Difference Between AI and Data Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has captured the attention of almost everyone from the top executives of an organization to an average person walking down the street. It’s hard to believe how just an idea became a game changer for individuals and businesses alike. What was once considered hype has become a worldwide sensation in a very short span of time. Today, we are in the middle of the evolution of digital age, where there’s an enormous amount of computing power and data in the hands of almost everyone. Data is the most important asset these days. And now, we have the ability to consume and process volumes of data which weren’t possible before. Organizations are embracing data-driven decision making and companies are turning towards AI for their products boasting. Unfortunately, analytics and AI communities are not doing anything to collaborate and communicate with each other, which in turn, bridge the gap between the two fields.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
According to Schalkoff, Artificial Intelligence (or simply called AI) is a field of study that seeks to explain and emulate intelligent behavior in terms of computational processes. In a more general sense, AI is a technology that helps facilitate various processes in a more autonomous and automatic fashion, with little or no intervention from a human user. AI is creation of intelligent machines that work, think, and respond like humans. It is a remarkably successful technology that aims to implement human-like intelligence in machines and to create systems that gather data, process it, predict outcomes and ultimately improve human life. AI comprises of a set of algorithms that use information in form of data to make decisions and carry out tasks just like humans would. Almost all AI programs are developed for some sort of problem-solving whether it’s interpreting a visual scene, parsing a sentence or planning a sequence of robot actions.

What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics is the science of analyzing raw data with the goal of making conclusions and supporting decision-making out of that information in order to enhance productivity and business gain. It’s all about data; more data has been created in the last couple of years than in the entire history of the human race. Previously, most electronic datasets were structured and fit into databases. But today our digital lives are making big data even bigger, thanks to the connected world and most of the data generated is not in structured format, for example, images, videos, and voice data files. This is where data analytics come to the picture. These huge volumes of data need to be analyzed in order to generate actionable insight out of it. Data analytics refers to the analysis of large datasets for the support of decision-making. Typically data analysis can be divided into several phases. Data are assessed, cleaned and filtered, visualized and analyzed, and the results are finally interpreted and evaluated.
Difference between AI and Data Analytics
Definition
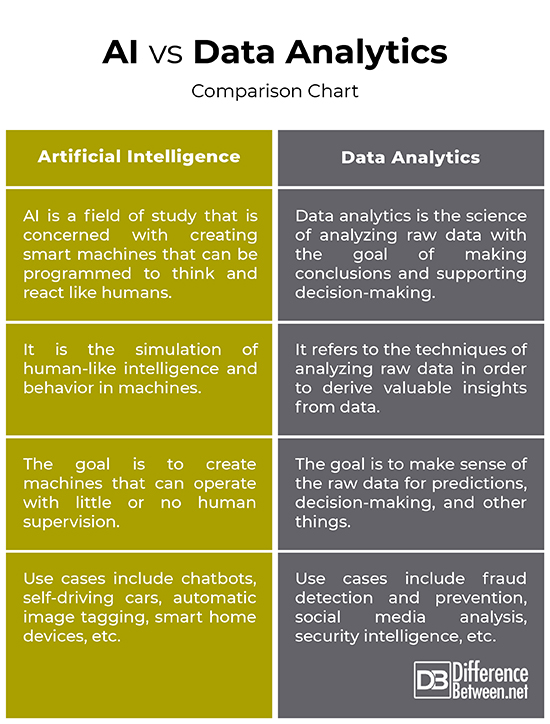
– AI is the simulation of human-like intelligence and behavior in machines, especially computer systems. AI is a branch of computer science that is concerned with creating smart machines that can be programmed to think and react like humans and mimic their actions. Data analytics, on the other hand, refers to the techniques of analyzing raw data in order to derive valuable insights from data. It refers to the analysis of large datasets, using specialized computer systems, to draw conclusions out of the information they contain for the support of decision-making.
Goal
– The goal of AI is to create expert systems which exhibit intelligent behavior – systems that understand, think, learn, respond, react and behave like the way humans do. The idea is to create machines that can operate with little or no human supervision so that they can find solutions to complex problems in a more human-like fashion. The goal of data analytics is to make sense of the raw data for predictions, decision-making, and a lot of other things. The raw data is arranged and organized, interpreted and evaluated so that relevant or useful information can be extracted from it.
Applications
– Data analytics applications can be broadly classified as descriptive, predictive and prescriptive. Descriptive analytics mines massive data repositories to extract potential patterns in the data; predictive analytics combine massive data from different sources to predict future trends or events; and prescriptive analytics help assess the impact of different possible decisions. Oil and gas exploration industries use prescriptive analytics to optimize the exploration process. Industries use predictive analytics to predict machine failures.
AIs are designed to be used in robots, such as those designed for industrial applications while some are used for rescue missions, able to navigate various terrains. Other AIs are good for data crunching and facilitating various data analytics tasks. AI is a crucial part of daily human lives and it’s almost everywhere – from automated customer support and digital voice-based assistant to healthcare industry and finance sectors, to self-driving cars and smart home devices, everywhere.
AI vs. Data Analytics: Comparison Chart
Summary of AI vs. Data Analytics
In a nutshell, AI is a collection of technologies that aim at extracting insights and patterns from large datasets, and making informed decisions based on the information. For this AI require quality data and without quality data analytics tools, AI cannot assess data and make predictions, thereby cannot provide valuable insights. So, both data analytics and AI are closely related to each other and understanding the difference between the two is all about choosing the right tools for the right job.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/804/27774351928_986b1688fe_b.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/1942/30188200627_c5ea2a3779_b.jpg
[2]Voulgaris, Zacharias and Yunus Emrah Bulut. AI for Data Science. New Jersey, USA: Technics Publications, 2018. Print
[3]Whitby, Blay. Artificial Intelligence: A Beginner's Guide. Oxford, England: Oneworld Publications, 2012. Print
[4]Deshpande, Anand and Manish Kumar. Artificial Intelligence for Big Data. Birmingham, United Kingdom: Packt Publishing, 2018. Print
[5]Runkler, Thomas A. Data Analytics: Models and Algorithms for Intelligent Data Analysis. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2016. Print
[6]Pyne, Saumyadpta, et al. Big Data Analytics: Methods and Applications. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2016. Print
