Difference Between Healthy Aging and Unhealthy Aging
Both healthy and unhealthy aging are concerned with physical, mental, and social decline. Understandably, the former involves optimum functioning while the latter is concerned with detrimental or unbalanced wellbeing. The following discussions further delve into their distinctions.

What is Healthy Aging?
According to the American Geriatrics Society (AGS), healthy aging entails pivoting to age’s impact on physical, social, and mental needs and expectations, ultimately adopting a “lifespan approach” (that human development is a lifelong process of change, involving both growth and decline) to care, that helps every aging individual to live the healthiest life possible (2018). Age friendly concepts regarding engagement, activity, optimal function, and contribution are emphasized. Also, Lara and colleagues (2013) identified the following fundamental domains of healthy aging:
- Physiological and metabolic health
- Physical Capability
- Cognitive Function
- Social Wellbeing
- Psychological Wellbeing
The AGS highlights the following key areas in promoting healthy aging:
- Policy solutions for older people
It is helpful to have greater advocacies which support policies that can promote health and independence in age-friendly environments.
- Education on healthy aging
It is important to have a better public and professional education that can address discrimination against older people, inappropriate expectations on aging, and other pertinent issues.
- Commitment to geriatrics expertise
Having a deeper loyalty to needed geriatrics expertise can ensure the ability to remain active even when physical conditions change. Welcoming professional advice and intervention can optimize adults’ functional status.
- Social and scientific research
Renewed focus on healthy aging studies can help us better understand the process of how we change over time. Such evidences can improve the clinical application of healthy aging technics.
What is Unhealthy Aging?
Unhealthy aging involves going through the process of becoming older in a detrimental or unbalanced manner. Hence there are significantly harmful occurrences regarding an adult’s physiological and metabolic health, physical capability, cognitive function, social wellbeing, and/or psychological wellbeing.
The following are identified as warning signs of deteriorating health in aging adults (Exceptional Living Centers, 2020):
- Changes in personality/ Not making sound decisions
A shift in overall mood, personality, and decision making abilities may be symptoms of neurological conditions.
- Forgetfulness
Problematic forgetfulness which interrupts daily routine may be an indicator of dementia.
- Difficulty going up stairs
Mobility issues should prompt concern for possible falls.
- Loss of appetite
Bad health may be manifested as poor eating habits.
- Unexplained bruising
Unexplained cuts, bruises, or burns may indicate falls or accidents which were forgotten or kept from others.
- Inordinately disorganized house and/or bad hygiene
Those with deteriorating health may forget or lose the motivation to cleanup and or maintain good hygiene.
- More frequent illnesses
Being prone to different kinds of infections is a sign of deteriorating immune system which warrants a higher level of medical attention.
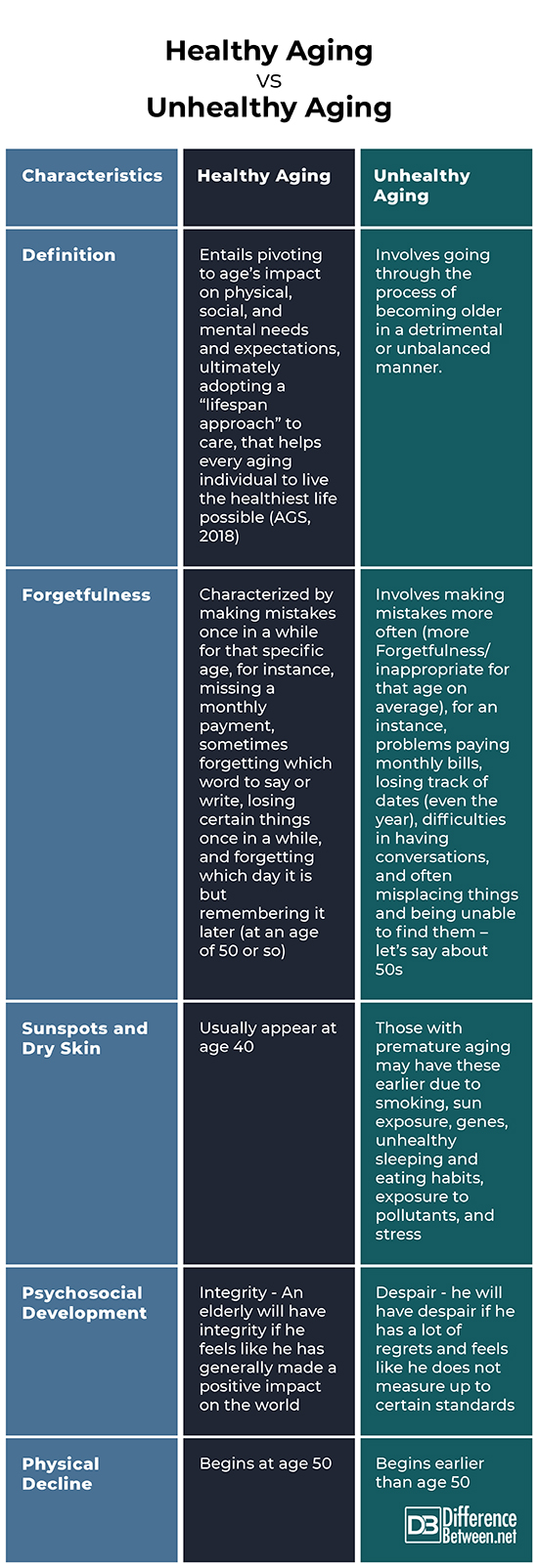
Difference between Healthy Aging and Unhealthy Aging
Definition
According to the American Geriatrics Society (AGS), healthy aging entails pivoting to age’s impact on physical, social, and mental needs and expectations, ultimately adopting a “lifespan approach” (that human development is a lifelong process of change, involving both growth and decline) to care, that helps every aging individual to live the healthiest life possible (2018). On the other hand, unhealthy aging involves going through the process of becoming older in a detrimental or unbalanced manner. Hence there are significantly harmful occurrences regarding an adult’s physiological and metabolic health, physical capability, cognitive function, social wellbeing, and/or psychological wellbeing.
Forgetfulness
According to the National Institute on Aging (NIH), normal aging is characterized by making bad decisions once in a while, missing a monthly payment, sometimes forgetting which word to say or write, losing certain things once in a while, and forgetting which day it is but remembering it later. In comparison, the forgetfulness of those with Alzheimer’s Disease involve making poor decisions most of the time, problems paying monthly bills, losing track of dates (even the year), difficulties in having conversations, and often misplacing things and being unable to find them.
Sunspots and Dry Skin
Suns spots or age spots usually appear at age 40; the skin also usually becomes drier as people near their 40s. However, those with premature aging may have these earlier due to smoking, sun exposure, genes, unhealthy sleeping and eating habits, exposure to pollutants, and stress (Watson, 2019).
Psychosocial Development
According to Erik Erikson’s psychosocial development theory, those who are in the old adult stage go through a crisis called “integrity vs. despair”. An elderly will have integrity if he feels like he has generally made a positive impact on the world while he will have despair if he has a lot of regrets and feels like he does not measure up to certain standards.
Physical Decline
It is expected to have physical decline during old age. For instance, blood vessels and arteries stiffen; bones tend to shrink and weaken; the changes in the intestines’ structures may lead to constipation; metabolism slows down; and sexual needs and performance may decrease. Research showed that physical decline usually begins at age 50 and worsens as people get older (Sagon, 2016). Hence, experiencing such decline at an earlier age warrants a higher level of medical attention.
Healthy Aging vs Unhealthy Aging
Summary
- Healthy aging entails pivoting to age’s impact on physical, social, and mental needs and expectations, ultimately adopting a “lifespan approach” to care, that helps every aging individual to live the healthiest life possible.
- Unhealthy aging involves going through the process of becoming older in a detrimental or unbalanced manner.
- Physical decline usually begins at age 50 (i.e. cardiovascular and gastrointestinal changes) though age spots and dry skin usually appear at age 40.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]American Geriatrics Society (2018). We all want healthy aging, but what is it really? EurekAlert! https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2018-11/ags-waw110118.php#:~:text=Healthy%20aging%20involves%20pivoting%20to,live%20the%20healthiest%20life%20possible.
[1]Exceptional Living Center (2020). 9 warning signs of deteriorating health in aging adults. https://exceptionallivingcenters.com/9-warning-signs-of-deteriorating-health-in-aging-adults/
[2]National Institute on Aging (2020). Memory, forgetfulness, and aging: What’s normal and what’s not. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/memory-forgetfulness-and-aging-whats-normal-and-whats-not
[3]Sagon, C. (2016). Stay active: Physical decline starts earlier than thought. Healthy Living. https://www.aarp.org/health/healthy-living/info-2016/fitness-aging-physical-decline-cs.html
[4]Watson, K. (2019). Everything you need to know about premature aging. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/beauty-skin-care/premature-aging
[5]Image credit: https://pxhere.com/en/photo/1450685
[6]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Aging_Factors.jpg
