Difference Between Waymo and Tesla
Google Self-Driving Car (Waymo) vs. Tesla
The idea of a self-driving car is not new; in fact, the driverless car era began in the early 1920s, when cars began to becoming a mass technology. In 1925, an electrical engineer in the U.S. Army named Francis P. Houdina developed the means to control a car using radio signals. He attached an antenna to a 1926 Chandler to control its steering wheel, accelerator and brakes. The Houdina Radio Radio Control Co. held a demonstration on the streets of New York City the same year on July 27. Although, his demonstration was a failure because the vehicle crashed, it was a magical achievement in many ways. Self-driving technology remained elusive in the following decades, but the idea continued to intrigue people.
Today, many companies are trying hard to turn that dream of self-driving cars into reality. In fact, vehicles of today are already semiautonomous systems, so we are probably not very far away from the driverless cars era. There’s a big race happening right now and it’s tough to say who would be able to make a fully-autonomous car that behaves better than a human driver. Fortunately, Google Self-Driving Car and Tesla lead the race, while other companies are still trying to do it. With so many levels of autonomous driving, there’s easy to see the contrast between the two.

What is Google Self-Driving Car (Waymo)?
Google began working on the autonomous cars in 2009, at the company’s secretive X lab run by co-founder Sergey Brin. In October 2010, Google disclosed its Autonomous Car program. It’s been a slow and steady roll since then. In 2016, Alphabet announced that Google’s self-driving car project would be spun off into a new standalone self-driving company. The Google’s driverless car project graduated from X and became its own company, Waymo. Only eight years after Google’s X lab took on the self-driving initiative, Waymo’s self-driving car logged two hundred million miles. Waymo also started “Drive Me” trials using Chrysler Pacifica minivans in Phoenix, Arizona. In 2018, Waymo announced it would start its driverless taxi service in Phoenix.

What is Tesla?
Tesla, the global leader in electric cars, is yet another technology challenger in the automatic vehicles (AV) commercialization race. However, the idea of autonomous cars started way before Elon Musk and his Tesla cars. The experiments on driverless cars have been conducted since the 1920s, the only real advancements in the technology accelerated in the 2000s with the US government-sponsored DARPA Grand Challenge in 2004 and Urban Challenge in 2007. The company was founded in 2003 by a group of engineers who believed that people didn’t need to compromise to drive electric cars and that electric cars can be better. Tesla plans to bring Level 5 autonomy in its vehicles by 2020, but whether these are just speculations is still to be proved.
Difference between Google Car and Tesla
Expertise
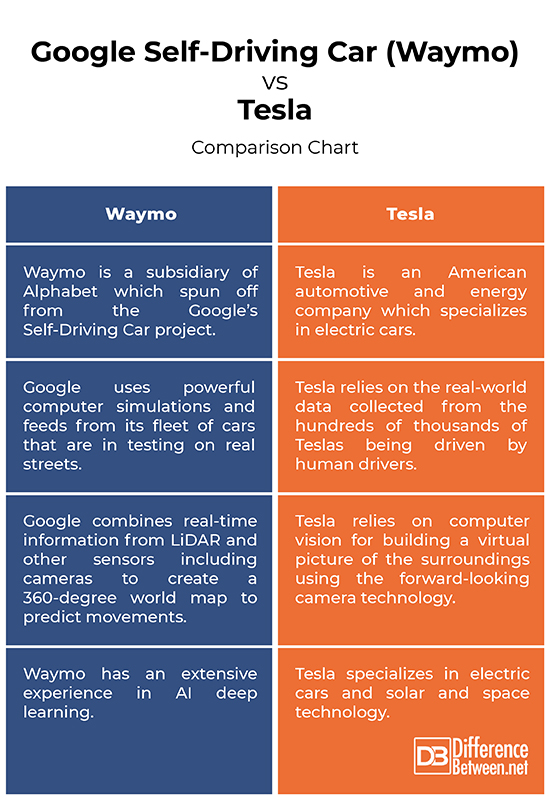
– Google is a search engine giant and a technology company specializes in all facets of IT. The Google’s self-driving project, which is now Waymo (a subsidiary of Alphabet), formally started in 2009. In 2016, Alphabet announced that Google’s self-driving car project would be spun off into a new standalone self-driving company. Tesla is an American automotive and energy company which specializes in electric cars and solar and space technology, and is led by the visionary entrepreneur Elon Musk.
Experience
– Waymo has an extensive experience in AI deep learning – which is the heart of the autonomous vehicles – perhaps more than any of its competitors in the AV commercialization race, including Tesla. On top of it, Google has more complete engineering experience in building an OS for AVs than probably any other company. Tesla, on the other hand, earned quite a reputation for itself for producing an all-electric luxury car from scratch using mostly Tesla-designed components and Autopilot software coded by Tesla engineers.
AV System
– Waymo uses a more expensive in-house 64-beam LiDAR – the heart of the system – which is mounted on the roof of the car and it sends 64 beams of light to get information about the terrain. By combining real-time information from LiDAR and other sensors including cameras with high-resolution maps of the road, it generates a 360-degree world model to predict movements for nearby vehicles while avoiding obstacles and following traffic rules. Tesla, on the other hand, does not use LiDAR but relies heavily on computer vision for building a virtual picture of the surroundings using the forward-looking camera technology from Mobileye – the largest supplier of camera-based driver-assistance safety systems.
Data
– While both Waymo and Tesla are doing everything to collect and process data to make a fully autonomous vehicle that can drive all by itself without any human interference, they have different approaches for data processing. Google uses powerful computer simulations and feeds from its fleet of cars that are in testing on real streets. Tesla, on the other hand, relies on the real-world data collected from the hundreds of thousands of Teslas being driven by human drivers operating in SAE level-2 or level-3 AV mode.
Google Self-Driving Car (Waymo) vs. Tesla: Comparison Chart
Summary of Google Self-Driving Car (Waymo) vs. Tesla
Formerly Google’s Self Driving Car project, Waymo has an extensive experience in AI deep learning – which is the heart of the autonomous vehicles – perhaps more than any of its competitors in the AV commercialization race, including Tesla. Tesla, on the other hand, specializes in electric cars and energy products and led by a visionary leader Elon Musk. While Waymo uses a its in-house 64-beam LiDAR technology to generate a 360-degree world map to predict movements, Tesla relies on computer vision for building a virtual picture of the surroundings using the forward-looking camera technology by Mobileye.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Dhawan, Chander. Autonomous Vehicles Plus: A Critical Analysis of Challenges Delaying AV Nirvana. Victoria, Canada: FriesenPress, 2019. Print
[1]Coppola, Pierluigi and Domokos Esztergár-Kiss. Autonomous Vehicles and Future Mobility. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2019. Print
[2]Redding, Anna Crowley. Google It: A History of Google. New York, United States: Feiwel & Friends, 2018. Print
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Waymo_self-driving_car_side_view.gk.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tesla,_Inc.#/media/File:Tesla_roadster_2020_prototype.jpg

Do you have an email for photos? I would like to correct some of the content in the article on Francis P Houdina.