Difference Between Psychodynamic and Cognitive Approach
Both psychodynamic and cognitive approach seek to improve the theory or approach that came before them. They aim to better understand and employ more efficient techniques concerning behavior. Specifically, psychodynamic approach agrees with the tenets of the psychoanalytic theory like the impact of childhood experiences and the unconscious while cognitive approach came later; it focuses on mental processes such as memory, thinking, attention, perception, and awareness. The following discussions further delve into their differences.
What is Psychodynamic Approach?
The psychodynamic approach refers to the theories and therapeutic techniques established by Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis and an Austrian neurologist, and further developed by the “neo-Freudians”, his initial followers. Psychodynamic theorists agree with the tenets of the psychoanalytic theory like the impact of childhood experiences and the unconscious. Nevertheless, they challenged some of Freud’s theories; largely, they softened the influence of sex and gave importance to the effect of society and culture.
The following are some of the psychodynamic theorists/psychologists:
- Carl Gustav Jung
Jung, the founder of “Analytical Psychology” as well as a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst, initially had a very close association with Freud. However, it was eventually impossible for Jung to follow Freud’s doctrine. He was a mature scholar before he met the founder of psychoanalysis; he then eventually developed an independent school of thought. One of his concepts is the presence of the “collective unconscious”, a structure of the mind that extends across persons; it can be manifested through mythology, dreams, and cross-cultural data (Engler, 2016).
- Alfred Adler
Adler’s theory is called “Individual Psychology”; he was an Austrian psychotherapist and medical doctor. His views present an optimistic perspective of behavior. His concept of “social interest” espouses a sense of connection with all humankind (Feist, 2009). He also explained that people are motivated by inferiority feelings and that each human being should be considered as an individual whole.
- Karen Horney
Horney was a German-born American psychoanalyst; she is known for her theories of neurosis and feminine psychology. She challenged the theory of “penis envy”; Freud proposed that very young girls feel envious and deprived upon the realization that they do not possess a penis. The feminine psychologist also suggested that men experience “womb envy”; that men are in fact feeling anxious that they do not have wombs which can nurture life. Moreover, Horney explained that neurosis is due to issues regarding interpersonal relationships.
Borstein (2020) identified the following basic Psychodynamic assumptions:
- Dominance of the Unconscious
Psychological processes are generally unconscious. For example, people are not usually aware of their genuine or accurate emotions, motives, past experiences, etc.
- Influence of Childhood Experiences
Childhood experiences are fundamental in shaping personality. For example, not having enough parental love in childhood can result to current and future negative behavior.
- Psychic Causality
Behavior is influenced by distinct natural and psychological processes. Each feeling, thought, or action does not just occur meaninglessly or without any reason. For example, your dreams can say something about your innermost fears, motives, and inner conflicts.
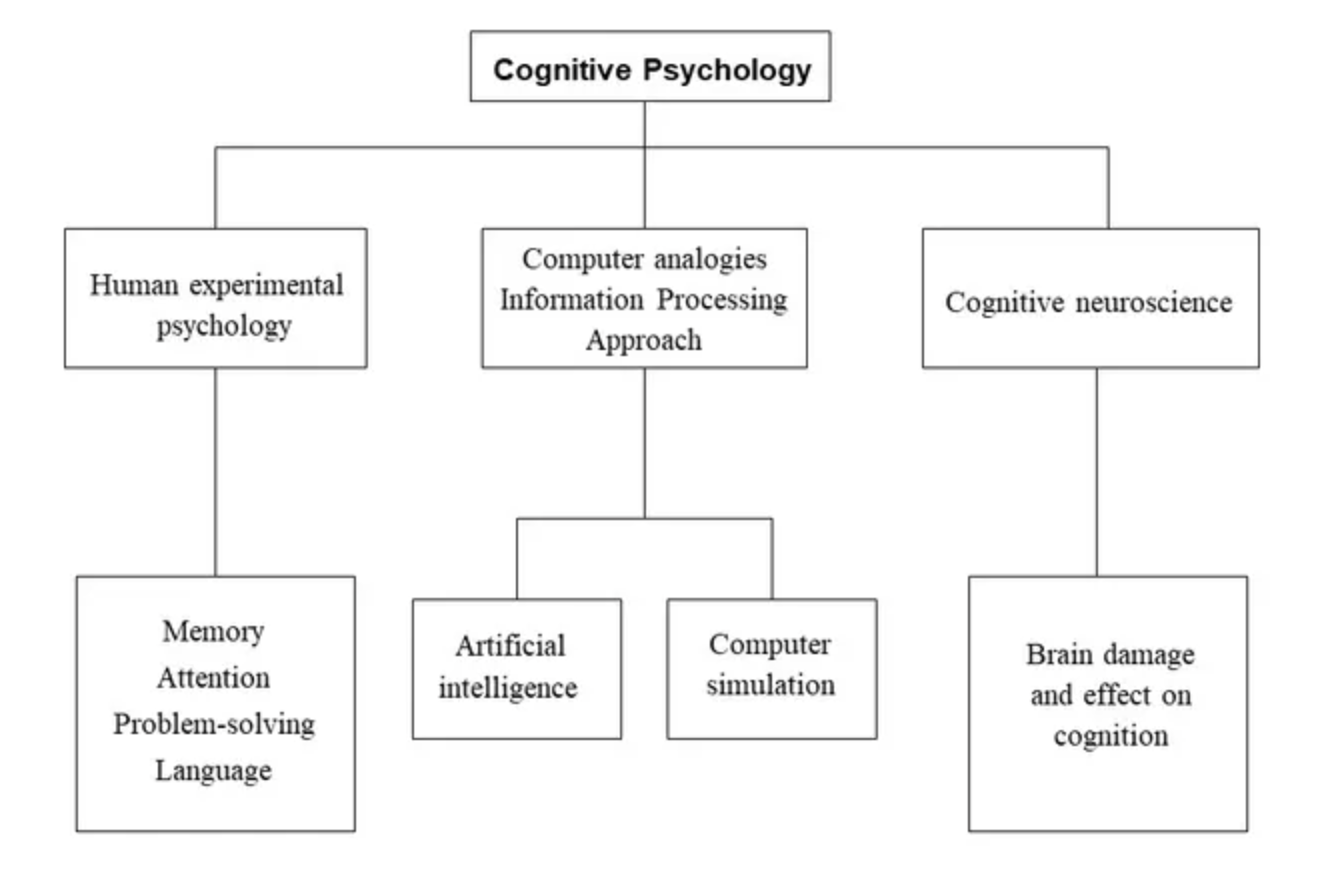
What is Cognitive Approach?
The cognitive approach focuses on mental processes such as memory, thinking, attention, perception, and awareness. Cognitive psychology arose as a response to the emphasis of the behavioral approach on external behavior, due to the development of better experimental methods, and because of the comparison between how humans and computers process information (McLeod, 2020).
Some of the notable cognitive psychologists include the following:
- Ulric (Dick) Neisser
Neisser, an American-German psychologist, was the “father of cognitive psychology” who wrote the book “Cognitive Psychology” in 1967. He expounded on research regarding attention, perception, remembering, problem solving, and pattern recognition. He also stated that various kinds of information contribute to how we understand ourselves and found out that we can learn how to simultaneously perform two difficult tasks (Hyman, 2012).
- Jerome Seymour Bruner
Bruner, an American psychologist, is one of the pioneers of cognitive approach; he worked on mental sets, perception, and children’s cognitive development. He suggested that very young learners can substantially benefit from appropriately organized instruction (McLeod, 2019).
- Jean Piaget, a Swiss Psychologist, is famous for his theory of cognitive development. He explained how children process information differently as compared to adults. Piaget also expounded on “schemas”, “assimilation”, and “accommodation” (Cherry, 2020).
Cognitive psychology’s basic assumptions include the following (McLeod, 2020):
- The mind works like a computer.
Humans are information processors. For instance, input process occurs when a stimulus is analyzed; storage process is concerned with coding and manipulation; and output process covers the pertinent response to the stimulus.
- Mediational processes occur between stimulus and response.
A mental event happens after input is received from the environment; this mediational process (i.e., perception, memory, attention, etc.) then results to a certain behavior (output).
- Psychology is a science.
Scientific methods are employed in investigating behavior; the results are then fundamental in making inferences regarding mental processes.
Difference between Psychodynamic and Cognitive
Definition
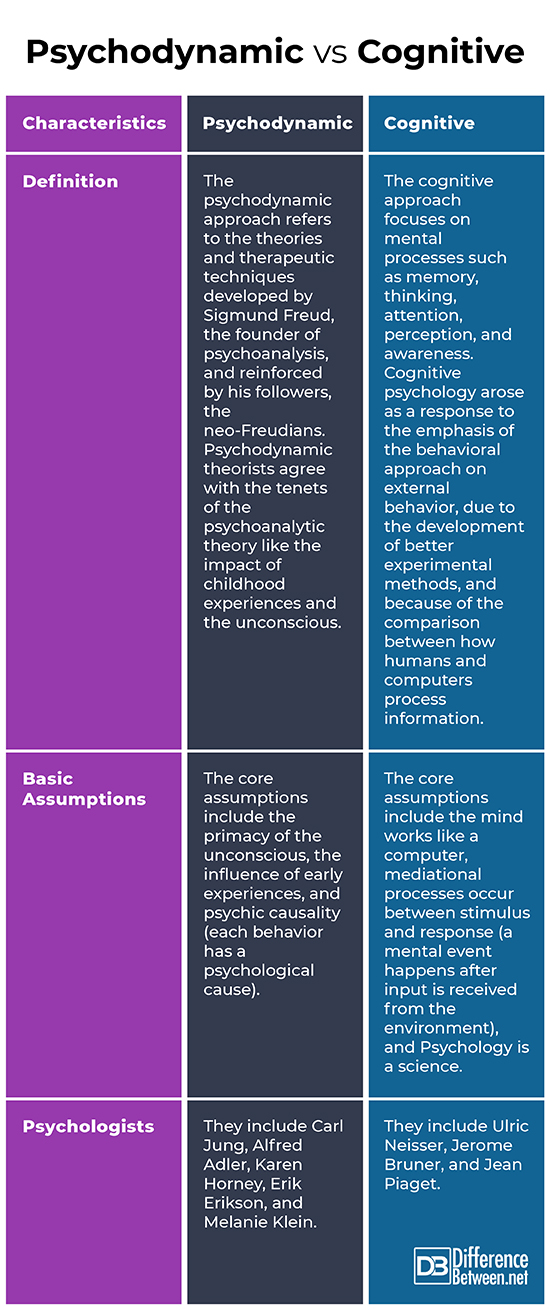
The psychodynamic approach refers to the theories and therapeutic techniques developed by Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, and reinforced by his followers, the neo-Freudians. Psychodynamic theorists agree with the tenets of the psychoanalytic theory like the impact of childhood experiences and the unconscious. In comparison, the cognitive approach focuses on mental processes such as memory, thinking, attention, perception, and awareness. Cognitive psychology arose as a response to the emphasis of the behavioral approach on external behavior, due to the development of better experimental methods, and because of the comparison between how humans and computers process information (McLeod, 2020).
Basic Assumptions
The core assumptions of the psychodynamic perspective include the primacy of the unconscious, influence of early experiences, and psychic causality. In comparison, those of cognitive approach include the mind works like a computer, mediational processes occur between stimulus and response, and Psychology is a science.
Psychologists/ Theorists
Psychodynamic psychologists include Carl Jung, Alfred Adler, Karen Horney, Erik Erikson, and Melanie Klein. On the other hand, cognitive psychologists include Ulric Neisser, Jerome Bruner, and Jean Piaget.
Psychodynamic vs Cognitive
Summary
- Psychodynamic theorists agree with the tenets of the psychoanalytic theory like the impact of childhood experiences and the unconscious.
- Cognitive approach focuses on mental processes such as memory, thinking, attention, perception, and awareness.
- The psychodynamic psychologists include Carl Jung, Alfred Adler, Karen Horney, Erik Erikson, and Melanie Klein while those of cognitive approach include Ulric Neisser, Jerome Bruner, and Jean Piaget.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Cherry, K. (2020). Jean Piaget biography. Very Well Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/jean-piaget-biography-1896-1980-2795549
[1]Hyman, I. (2012). Remembering the father of cognitive psychology. Association for Psychological Science. https://www.psychologicalscience.org/observer/remembering-the-father-of-cognitive-psychology
[2]McLeod, S. (2019). Bruner-Learning theory in education. Simply Psychology. https://www.simplypsychology.org/bruner.html
[3]McLeod, S. (2020). Cognitive psychology. Simply Psychology. https://www.simplypsychology.org/cognitive.html
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Personality_systematics.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://www.simplypsychology.org/Cog-OHP2.jpg?ezimgfmt=rs:666x442/rscb24/ng:webp/ngcb24
