Difference Between Inflammation and Swelling
What are Inflammation and Swelling?
These are medical conditions where the affected area become red, warm, painful and swollen. However swelling results due to acute inflammation. These conditions are often thought to be synonyms, but there are some points of differentiation discussed below.
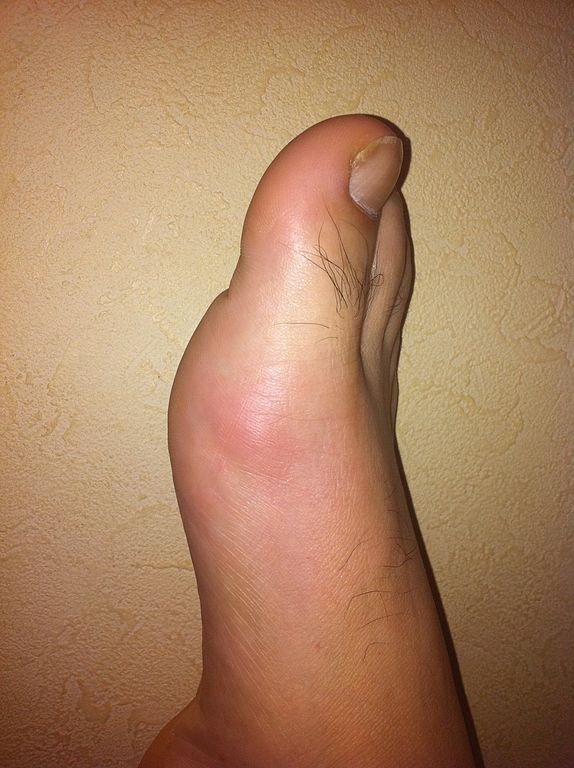
Inflammation
Inflammation is body’s reaction to any injury. It can also be described as the body’s capacity to heal itself after a tear, a wound or trauma; safeguard itself from foreign invaders, like viruses and bacteria; and restore injured tissue. However chronic inflammation can result in several serious health conditions like some cancers and rheumatoid arthritis.
If inflammation continues, it may eventually be called as chronic inflammation, with continuous low-level oedema, extended tissue damage, and very slow healing.
Swelling
Swelling occurs due to enlargement of body organs, skin or other parts. It usually is a result of inflammation or a build-up of fluid. Swelling can take place internally, or it can even affect the body externally (outer skin and muscles).
Difference between Inflammation and Swelling
Definition
Inflammation
A localized physical condition where part of the body becomes red, hot, swollen, and mostly painful. It is a vital response to injury or infection.
Swelling
It is an abnormal enlargement of a part of the body, usually triggered due to the result of accumulation of fluid.
Symptoms
Inflammation
Loss of joint function, join pain and stiffness, redness because the capillaries in the area are filled with more blood than usual, swelling, heat, loss of function in the region of the inflammation (immobility). If it is a chronic inflammation, the symptoms include
- Digestive issues like gas, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, acid reflux, etc.
- Brain fog
- Gum disease
- Frequent cold and cough
- High blood sugar
- Lingering and random pains
- “Spare tire” around your waist
- Skin problems like eczema or psoriasis
- Erectile dysfunction
- Face is puffy
- Ulcers and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Constant fatigue or lethargy
- Allergies and asthma
Swelling
Nausea, shortness of breath and sometimes low oxygen levels in the blood, vomiting, dizziness, bruises, weakness, Malaise, discoloration, decreased Urine Output, fever, fatigue, insomnia, feels hot to touch, flu-like symptoms, pain and enlargement of skin or muscles.
Causes
Inflammation
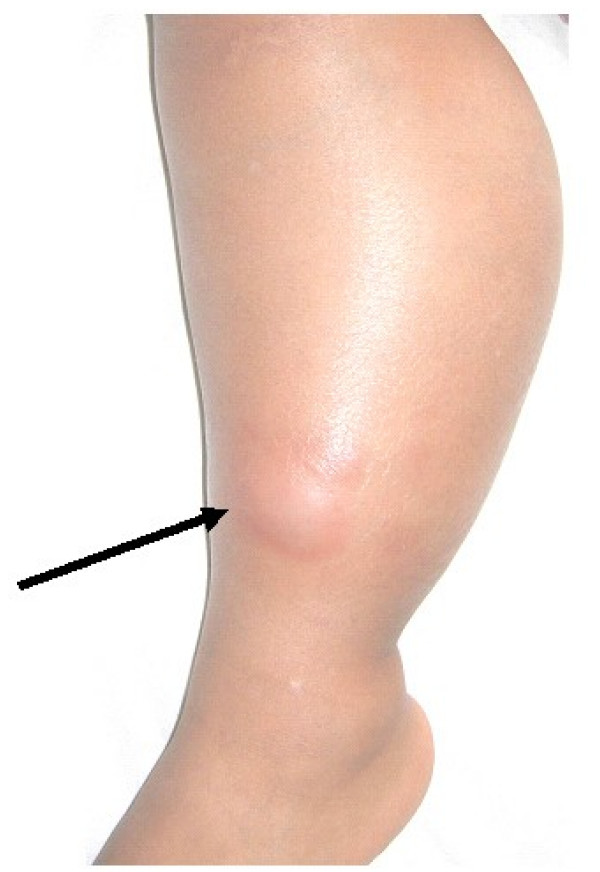
Conditions that can result in acute inflammation include; acute bronchitis, a sore throat from a cold or flu, acute appendicitis, rigorous exercises, stress, cut on the skin, poor diet, 2 Diabetes, food allergies, infected ingrown toenail, dermatitis, unbalanced levels of certain hormones, such as oestrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, tonsillitis, particular synthetic fibres found in products like latex, adhesives, and plastics trigger inflammation, Oils—such as safflower, sunflower, corn, soy, and peanut—that contain high levels of linoleic acid often cause an inflammatory response. Sinusitis and infective meningitis.
Swelling
Causes of external swelling include; insect bites, rash, hives, injury, fluid retention, pregnancy, menstruation, hormonal changes, infection.
Other common causes of internal swelling include; kidney failure, certain forms of cancer, heart failure, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn’s disease, anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction), venomous insect bite and blood vessels enlargement due to dehydration causing swollen stomach, face and even hands and ankles.
Ways to reduce inflammation and swelling
Inflammation
- Cut out fast food, processed foods, red meat. Eat more of plant-based diets, nuts, vegetables and adopt a vegan lifestyle. Eat more of organic stuff free from pesticides.
- Eat tomatoes, spinach, kale, almonds, walnuts, fatty fish like salmon, tuna and sardines, fruits like mandarins. blueberries and strawberries.
- Brush and floss your teeth every single day to stave off inflammation.
- Meditate to alleviate stress. Meditation turns off the damage of stress to the body
- Sleep and exercise well
- Do yoga and drink lot of green tea
- Ban electronic gadgets from the sleeping room.
- Say NO to sweetened beverages
- Don’t eat things which you can’t pronounce.
Swelling
- As swelling is a result of accumulation of fluids, one can raise the affected area above the level at which one’s heart is.
- Drink lot of water to remove toxins and accumulated fluids in the swollen area.
- Compress the swelling using a bandage without restricted the blood flow.
- Heating pad relieves the swelling pain.
- Do not consume foods which contain sodium when you have swelling. Consume lot of lemon and cucumber water as they reduce swelling.
- Wrap an ice pack in a towel and press it to the affected area. It is recommended to alternate between fifteen minutes on and fifteen minutes off to help bring down pain and swelling.
- Immerse your achy, swollen joints in a warm Epsom salt bath. Epsom salt relieves pain, increases blood circulation and reduces swelling.
Medicinal drugs
Inflammation
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like Aspirin, Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, Midol, Nuprin) Ibuprofen, Naproxen sodium, Naproxen Aleve and Diclofenac.
Swelling
Ibuprofen and Naproxen and Acetaminophen.
Summary of Inflammation Vs. Swelling
The points of difference between Inflammation and Swelling have been summarized below:

- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Ellis, L. B. (1941). The causes and treatment of edema. New England Journal of Medicine, 224(25), 1060-1067.
[1]Hunter, P. (2012). The inflammation theory of disease: The growing realization that chronic inflammation is crucial in many diseases opens new avenues for treatment. EMBO reports, 13(11), 968-970.
[2]Maroon, J. C., Bost, J. W., & Maroon, A. (2010). Natural anti-inflammatory agents for pain relief. Surgical neurology international, 1.
[3]Punchard, N. A., Whelan, C. J., & Adcock, I. (2004). The Journal of Inflammation. Journal of Inflammation, 1, 1.
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/97/Tuberculosis_leg_swelling.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3c/Gouty_inflammation.jpg/574px-Gouty_inflammation.jpg
