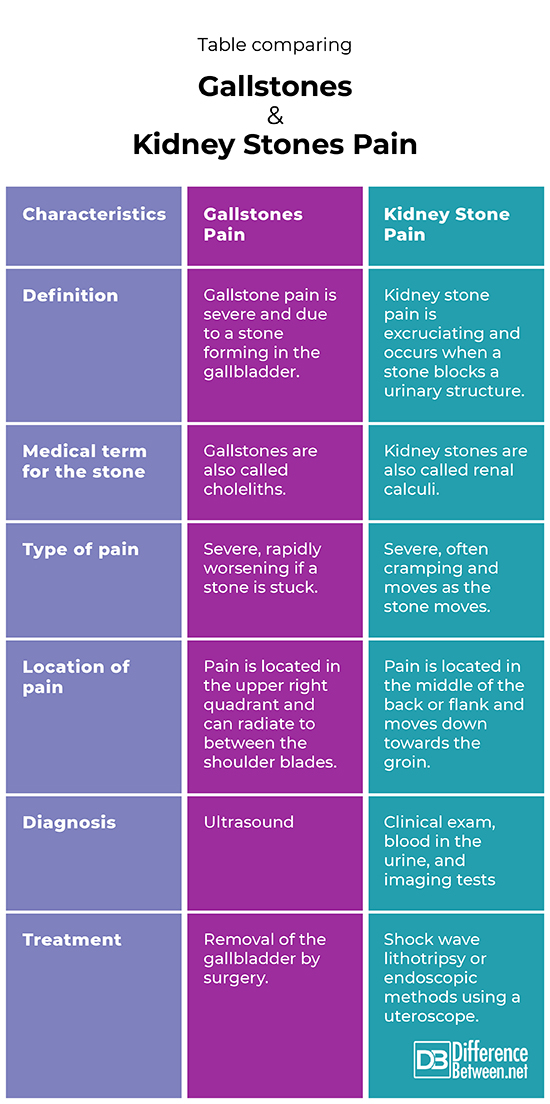
Definition
Gallstone pain is a severe pain due to a stone forming in the gallbladder. Kidney stone pain is excruciating and occurs when a stone blocks a urinary system structure.
Medical term for the stone
Gallstones are called choleliths. Kidney stones are called renal calculi.
Type of pain
The pain of gallstones can be severe and very quickly worsens if a stone is stuck in a duct. The pain of kidney stones is very severe; it can feel crampy and often moves as the stone passes down the ureters towards the bladder.
Location of the pain
Pain of gallstones is located in the upper right part of the abdomen where the liver is and it usually is also felt in the back between the shoulders. Pain of kidney stones begins in the back and side beneath the ribs and moves downwards towards the bladder.
Diagnosis
Gallstones are most easily diagnosed by ultrasound. Kidney stones are diagnosed by clinical exam and imaging tests such as CT scans.
Treatment
Gallstones pain is treated by removing the gallbladder completely in a laparoscopic procedure. Kidney stones pain is alleviated once the stones pass and if needed, treated using shock wave lithotripsy or endoscopic methods such as using a uteroscope.
Table comparing Gallstones and Kidney stones pain
Summary of Gallstones Vs. Kidney stones pain
- Gallstones pain is focused in the upper right side of the abdomen and between the shoulder blades.
- Kidney stones pain starts in the middle of the back and usually moves down as the stones move towards the bladder.
- Both gallstones and kidney stones cause severe disabling pain when stones become lodged in a duct.
Do gallstones pass through urine or stool?
Gallstones can, on occasion pass into the small intestine through the common duct and then be eliminated in the stool.
Is there a connection between kidney stones and gallstones?
There is a connection between both condition in people who have IBD, since research has shown that both kidney stones and gallstones are also linked to inflammation in the bowel.
How can you tell if you have kidney stone pain?
The pain begins in the back, can be crampy and severe, and it tends to move down the side and into the lower abdomen as the stone moves from ureter to bladder.
What dissolves kidney stones fast?
Doctors can dissolve uric acid stones using prescription strength potassium citrate. Shockwave therapy can also help break apart stones.
Does walking help pass kidney stones?
Walking can help kidney stones to pass.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Fagagnini, Stefania, et al. "Risk factors for gallstones and kidney stones in a cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases." PloS one 12.10 (2017): e0185193.
[1]Lindenmeyer, Christina. “ Cholelithiasis.” Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2020, https://www.merckmanuals.com/en-ca/professional/hepatic-and-biliary-disorders/gallbladder-and-bile-duct-disorders/cholelithiasis?query=Gallstones
[2]Preminger, Glenn M. “Urinary Calculi (Nephrolithiasis; Stones; Urolithiasis)”” Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2020, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/genitourinary-disorders/urinary-calculi/urinary-calculi
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lenticular_kidney_stone.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:%D0%96%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%B8_%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%9A%D0%B0,Gallstones!!.jpg
