Difference Between Hype Cycle and Business Intelligence
Emerging technologies, as magical or powerful as they may sound, bring many questions of possibilities in the people’s minds in regards to their usability and future prospect. In today’s fast paced world, technologies are evolving at an accelerated pace and innovations are key drivers of future change. These technologies promise to take us leap years ahead, help us meet people and create stuffs – faster and easier. However, at the same time, these new technologies many times pose challenges and problems that outweigh their potential benefits.
For example, cloud computing is probably one of the biggest technological breakthroughs of this era that has made unparalleled advancements with emerging techs such as AI, IoT, VR, and AR. But at the same time, security is the biggest challenge to cloud computing. So, thousands of questions come into our minds regarding the usability of the new technology, like how useful is it? Will it replace the older tech? How will it shape the future? Such questions are answered by the Gartner’s Hype Cycle – a model that traces the evolution of new technologies as they mature over time.
What is Hype Cycle?
Hype Cycle is a branded graphical model developed and used by the global research and advisory company, Gartner Inc., to provide in-depth insights into latest emerging technologies. The Gartner Hype Cycle is a graphical illustration of the life cycle of a new technological innovation, starting from its inception to maturity and mass adoption. It represents the expectations around an innovation and its potential impact on businesses, society, and people. Gartner has a long standing reputation for researching, analyzing, and disseminating information regarding emerging techs.
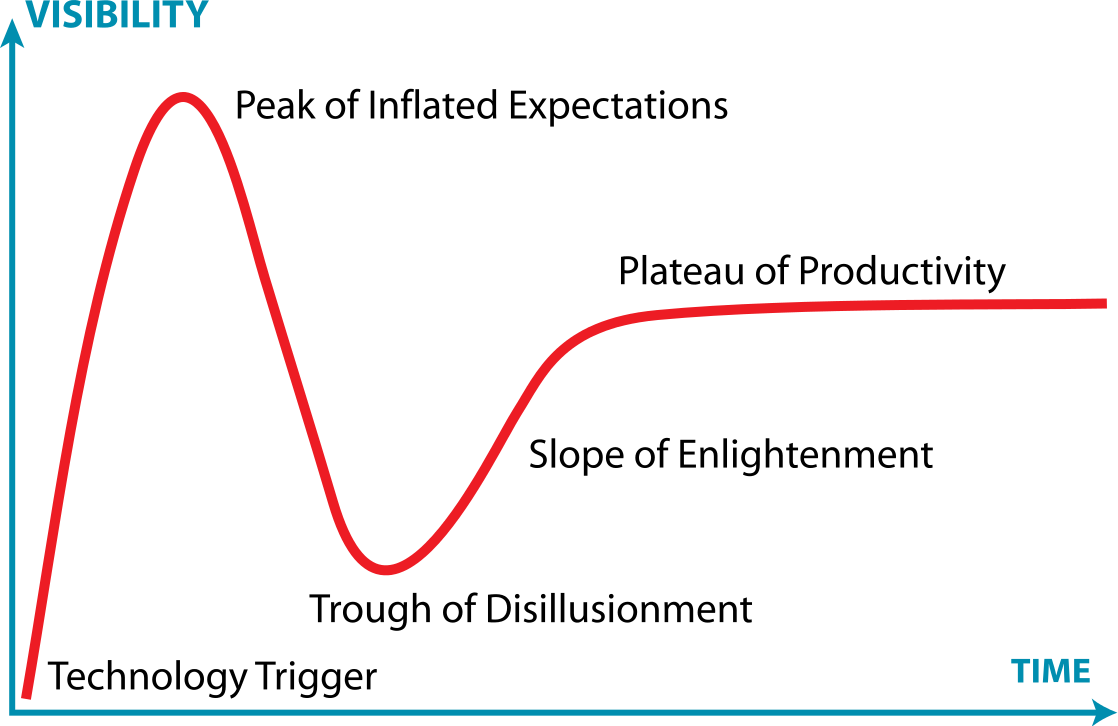
Hype Cycle represents the maturity of the new technology as it progresses through five distinct phases:
- Innovation Trigger – The life cycle begins with a breakthrough or a product launch with a lot of media attention and public interest.
- Peak of Inflated Expectations – The technology is publicized followed by the success stories that capture the excitement around the technology and the market is flooded with competing products.
- Trough of Disillusionment – Results outweigh the early expectations, followed by slow growth and adoption. Market goes into a downward frenzy as less favorable stories start to emerge.
- Slope of Enlightenment – Some early adopters pass the initial hurdles as they begin to see the benefits of the technology and take the next step.
- Plateau of Productivity – This is the stage of mainstream adoption wherein companies start to generate revenues and the underlying value of the tech translates into real-world applications.

What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence (BI) comprises a set of emerging technologies, applications and strategies used by enterprises to convert raw data into actionable information. Today, every organization, whether big or small, is driven by data, but the data require a lot of work before it’s actually being used for something useful. Raw data, in its current form, is of no use to the business person who needs it to make decisions. It needs integration, modeling, design, architecting and other work before it can be converted into actionable information. BI is to extract business value hidden within the piles of unstructured data sets. BI combines a set of practices such as data analytics, data mining, and data visualization to help enterprises make more value-driven decisions.
Difference between Hype Cycle and Business Intelligence
Tool
– Hype Cycle is a branded tool developed and used by Gartner to demonstrate the various stages of the life cycle of an emerging technology as it progresses and matures over the course of time, from its inception to widespread adoption. It represents the expectations around an innovation and its potential impact on businesses, society, and people.
Business Intelligence (BI) is a collection of tools, technologies, processes and practices designed to gather, process, analyze and visualize large volumes of unstructured data that organizations accumulate over time. BI extracts business value hidden within the piles of unstructured data sets.
Purpose
– Hype Cycle is a graphical illustration of a common pattern that arises with every new technological innovation, which helps to identify the real drivers of the technology’s commercial value from hype. Hype Cycle assesses the perceived value of a technological trend or innovation in regards to the market assessment of its future expected value.
Business Intelligence helps organizations make better, informed decisions based on present and historical data within the context of their business. It leverages software and services to convert data into actionable insights that will help businesses increase productivity, generate revenues and enhance growth.
Hype Cycle vs. Business Intelligence: Comparison Chart

Summary
Globalization changes the way enterprises use business intelligence as the demand for BI applications continue to grow at an accelerated pace. Gartner Hype Cycle on BI depicts the technology of business intelligence as a service as being on top of the Hype Cycle, which indicates the growing trend around this new technology. Well, both the tools are extremely useful when it comes to forecasting the future, at least to some extent. Hype Cycle seems to be inevitable, so you can assume it will occur with virtually every technological trend or innovation.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Jerry, Paul, et al. Riding the Hype Cycle: The Resurgence of Virtual Worlds. Oxford, United Kingdom: Inter-Disciplinary Press, 2019. Print
[1]Fenn, Jackie and Mark Raskino. Mastering the Hype Cycle: How to Choose the Right Innovation at the Right Time. Boston, Massachusetts: Harvard Business Press, 2008. Print
[2]Loshin, David. Business Intelligence: The Savvy Manager's Guide (Second Edition). Massachusetts, United States: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2012. Print
[3]Sherman, Rick. Business Intelligence Guidebook: From Data Integration to Analytics. Massachusetts, United States: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2014. Print
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4d/Business-Intelligence-Analytics-Services-1.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gartner_Hype_Cycle.svg
