Difference Between Thyroid and Parathyroid
The thyroid is an endocrine gland in the neck area that produces thyroid hormone. The parathyroid is a group of endocrine glands on the thyroid that produce parathyroid hormone.
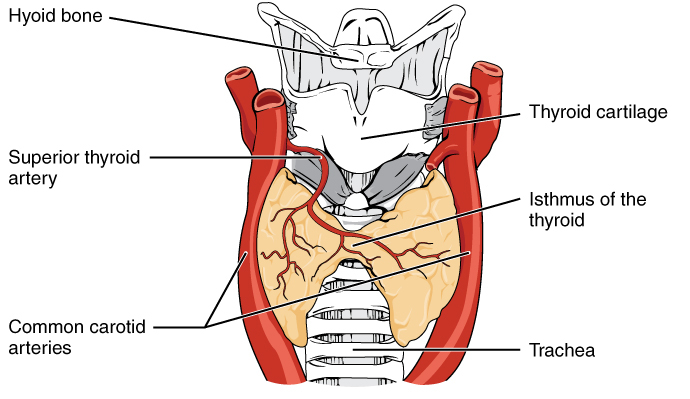
What is Thyroid?
Definition of Thyroid:
The thyroid is a gland of the endocrine system that is positioned below the voice box in the front facing part of the neck and produces thyroid hormones.
Structure of Thyroid:
The thyroid consists of two lobes, a left, and a right lobe, attached by a region of tissue that is known as the isthmus. The lobes give the gland a butterfly looking shape. The gland is made up of structures known as follicles, which contain a sticky substance known as a colloid. It is in this region where the thyroid hormones are made using molecules of iodine. Each follicle is surrounded by a layer of epithelial cells.
Function of Thyroid:
Various hormones are formed in the colloid region of the follicle from iodine precursors. Peroxidase enzymes act on tyrosine and iodine to form thyroid hormones. Two types are formed: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). The triiodothyronine is made of three iodines while the thyroxine is made of four iodines.
Regulation involved in Thyroid:
Secretion of endocrine hormones from the thyroid gland is controlled by negative feedback mechanisms that involve the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland of the brain. If there are reduced levels of triiodothyronine and thyroxine in the blood plasma then the hypothalamus is triggered to secrete thyrotropin-releasing hormone or TRH. This hormone has the effect of then activating the anterior pituitary gland to release the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) which goes to the thyroid gland. The hormone TSH activates the production of hormones. When the levels of hormones in the blood are high it feeds back to the brain which stops releasing TRH. This then halts the TSH and thus the release of more hormones.
Thyroid Disorders:
The two main disorders of the thyroid gland are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism is when you have too little thyroid hormone produced which causes symptoms like feeling cold, weight gain, and slow metabolic rate. Hyperthyroidism is when you have too much thyroid hormone. People with this condition have a metabolic rate that is too fast so they tend to feel hot, lose weight and also have bulging eyes.
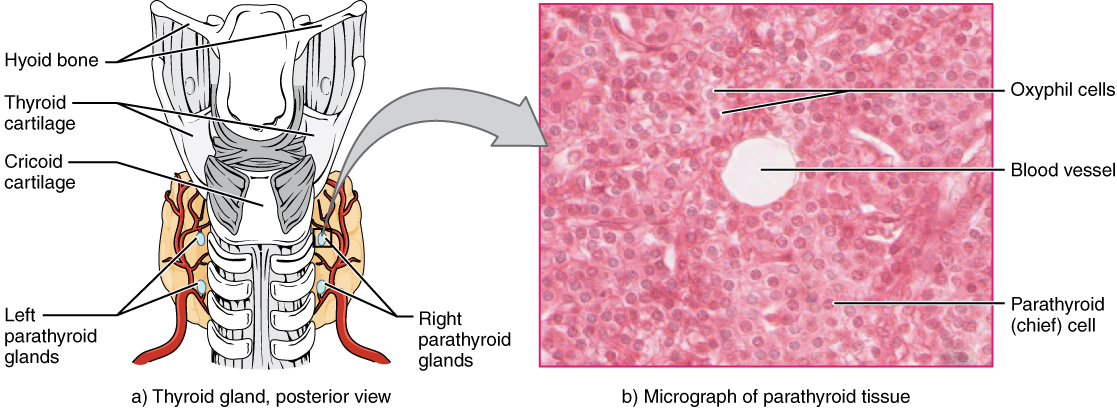
What is Parathyroid?
Parathyroid Definition:
The parathyroids are small endocrine glands that are located on the back of the thyroid gland in the neck region, and they produce parathyroid hormone.
Structure of Parathyroid:
They are small round glands that consist of oxyphil cells and chief cells and are set apart from the thyroid by means of a connective tissue layer. It is the chief cells that produce parathyroid hormone (PTH) that is released into the bloodstream.
Function of Parathyroid:
The parathyroid glands function is to produce PTH which works to regulate the calcium levels in the body, which is important since our nervous system relies on calcium ions to function. The PTH triggers the release of calcium ions from bone tissue by activating osteoclast cells which break down bone. It also stops the activity of the osteoblasts which are the bone cells that are involved in actually laying down more bone. It also activates the production of calcitriol which is a hormone that helps trigger the intestines to absorb more calcium from food.
Parathyroid Regulation:
The secretion of parathyroid hormone is largely controlled by the levels of calcium that are in the bloodstream. The alterations in bloodstream concentrations of calcium are sensed by G-protein coupled receptors of the chief cells in the parathyroid gland. A negative feedback mechanism is in play here with low calcium triggering more PTH to be released. As calcium levels in the blood plasma increase so the PTH is triggered to stop releasing the hormone.
Disorders involved in Parathyroid:
There can be both too much activity of the parathyroid glands, or too little. An overactive gland causes hyperparathyroidism. This disorder can cause excessive amounts of calcium to be taken out of the bones. The problem then is that bone density may weaken to such an extent that people are likely to have bone fractures. It also has a negative effect on the nervous system. Too little activity of the gland causes hypoparathyroidism, which can occur due to surgery or from an injury. This has an adverse effect on the nervous system and can lead to convulsions and muscle spasms and twitching.
Difference between Thyroid and Parathyroid?
Definition
The thyroid is a gland of the endocrine system found in the neck region, which secretes thyroid hormone. The parathyroids are glands found attached to the thyroid that secretes parathyroid hormone.
Anatomy
The anatomy of the thyroid includes epithelial cells and a colloid in the follicle region. The anatomy of the parathyroids includes oxyphil and chief cells.
Lobes
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped two lobe structure. The parathyroid has no lobes.
Size and number
There is only one thyroid gland which is quite large in size. There are four or more parathyroid glands which are small structures.
Hormones
The hormones produced by the thyroid include triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). The hormone produced by the parathyroid is parathyroid hormone (PTH).
Regulation
The secretion of hormones from the thyroid gland is regulated by TRH from the hypothalamus and TSH from the anterior pituitary, responding to hormone levels. Secretion of parathyroid from the parathyroid gland is regulated by G-coupled receptors on the chief cells responding to calcium levels.
Function
The thyroid regulates metabolism. The parathyroid regulates calcium levels.
Disorders
Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are disorders of the thyroid. Hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism are disorders of the parathyroid.
Table comparing Thyroid and Parathyroid

Summary of Thyroid Vs. Parathyroid
- The thyroid and parathyroid are both endocrine glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
- Both thyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone are regulated by negative feedback loops.
- Thyroid hormones regulate the metabolism of the body.
- Parathyroid hormone regulates blood calcium levels.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Kumar, Rajiv, and James R. Thompson. "The regulation of parathyroid hormone secretion and synthesis." Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 22.2 (2011): 216-224.
[1]Kumar, Rajiv, and James R. Thompson. "The regulation of parathyroid hormone secretion and synthesis." Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 22.2 (2011): 216-224.
[2]Mortensen, J. D., Lewis B. Woolner, and Warren A. Bennett. "Gross and microscopic findings in clinically normal thyroid glands." The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 15.10 (1955): 1270-1280.
[3]Trier, Jerry Steven. "The fine structure of the parathyroid gland." The Journal of Cell Biology 4.1 (1958): 13-22.
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anterior_thyroid.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1814_The_Parathyroid_Glands.jpg

Why does the parathyroud gland get wonky?