Difference Between Parallel Port and Serial Port
In the computer world, a port is a means to connect the external devices to the central processing unit (CPU). Effectively they are the sockets found on the back of the PCs and are used to communicate with printers, keyboards, modems, and monitors, or just about any peripheral or component. The ports either connect directly onto the motherboard or onto an expansion card. We are here to talk about two of the commonly used ports – serial ports and parallel ports.
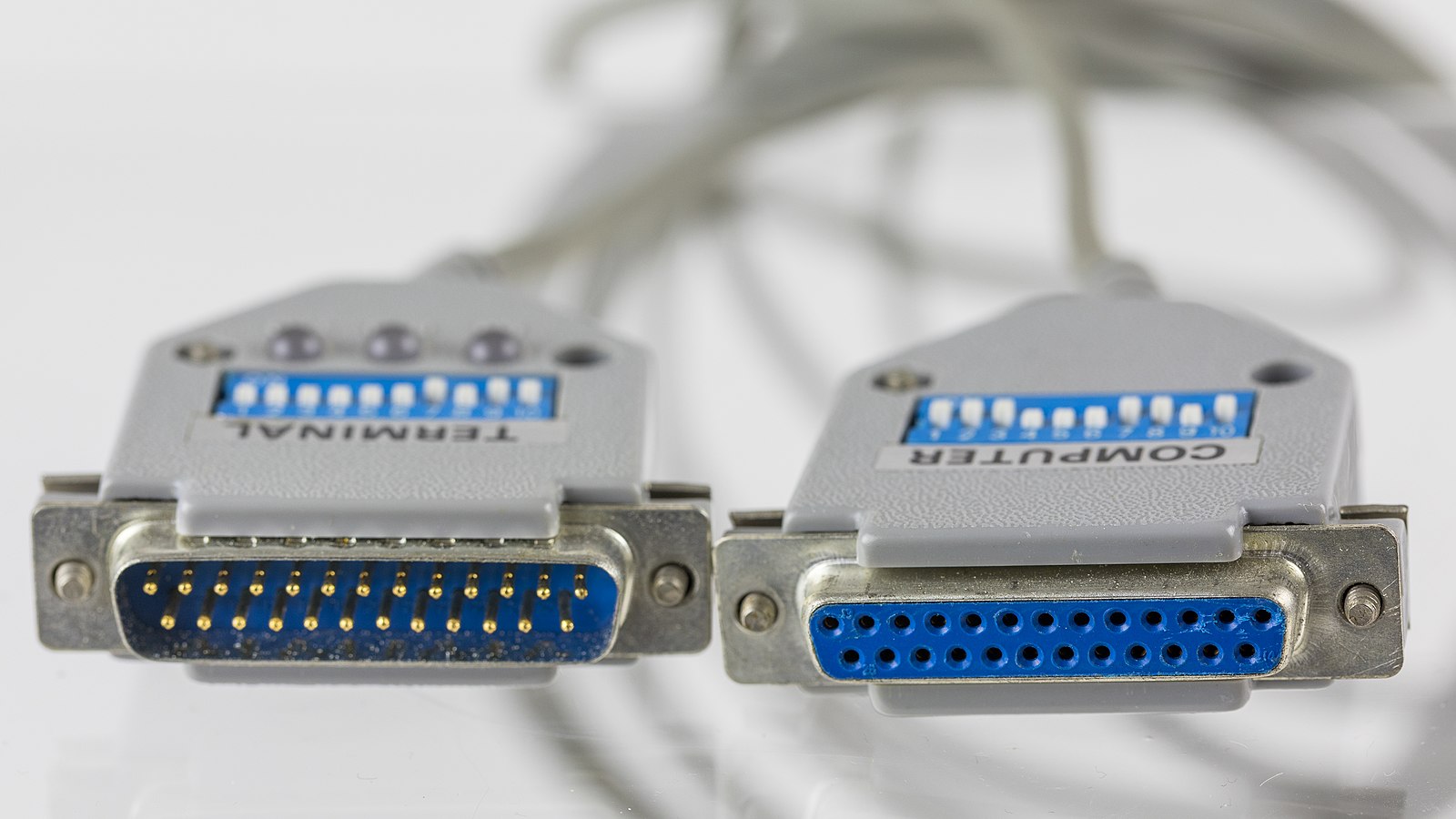

What is a Parallel Port?
A parallel port is an external interface found on the back of the personal computers and is used to connect to just about anything you’d want to hook to a computer. It acts as an interface for connecting computer peripherals such as printers, or any other device that requires relatively high bandwidth. The parallel port is one of the most versatile I/O ports in the system because it can be used for a variety of devices, including optical drives, scanners, external CD-ROM, and so on. The name parallel describes the way how the data is sent; it implies parallel communication meaning multiple bits of data is sent all together at the same time without any hold-up. The parallel port uses DB25 female pin connector and the end of the cable that connects to devices uses a centronics connector – after the name of the company that designed the standard interface for connecting a printer to a computer.
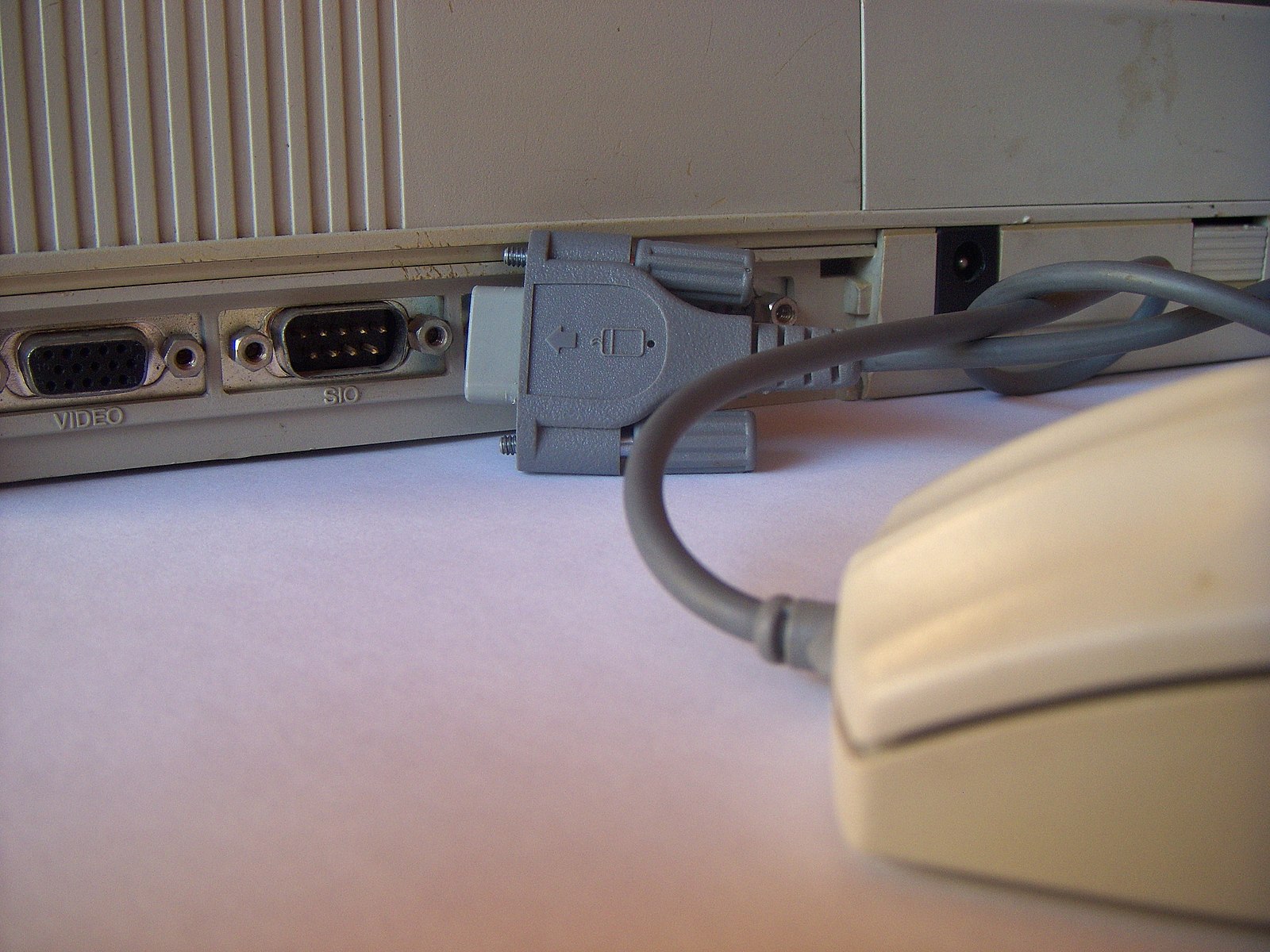

What is a Serial Port?
A serial port is yet another type of port and a great alternative to the parallel ports where the bits of data is sent one at a time in a single stream of 1s and 0s. Unlike the parallel port, it is a serial communication interface through which data is transferred on a single wire or a pair of wires, or in case of wireless communication, a single transmission path. Also known as COM (communication) ports, there are many different types of serial interfaces available for computers, such as the ubiquitous RS-232 port, the RS-485 port, IEEE-394, and the USB. The serial port uses a standard 9-pin D-shaped connector and is used to connect devices such as mouse, modems, gaming controllers, older printers, etc. It is one of the oldest interfaces used to connect mainly modem and printers to the computer. But the modern serial ports are used for specialist devices such as security cameras, flat-screen monitors, GPS receivers, and so on.
Difference between Parallel Port and Serial Port
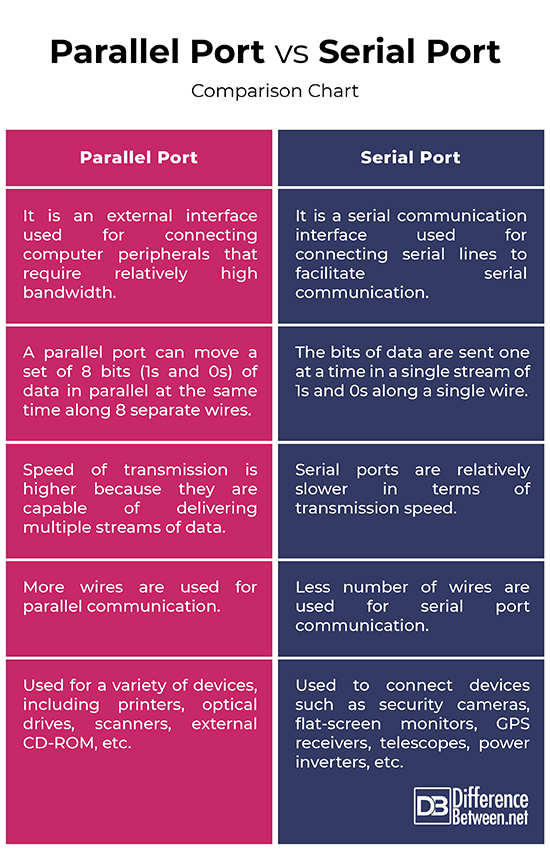
Basics
– A parallel port is an external interface used for connecting computer peripherals such as printers, or any other device that requires relatively high bandwidth, to your personal computers. The parallel port uses DB25 female pin connector and the end of the cable that connects to devices uses a centronics connector. A serial port on the other hand, is a serial communication interface used for connecting serial lines to facilitate serial communication. The serial port uses a standard 9-pin D-shaped connector previously used to connect modems and printers to the computer.
Transmission
– A parallel port can move a set of 8 bits (1s and 0s) of data in parallel at the same time along 8 separate wires meaning multiple bits of data is sent simultaneously. The parallel port uses a 25-pin D-shaped connector, or commonly referred to as DB25 connector. A serial port is a great alternative to the parallel port where the bits of data is sent one at a time in a single stream of 1s and 0s along a single wire. The serial port uses a standard 9-pin D-shaped connector and is used to connect devices such as mouse, modems, gaming controllers, older printers, etc.
Performance
– Parallel transmission is relatively much faster than serial transmission even with the same signal frequency. So, speed of transmission is higher in parallel ports because they are capable of delivering multiple streams of data all at once, thereby eliminating crosstalk and errors. So, relatively more wires are used in parallel port communication. Serial ports are relatively slower in terms of transmission speed because they are able to transmit only a single stream of data at a time over a single wire. Unlike parallel communication, you can increase the length of the wire as needed in serial communication.
Devices
– The parallel port is one of the most versatile I/O ports in the system because it can be used for a variety of devices, including printers, optical drives, scanners, external CD-ROM, hard drives, and so on. The serial port is used to connect devices such as mouse, modems, gaming controllers, older printers, etc. However, the modern serial ports are used to connect devices such as security cameras, flat-screen monitors, GPS receivers, telescopes, power inverters, etc.
Parallel Port vs. Serial Port: Comparison Chart
Summary of Parallel Port vs. Serial Port
In a nutshell, a parallel port is a parallel interface for connecting computer peripherals that require relatively high bandwidth. It is a connection of eight or more wires through which bits of data can be transmitted simultaneously. With a serial interface, bits of data are transmitted one at a time over a single wire, or in case of wireless communication, a single transmission path. Serial ports are relatively slower than parallel ports in terms of transmission speed. And a parallel interface accommodates a higher volume of data than a serial interface because multiple bits of data are transmitted all at once through a parallel interface.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Soper, Mark Edward. Absolute Beginner's Guide to A+ Certification. Indiana, United States: Que Publishing, 2004. Print
[1]Axelson, Jan. Parallel Port Complete: Programming, Interfacing & Using the PC's Parallel Printer Port. Wisconsin, United States: Lakeview Research, LLC, 1996. Print
[2]Banks, Maggie. OCR AS GCE Applied ICT Double Award. New Hampshire, United States: Heinemann, 2005. Print
[3]Norton, Peter. Introduction to Computers: Special Indian Edition. New Delhi, India: Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2006. Print
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Serial_port_mouse.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Parallel_port_cable,_D-sub_25_male_and_female_connectors_with_DIP_switches_integrated-0366.jpg
