Difference Between Augmented and Predictive Analytics
Artificial Intelligence is undoubtedly the major driving force behind some of the greatest technological evolutions and digital transformations we are witnessing today. AI has long surpassed our imagination about what this powerful tech can do. Although, AI has been around for decades, it has emerged as a powerful driving force due to two main factors: the unprecedented compute ability to crunch massive piles of data with machine learning algorithms, and the hottest marketing buzz around AI and ML. AI is already a major part of our lives in many types and forms. However, the most impactful in the immediate future is augmented intelligence. It is an alternate conceptualization of AI that empowers humans to leverage data to make better, informed decisions.

What are Augmented Analytics?
One of the major impacts of augmented intelligence is the need to determine the credibility of data in context. One critical issue that plagues most of the businesses today is the fact that there are too many types of data that need to be analyzed to understand the context of data. Today, data is not just limited to numbers; almost everything from photos and videos to browsing activities, social media updates, and conversations generate a massive crunch of data, most of which are unstructured, so hard to analyze. The major problem is data is useless unless we find some ways to extract actionable insights from it. This is where ‘augmented analytics’ part comes in.
Although, the term augmented analytics was first introduced in a research paper published by Gartner in 2017, it has become an indispensable part of the future for all organizations out there. Augmented analytics is the use of AI and machine learning (ML) to automate analytics processes, starting from gathering data to preparing and cleaning data, building analytics models, and generating actionable insights from the data, and finally communicating those insights to those who need them. It simplifies data analysis and makes it easily accessible for more people to get value from data.
What are Predictive Analytics?
Predictive Analytics is a branch of advanced analytics that uses a variety of statistical techniques to make predictions about possible future outcomes based on historical data. It is a sub-category of data analytics that looks into large, unmanageable datasets to discover hidden patterns in the data. Computers use predictive analytics to determine what’s most likely to happen in the future based on data from what’s happened in the past. Scientists and engineers have been using predictive models since the first moon project. Well, the predictive models are used to achieve CRM objectives such as marketing campaigns, customer services and sales.
Predictive analytics uses machine learning algorithms and statistical analysis techniques to create predictive models that can predict the outcome based on a class, category or numerical value. For instance, most banks or financial institutions that offer loans to individuals or corporate entities run risk assessment modeling to predict the chances of the loan being paid back. Financial analysts rely heavily on such predictive models before issuing loans. Predictive analytics aims to answer business questions by analyzing data and identifying a range of possible outcomes.
Difference between Augmented and Predictive Analytics
Definition
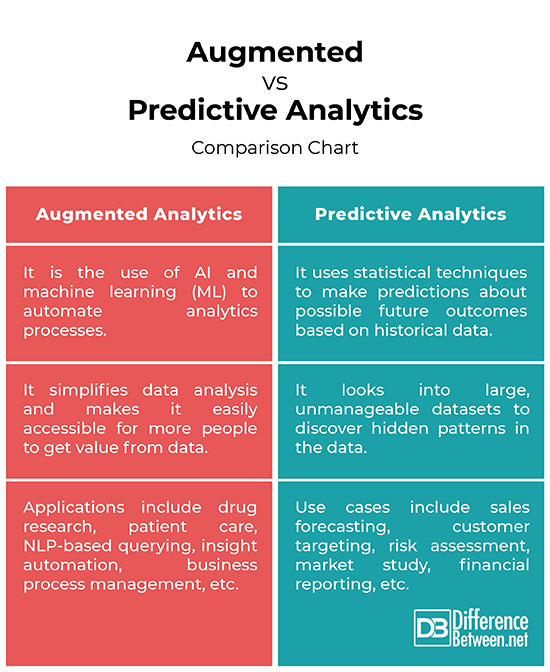
– Augmented analytics is the use of AI and machine learning (ML) to automate analytics processes makes it easily accessible for more people to get value from data in analytics and BI platforms. The term augmented analytics was first mentioned in a research paper published by the global research and advisory firm Gartner. Predictive analytics, on the other hand, is a branch of advanced analytics that leverages a variety of advanced statistical techniques to make predictions about possible future outcomes based on historical data.
Usage
– Augmented analytics simplifies data analytics for businesses to gather, identify, analyze and visualize their data in order to generate actionable insights from data. It helps businesses recognize hidden trends and patterns in data so they can make better, informed business decisions. Computers use predictive analytics to determine what’s most likely to happen in the future based on data from what’s happened in the past. It helps extract information from unmanageable data sets to identify patterns, relationships and associations.
Applications
– The idea behind augmented analytics is to support human intelligence and speed up the repetitive tasks by making smarter decisions. It helps maximize marketing efforts by closing on the field of prospects for a product or service; it can be integrated into business processes to enhance business operations. Predictive analytics can be used for fundraising, sales forecasting, customer targeting, risk assessment, market study, financial reporting, patient wellness, etc.
Augmented vs. Predictive Analytics: Comparison Chart
Summary
Augmented analytics uses machine learning and AI techniques to automate multiple aspects of data, starting from gathering data to preparing and cleaning data, building analytics models, and generating actionable insights from the data. Predictive analytics, on the other hand, uses machine learning algorithms and statistical analysis techniques to create predictive models that can predict the outcome based on a class, category or numerical value.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Agrawal, Rashmi, et al. Big Data, IoT, and Machine Learning: Tools and Applications. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2020. Print
[1]Marr, Bernard. Tech Trends in Practice: The 25 Technologies that are Driving the 4th Industrial Revolution. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2020. Print
[2]Kotu, Vijay and Bala Deshpande. Predictive Analytics and Data Mining: Concepts and Practice with RapidMiner. Burlington, Massachusetts: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2014. Print
[3]Wu, James and Stephen Coggeshall. Foundations of Predictive Analytics. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2012. Print
[4]Dr. Bari, Anasse, et al. Predictive Analytics For Dummies. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2014. Print
[5]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4903/45643400694_6af7a5ca5b_c.jpg
[6]Image credit: https://pxhere.com/en/photo/1447399
