Difference Between Regulated and Unregulated Power Supply
The term power supply can be broadly defined as anything that supplies power to literally every electrical and electronic system. In its simplest definition, a power supply is an electrical or electronic component that converts an available AC input voltage into a desired DC output voltage or to multiple DC outputs. Every electronic circuit or system needs a stable DC voltage for its intended operation. The desired DC voltage is normally obtained by converting the AC mains or line voltage into a DC voltage. However, the obtained DC voltage does not remain constant due to the variations in load current, variations in mains voltage and changes in ambient temperature. Such a system is called an unregulated power supply because the output changes significantly when its input load varies. So, the filtered output is then applied to a voltage regulator which provides a stable DC output voltage. Such a system is called a regulated power supply because it supplies a stable voltage. Let’s explore the technical differences between regulated and unregulated power supply.

What is a Regulated Power Supply?
A regulated power supply is an electronic circuit that is designed to produce a constant DC power supply or voltage that is independent of the current drawn from the temperature on the top of any variations in the AC line voltage. The term regulated here refers to a unit which maintains a constant output voltage irrespective of the changes in the input voltage or frequency and independent of the variations in the output load conditions. Simply put, it converts unregulated AC voltage into constant DC voltage. It makes sure the output remains unchanged irrespective of any changes in the input. It supplies a stable voltage to a device or circuit that must be operated within specified power supply limits.
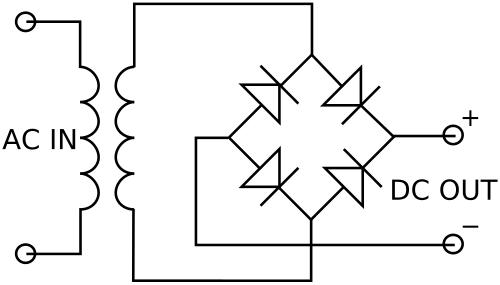
What is an Unregulated Power Supply?
Unlike regulated power supply, the output voltage of an unregulated power supply is not regulated meaning the output voltage changes as the load varies so they do not have voltage regulation. It provides a constant amount of power. It provides a predetermined output based on the input and load voltage and even a little variation in the input directly affects the output voltage. An unregulated power supply consists of a transformer, a rectifier and a filter. These little variations in the output voltage are called ripple voltage. So, none of the electronic circuits work properly with unregulated power supply. They require constant voltage supply regardless of the variations in the input voltage or load current. To do this, a voltage stabilizing device called voltage regulator is used.
Difference between Regulated and Unregulated Power Supply
Definition
A regulated power supply is an embedded circuit which produces a constant output voltage irrespective of the changes in the input voltage or frequency and independent of the variations in the output load conditions. It supplies a stable voltage to a device or circuit that must be operated within specified power supply limits. Conversely, an unregulated power supply is the one that provides a predetermined output based on the input and load voltage and even a little variation in the input directly affects the output voltage.
Output Voltage
The output voltage of a regulated power supply stays at a predetermined value and is independent of the current drawn from the temperature on the top of any variations in the AC line voltage. Any variation in the input voltage will not affect the output voltage because of a voltage stabilizing device called voltage regulator used. The output voltage of an unregulated power supply, on the contrary, is not regulated meaning the output voltage changes as the load varies so they do not have voltage regulation. The output voltage increases as the output current decreases and vice-versa.
Applications
The regulated power supplies are used for all applications that require an exact amount of output voltage such as television, computers, mobile chargers, appliances, medical and measurement devices as well as for electromechanical applications. Because they maintain voltage at a desired level, they can be used in almost all kinds of electronic devices. The unregulated power supplies can be used in applications where good regulation or low ripple is not required, such as LED lamps, relays, solenoids, actuators, DC motors and anything that is ideal for non-critical loads.
Regulated Power Supply vs. Unregulated Power Supply: Comparison Chart

Summary of Regulated Power Supply vs. Unregulated Power Supply
Well, which one’s actually ideal for use depends on your requirements. Unregulated power supplies are low-cost alternatives to regulated power supplies and can be used in applications which do not require precise output voltage. However, one major downside to such power supplies is that the output voltage changes with the variations in the input voltage or load current. If you want to use devices which are sensitive to load variations, then you might want to use regulated power supply because it makes sure the output remains unchanged irrespective of any changes in the input. Therefore, regulated power supplies are used for all applications that require an exact amount of output voltage.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Tarter, Ralph E. Solid-State Power Conversion Handbook. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 1993. Print
[1]Kishore, Lal K. Operational Amplifiers and Linear Integrated Circuits. New Delhi, India: Pearson Education India, 2009. Print
[2]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/68/Unstabilized_AC-DC_transformer.svg/500px-Unstabilized_AC-DC_transformer.svg.png
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Power_supply_1.jpg
