Difference Between Dextroamphetamine and Adderall
Both are commonly prescribed over the counter mediations for narcolepsy and ADHD. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, or ADHD, is a chronic condition that affects millions of children and can persist into adulthood. It is a mental health disorder that affects your ability to pay attention for a prolonged period of time. It is characterized by its symptoms, which include hyperactivity, inattention, and impulsivity. It is a complex brain disorder that is often reveled by a tendency to change the subject, lack of perseverance, and disorganization. Children with ADHD are easily distracted and find it difficult to stay concentrated or stay focused regardless of how hard they try.

What is Dextroamphetamine?
Despite the advances in medical sciences in the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of ADHD in children and adults alike, the condition remains controversial. One of the major controversies surrounding ADHD is the use of psychostimulants in the treatment of the brain disorder. Psychostimulants such as dextroamphetamine are by far the most widely researched and commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of ADHD. Dextroamphetamine is a powerful central nervous system stimulant that affects the chemicals in the brain and nerves by releasing dopamine and norepinephrine from presynaptic nerve endings that contribute to hyperactivity and impulsive control.
Dextroamphetamine is among the very few immediate release (IR) stimulant medications approved by the FDA for use in children with ADHD, and it continues to play a therapeutic role in other medical conditions such as narcolepsy and depression. This medication improves both the cognitive (impulsivity and inattention) and non-cognitive (hyperactivity) domains of the disorder. What it actually does is increase the production and inhibit the reuptake of these three neurotransmitters: dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin. It basically activates the chemicals in the area of the brain that helps you pay attention and focus.
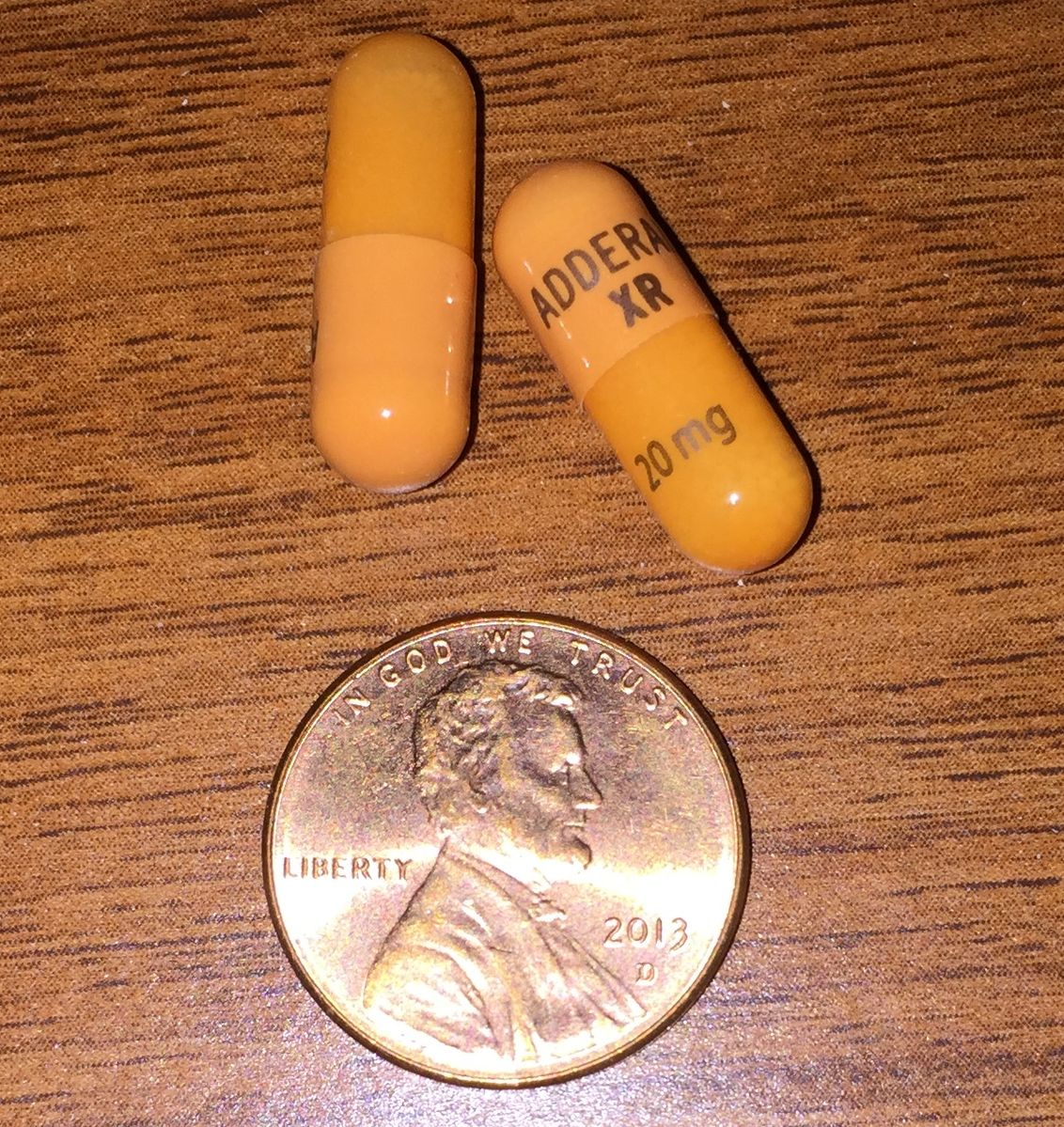
What is Adderall?
Adderall is the trade name for a combination of two drugs: amphetamine and dextroamphetamine. It is a FDA-approved prescription drug primarily used for the treatment of ADHD and narcolepsy – a condition that causes daytime sleepiness. It is a mixture of amphetamine salts and thus, a close relative of methamphetamine, commonly known as meth. When ingested, it takes effects on the brain within an hour of use, affecting the neuroreceptors in the central nervous system and ultimately, increasing the effect of dopamine and serotonin. It can be used alone or with other medications to treat the symptoms of hyperactivity and impulse control.
Adderall is used by many college students for weight loss, but it is most commonly used as an academic performance enhancer. Many use it mental endurance to get through the challenges of schools and perform better academically, but there is no clinical evidence that proves that the drug actually improves student grades or learning outcomes. However, Adderall is a potent CNS stimulant used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. The dopamine and serotonin released by the stimulant helps overcome the deficit in ADHD patients and effectively heighten certain desirable attributes such as focus, alertness and attention.
Difference between Dextroamphetamine and Adderall
Drug Class
– Both Dextroamphetamine (brand name: Dexedrine) and Adderall are FDA-approved prescription medications that belong to a class of drugs known as stimulants. Both are central nervous system stimulants used for the treatment of the ADHD. Adderall is the trade name for a combination of two drugs: amphetamine and dextroamphetamine. The generic version of the stimulant Dexedrine is called dextroamphetamine. Both are nearly identical drugs, but Adderall tends to be more powerful because it contains a mixture of two drugs.
Active Ingredient
– Both dextroamphetamine and Adderall contain forms of the synthetic compound amphetamine, which is a central nervous system stimulant. Dexedrine contains the most potent form of amphetamine, d-amphetamine, which is one of the widely used stimulant drugs for the treatment of ADHD. Adderall, on the other hand, is a mixture of amphetamine salts and thus, a close relative of methamphetamine, commonly known as meth. It contains a 3:1 ratio of two IR drugs: d-amphetamine and l-amphetamine.
Medical Use
– Both the stimulants work by blocking the re-uptake of dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine into the pre-synaptic neuron, and increase the release of these monoamines into the extra-neuronal space. The dopamine released by the stimulants overcomes the deficit seen in ADHD patients. Adderall, however, is also used by college students as an academic performance enhancer to help them achieve better grades. Some students use Adderall for mental endurance, and as appetite suppressant, athletic enhancer and so on, but there is no evidence that it helps them improve their academic performance.
Dextroamphetamine vs. Adderall: Comparison Chart

Summary
While both Adderall and dextroamphetamine are FDA-approved medications used for the treatment of hyperactivity disorder and impulse control, Adderall is believed to be more powerful simply because it is a combination of two drugs. Both are safe to use for children below 3 years of age, but the use of Adderall as an academic and athletic enhancer is still up for debate. Also, long term users of Adderall developed an inability to feel pleasure without a chemical stimulant and these effects can continue even after you stop taking Adderall. Regardless, both the stimulants are used to treat the symptoms of ADHD and narcolepsy.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Diagnosis and Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Maryland, United States: Foundation for Advanced Education in the Sciences, 1998. Print
[1]Re, Anna Maria. Understanding ADHD: A Guide to Symptoms, Management and Treatment. Abingdon, United Kingdom: Routledge, 2020. Print
[2]Nigg, Joel T. What Causes ADHD?: Understanding What Goes Wrong and Why. New York, United States: Guilford Press, 2006. Print
[3]Norvilitis, Jill M. ADHD: New Directions in Diagnosis and Treatment. Rijeka, Croatia: Intech Open, 2015. Print
[4]Solanto, Mary V., et al. Stimulant Drugs and ADHD: Basic and Clinical Neuroscience. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press, 2001. Print
[5]Housman, Jeff and Mary Odum. Alters and Schiff Essential Concepts for Healthy Living (Eighth Edition). Burlington, Massachusetts: Jones & Bartlett Learning, 2019. Print
[6]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Amph_salts.jpg
[7]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adderall_20mg_capsules.JPG
