Difference Between Quantum Board and COB
Chip-on-Board (COB) vs Quantum Board
The technology of LED (light emitting diodes) lighting, especially with modern high power LEDs on the horizon, has developed very rapidly over the past few years. LEDs have acquired substantial economical relevance worldwide, thanks to their superior lighting capacity and high level of user acceptance. The market share of LED light sources and LED luminaries is increasingly rapidly at an unprecedented rate. Moreover, LEDs for lighting application are becoming widely adopted due to economic, energy and environmental reasons. With the increasing demand of LED applications, the need for high-power high-brightness LED lights grows gradually.
To design a single higher power LED chip, a large sized LED chip is proposed but there are applications where thousands of lumens are required from a single source. A common solution here is to use a chip-on-board (COB)-style LED. In order to increase the output optical power, a high power COB LED array packaging is universally preferred. In this configuration, an array of small-size high-power LED chips is mounted on a metal-based or ceramic-based board. In the last decade, a ceramic-based platform for high power LEDs swept the industry while replacing the previous lead-frame approach. However, there’s a new tech that’s creating quite a buzz across the growing LED community which is dubbed as “Quantum Boards”. Let’s take a look how the two technologies stack up against each other.
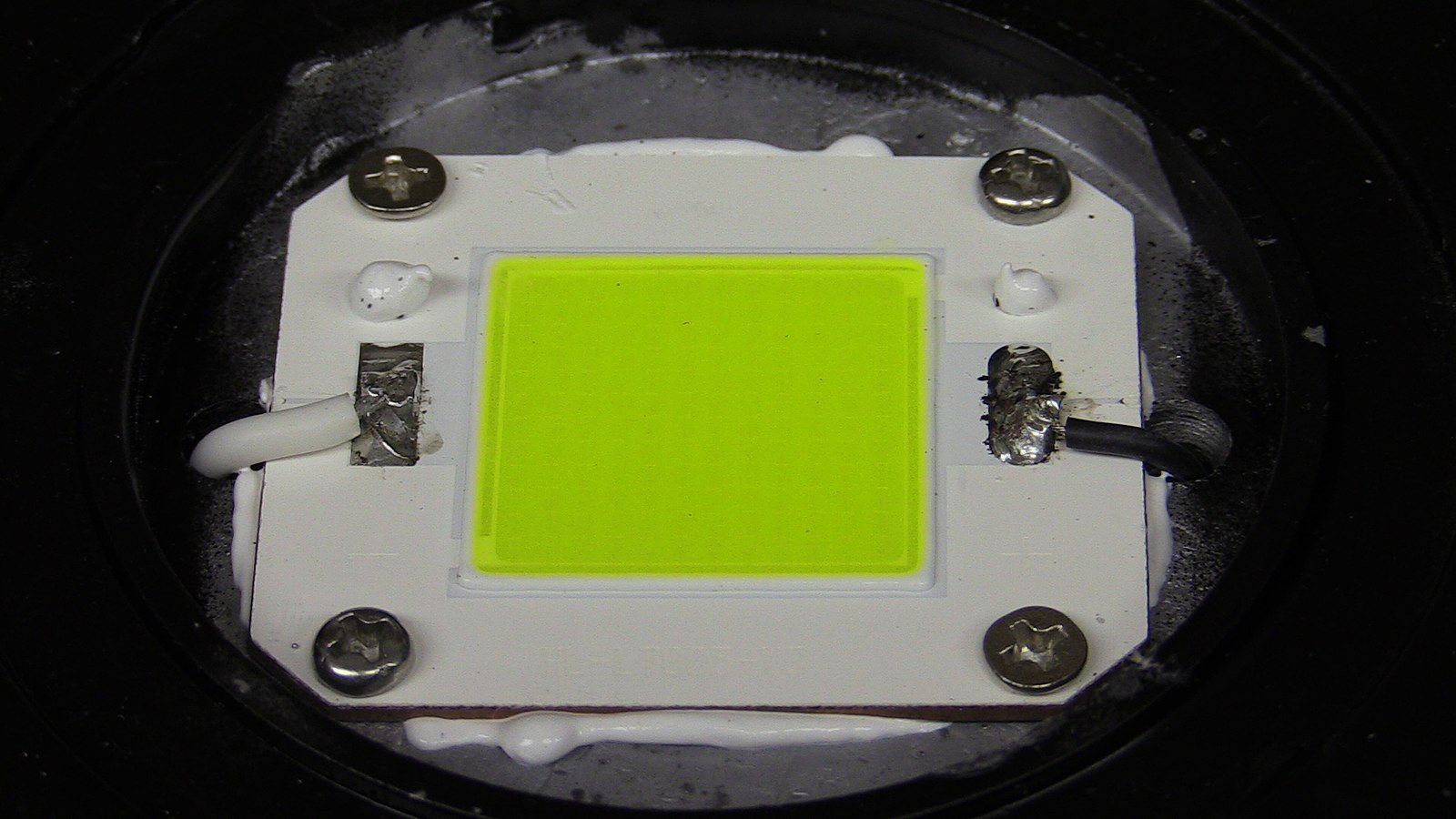
What is Chip-on-Board (COB)?
While the high-power LED packages can handle a few watts of power and thus hundreds of lumens of light output, there are applications which would require thousands of lumens from a single source. This is where a chip-on-board (COB)-style LED comes to the picture. In a multiple chip configuration, several chips are mounted in a housing, while in the COB LED technology, an array of chips is mounted on a common board or substrate. It usually consists of multiple smaller size high-power LED chips encapsulated on the metal-based or ceramic-based board. In modern COB LED configuration, the phosphor-silicone encapsulate mixture is molded on the chip array surface. With COB, the number of LED chips within a package can be up to several thousand pieces with much higher packaging densities that with single chip LED configuration.

What is Quantum Board?
Quantum boards by Horticulture Lighting Group (HLG) are the highest efficiency, high intensity horticulture light engines. HLG quantum board is a large circuit board with hundreds of mid-power LEDs mounted on it. The large circuit board makes for a more even light distribution. It consists of a number of micro-LEDs which are connected in series to form strings to achieve high voltage operation. Quantum boards are essentially the same as COBs except they span a much larger area to cover a larger heat sink. It has low power consumption, which can reduce the cost of additional heat sinks. The term quantum board was first coined by HLG for an LED grow light with the diodes evenly spread out on a board.
Difference between Quantum Board and COB
Technology used in terms of Quantum Board vs. COB
– There are applications which would require thousands of lumens from a single source. A common solution here is to use a chip-on-board (COB)-style LED. COB is an LED packaging technology that describes mounting several high-power LED chips onto a common board or substrate. HLG’s quantum board is a relatively new technology that’s creating quite a buzz across the growing LED community for their higher thermal efficiency and low power consumption. Quantum boards are a great alternative to their COB counterparts and are essentially the same as COBs except they span a much larger area for even light distribution.
Configuration in of Quantum Board and COB
– In chip-on-board LED configuration, an array of small-size high-power LED chips is mounted on a metal-based or ceramic-based board. A high power COB LED array packaging technology is universally preferred in order to increase the output optical power. In modern COB LED configuration, the phosphor-silicone encapsulate mixture is molded on the chip array surface. HLG quantum board, on the other hand, is a large circuit board with hundreds of mid-power LEDs mounted on it which are connected in series to form strings to achieve high voltage operation.
Advantages of of Quantum Board vs. COB
– Quantum boards are the highest efficiency, high intensity horticulture light engines with the diodes evenly spread out on a larger board, which in turn makes for a more even light distribution. They are great lights with much simpler thermal management and greater efficiency. Plus it has low power consumption which can reduce the cost of additional heat sinks. COBs, on the other hand, are good for DIY projects and they have great thermal resistance, larger cooling area and better lighting effects. Quantum boards are quite difficult to DIY than COB LEDs.
Quantum Board vs. COB: Comparison Chart

Summary
In a Chip-on-board LED configuration, an array of chips is mounted on a common board or substrate. It usually consists of multiple smaller size high-power LED chips encapsulated on the metal-based or ceramic-based board. It has great thermal resistance, larger cooling area and better lighting effects, plus it’s great for DIY projects. Quantum boards are a relatively new technology designed by the folks at the Horticulture Lighting Group and they are essentially the same as COBs except they span a much larger area which makes for a more even light distribution.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chip-On-Board_COB_LED_Module.JPG
[1]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4758/26551577968_b700867141_b.jpg
[2]Khan, T.Q. et al. LED Lighting: Technology and Perception. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2014. Print
[3]Jiang, Zheng Yi, et al. Advances in Manufacturing Technology. Zurich, Switzerland: Trans Tech Publications Ltd., 2012. Print
[4]Kitai, Adrian. Materials for Solid State Lighting and Displays. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2017. Print
