Difference Between Antibody Test IgG and IgM
When an individual is infected with a virus, like the SARS-Cov-2 which causes COVID-19, the person’s body starts to develop an immune response naturally by building antibodies to the virus. The antibodies attack the virus and eliminate the virus from the system. That is the basics of immunology. So, antibodies are nothing but large protein molecules that fight off against foreign objects that try to enter our body. Also known as immunoglobulins, antibodies are produced by our immune system as part of an immune response. They protect our body against antigens such as viruses, toxins or bacteria.
A serology test can be used to detect the antibodies in our system because our body builds different antibodies to fight off different antigens. For example, the antibody for SARS-CoV-2 is not the same as the antibody for any other virus, such as the chickenpox or HIV. An antibody test (serology test) is therefore very useful in diagnosing an acute infection. A serology test, however, does not detect the presence of the virus, but rather detect the antibodies that are produced by our body is fighting the virus. So, IgG and IgM represent different stages of an immune response. They are two common types of antibodies found in the blood.
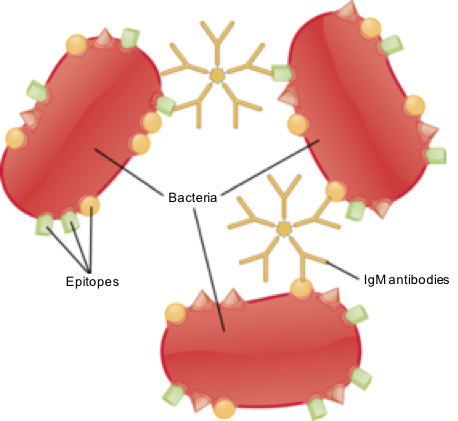
What is IgM Test?
An IgM antibody test looks for immunoglobulin M (IgM) in the blood. The IgM antibody is the largest antibody and the first to appear to fight off a new infection. The IgM is basically the first line of immune defense against fighting pathogens. In inflammatory diseases, the IgM can have both pathogenic and protective roles depending on the type of infection and tissue affected. IgM is present in jawed vertebrates (gnathostomes) that existed already during the Devon period over 400 million years ago. An IgM antibody test is very important because it generally comes up earlier on an infection, and it is detectable 4 to 7 days after an infection starts. The IgM antibodies are short-lived and their existence in the blood confirms that a new infection is present. So, an IgM test determines if someone has been recently infected or sometimes, it determines if someone is still infected.
What is IgG Test?
The immunoglobulin G (IgG) is the most common antibody found in the blood and a major effector molecule of the humoral response. The IgG accounts for about 75 percent of serum antibodies in humans. The IgG antibodies express their predominant activity during a secondary antibody response. In comparison to IgM antibodies, IgG antibodies have a relatively high affinity and persist in the circulation for a really long time. These antibodies are produced 7 to 14 days after infection and they are detectable for weeks, months and even years. And the antibodies remain in the blood even after an infection has passed. IgG antibodies are formed later than IgM antibodies and the test for IgG antibodies help determine the immunity status following a virus infection or active immunization. It can also help to diagnose persistent infection. So, IgG starts spiking as IgM starts coming down.
Difference between IgG Test and IgM Test
Antibodies
– IgG and IgM are two common types of antibodies found in the blood and they represent different stages of an immune response. The IgM antibody is the largest antibody found in the blood and lymph fluid, and the first to appear to fight off a new infection. IgM antibodies are the first line of immune defense against fighting pathogens. The immunoglobulin G (IgG), on the other hand, is the most common antibody found in the blood and a major effector molecule of the humoral response that accounts for about 75 percent of serum antibodies in humans.
Testing
– Compared to antibodies of the IgM class, IgG antibodies have a relatively high affinity and persist in the circulation for a long time. The IgM antibodies are short-lived and their existence in the blood confirms that a new infection is present. An IgM test determines if someone has been recently infected or sometimes, it determines if someone is still infected. An IgG test, on the other hand, helps determine the immunity status following a virus infection or active immunization, or sometimes, it helps diagnose a persistent infection. IgG starts spiking as IgM starts coming down.
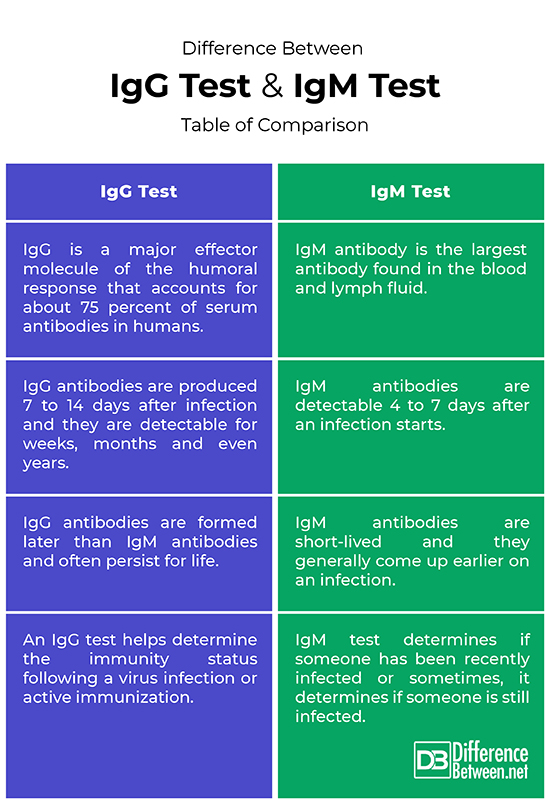
Difference between IgG Test and IgM Test: Table of comparison
Summary
So in a nutshell, IgM is the first type of antibody produced in the system in response to an infection. IgM antibodies are the largest subclass of antibody found in the blood and lymph fluid. They are the first line of immune defense against fighting pathogens. The IgM antibodies are short-lived and their existence in the blood confirms that a new infection is present. On the contrary, IgG antibodies are formed later than IgM antibodies and they persist in the circulation for a long time. IgG antibodies express their predominant activity during a secondary antibody response. Because IgG antibodies are usually sustained for a longer time, they play a fundamental role in lasting immunity.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Winn, Hung N. and John C. Hobbins. Clinical Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2000. Print
[1]Korsman, Stephen N. J. et al. Virology E-Book: An Illustrated Colour Text. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2012. Print
[2]Fischbach, Frances T. and Marshall B. Dunning. A Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests. Pennsylvania, United States: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009. Print
[3]Nimmerjahn, Falk. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Antibody Activity. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2013. Print
[4]Shakib, Farouk. The Human IgG Subclasses: Molecular Analysis of Structure, Function and Regulation. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2016. Print
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Immunoglobulin_(IgM)_antibodies_binding_to_adjacent_antigen_epitopes_on_the_surface_of_bacterial_cells..png
[6]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hepatitis_B_virus_phases_of_chronic_infection.png
