The Difference Between Durable Power of Attorney and General Power of Attorney
Power of attorney (POA) is a legal document that allows the “principal” to give someone he trusts, the “attorney-in-fact” or the agent (i.e., a trusted relative, friend, or acquaintance), the power and right to make decisions in his behalf and to act in his place. This is often utilized when the principal (the person who authorizes the attorney-in-fact or agent) cannot be present, is ill, or is disabled. Durable power of attorney and general power of attorney allow trusted agents to perform specified tasks in their principals’ best interests. The former remains in effect until the principal’s incapacitation or death while the latter ends when the principal is incapacitated or deceased. The following discussions further delve into their distinctions.

What is Durable Power of Attorney?
As its name suggests, durable power of attorney (DPOA) allows the attorney-in-fact to act on the principal’s behalf even if he or she is already incompetent at the time the agreement expires. For instance, the agent can continue (or start) to decide or act on behalf of the principal who has been diagnosed with dementia. Unless it will be rescinded while the principal is not incapacitated, it remains in effect until the principal’s death.
Its scope can be both general or limited (e.g., for a certain period of time, only concerning retirement accounts, or filing taxes); it depends on the specified activities and decisions. This kind of document serves as a protective barrier as it guarantees that the attorney-in-fact will make the needed decisions and transactions in the best interest of the principal. It must be noted that a durable power of attorney does not cover end-of-life care decisions.
The following are recommended to use a durable power of attorney:
- Those who have high-risk occupations
- People who are living overseas (or travelling long-term)
- Senior citizens
- Patients who are about to undergo complicated surgeries

What is General Power of Attorney?
A general power of attorney gives the attorney-in-fact the powers and rights that the principal has. It has a comprehensive scope (all businesses and personal matters) and ends on the principal’s incapacitation or death unless revoked before then. With this power of attorney, the trusted agent or organization can perform various tasks for the principal’s behalf such as signing documents, employing professional help, conducting financial transactions, treatment decisions, settling claims, and paying bills. This document is advantageous for those who want to maximize their agents’ freedom in handling assets and managing care.
The following includes the transactions usually covered by a general power of attorney:
- Opening and closing bank accounts
- Accessing safe deposit boxes
- Suing
- Selling and buying stocks
- Selling and buying real estate
- Filing taxes
- In any and all matters as allowed by the state
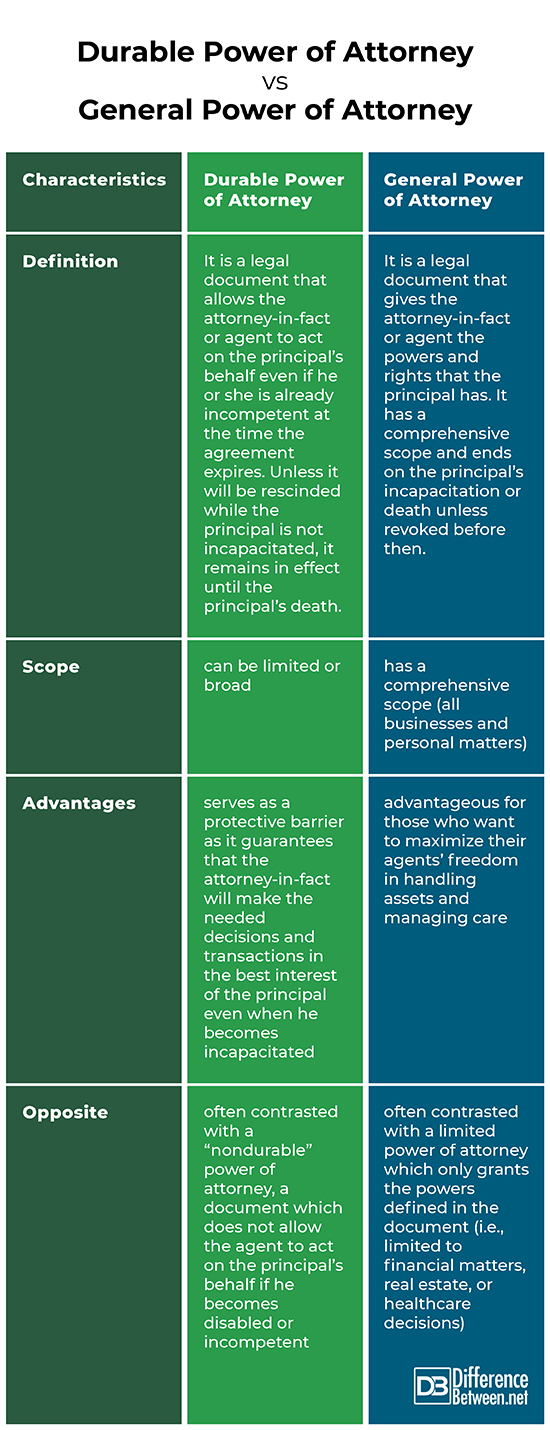
Difference between Durable Power of Attorney and General Power of Attorney
Definition
A durable power of attorney is a legal document that allows the attorney-in-fact or agent to act on the principal’s behalf even if he or she is already incompetent at the time the agreement expires. Unless it will be rescinded while the principal is not incapacitated, it remains in effect until the principal’s death. In comparison, a general power of attorney is a legal document that gives the attorney-in-fact or agent the powers and rights that the principal has. It has a comprehensive scope and ends on the principal’s incapacitation or death unless revoked before then.
Scope
A durable power of attorney can be limited or broad in scope. For instance, to restrict powers, most states show a list of powers for the principal to choose from. On the other hand, a general durable power of attorney may authorize the agent to make decisions and perform transactions in a wide range of matters even if the principal is incapacitated or deceased. As for a general power of attorney, it has a comprehensive scope (all businesses and personal matters) and ends on the principal’s incapacitation or death unless revoked before then.
Advantages
A durable power of attorney serves as a protective barrier as it guarantees that the attorney-in-fact will make the needed decisions and transactions in the best interest of the principal even when he becomes incapacitated. As for a general power of attorney, this document is advantageous for those who want to maximize their agents’ freedom in handling assets and managing care.
Opposite
A durable power of attorney is often contrasted with a “nondurable” power of attorney, a document which does not allow the agent to act on the principal’s behalf if he becomes disabled or incompetent. In comparison, a general power of attorney is often contrasted with a limited power of attorney which only grants the powers defined in the document (i.e., limited to financial matters, real estate, or healthcare decisions).
Durable Power of Attorney vs General Power of Attorney
Summary
- A durable power of attorney is a legal document that allows the attorney-in-fact or agent to act on the principal’s behalf even if he or she is already incompetent at the time the agreement expires.
- A general power of attorney is a legal document that gives the attorney-in-fact or agent the powers and rights that the principal has. It has a comprehensive scope and ends on the principal’s incapacitation or death unless revoked before then.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Legal Templates (2020). Durable power of attorney. https://legaltemplates.net/form/power-of-attorney/durable/#:~:text=A%20durable%20power%20of%20attorney%20allows%20your%20agent%20to%20make,you're%20diagnosed%20with%20dementia.&text=For%20instance%2C%20if%20you%20have,lose%20their%20decision%20making%20power.
[1]Shelton, D. (2015). The Oxford handbook of international human rights law. Oxford University Press.
[2]Schleiffarth, J. (2017). What is a general durable power of attorney? Avvo. https://www.avvo.com/legal-guides/ugc/what-is-a-general-durable-power-of-attorney-
[3]Image credit: https://www.thebluediamondgallery.com/handwriting/images/power-of-attorney.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://www.thebluediamondgallery.com/legal/images/power-of-attorney.jpg
