Difference Between Bronchitis and Cold
What are Bronchitis and Cold?
Both are caused due to viral infections. However, bronchitis is also caused because of some bacteria. Most of the symptoms are common between cold and bronchitis. However, there are many differences as well. The main difference between common cold and bronchitis relates to the severity of each.
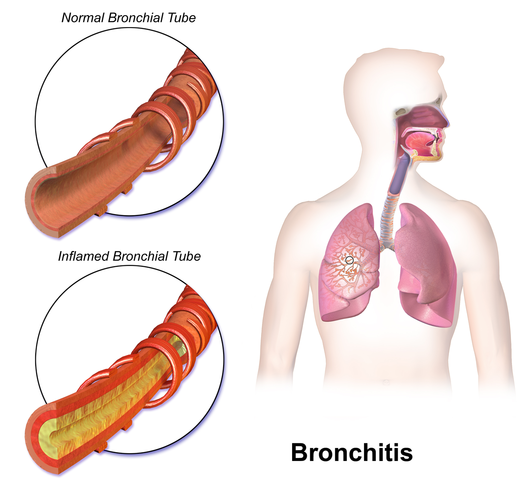
What is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of bronchial tubes, that carry air to and from the lungs. It is basically of two types; Acute bronchitis and Chronic bronchitis. Acute bronchitis is also known as a chest cold. Acute bronchitis accompanies cough that lasts around 3 weeks. Chronic bronchitis is called as a productive cough that lasts for 3 months or more every year for at least 2 years. Most patients with chronic bronchitis suffer from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Bronchitis often develops from the common cold.

What is Cold?
The common cold is a viral infection that occurs in the nose and throat i.e. the upper respiratory tract. It is mostly harmless and people recover from it in a span of 10 days. Children younger than 6 are at a greatest risk of common cold, but even adults also suffer from it 2 to 3 times annually. It sspreads easily and is usually self-treatable.
Difference between Bronchitis and Cold
Definition of Bronchitis and Cold
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining (large and medium-sized airways) of the bronchial tubes, that transport air to and from the lungs. Bronchitis could be either acute or chronic.
Cold
The common cold is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract, that primarily affects the nose and the throat. It can be caused by many different types of viruses. The medical condition is generally harmless and symptoms usually resolve within 2 weeks.
Diagnostic findings
Bronchitis
Cough and possible phlegm production.
Cold
Runny nose, sneezing, cough, nasal congestion and sore throat.
Symptoms of Bronchitis Vs. Cold
Bronchitis
This condition is more common in people suffering from asthma or emphysema. Fatigue or malaise, coughing up thickened mucus and shortness of breath, coughing spells, slight fever (fever of 100°F to 100.4°F (37.7°C – 38°C)) and chills, chest discomfort, back and muscle ache, production of mucus (sputum), that is usually clear, white, green or yellowish-gray in color — rarely, it can be streaked with blood. Acute bronchitis includes wheezing (a whistling or squeaky sound when one breathes).
Emergency symptoms include
Unexplained weight loss, acute breathing trouble, acute pain in the chest, a high fever, a cough that lasts longer than 10 days.
Cold
Watery eyes, itchiness, or redness, sinus pressure, low-grade fever, generally feeling unwell (malaise), runny nose, swollen lymph nodes, hoarseness, blocked ears, loss of smell or taste, dry cough, watery nasal secretions, body aches, chills, fatigue, stuffy nose, difficulty in breathing and discomfort in chest.
Causes for Bronchitis Vs. Cold
Bronchitis
Usually, the viruses that cause common cold also cause bronchitis. However, at many occasions, bacteria are to blamed. The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is cigarette smoking. Polluted air, mine dust, toxic gases and working around farm animals are some other reasons to cause bronchitis
Cold
Although many types of viruses can result in common cold, rhinoviruses are the major culprit.
Treatment
Bronchitis
Treatments include different vaccinations, quitting smoking as smoking aggravates bronchitis, pulmonary rehabilitation, and often inhaled bronchodilators and corticosteroids. Some patients may benefit from long-term oxygen therapy or lung transplantation.
Over-the-counter medications like pain relievers (analgesics), cough expectorants (for e.g., guaifenesin, pseudoephedrine or hydrocodone) or decongestants to treat symptoms. A type of medication known as mucolytics that is used to make phlegm easier to cough up.
Cold
Decongestants such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed), antihistamines, and pain relievers, Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory drug, Analgesic, Methanol, Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) are common over-the-counter medicines that treat symptoms like fever, body aches, sore throat and headache. Common alternative treatments to treat the common cold are vitamin C, echinacea, zinc, and other herbal treatments.
Site of infection
Bronchitis
In this medical condition, the viral or the bacterial infection occurs in the mucous membrane layer on the interior of the bronchi.
Cold
In common cold, the viruses infect the upper part of the pharynx, enveloping the complete region beginning from the back of the snout and extending to the back of the throat. The viruses cause inflammation of the nasopharyngeal region, resulting in the most common symptom of the common cold – sore throat and an itchy irritation in the mouth and the throat.
Summary of Bronchitis Vs. Cold: Comparison Chart
The points of difference between Bronchitis and Cold have been summarized below:

- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1c/Bronchitis.png/517px-Bronchitis.png
[1]Image credit: https://www.maxpixel.net/Blond-Blow-Woman-Blowing-Hand-Chief-Grey-Nose-699004
[2]Allan, G. M., & Arroll, B. (2014). Prevention and treatment of the common cold: making sense of the evidence. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 186(3), 190-199.
[3]Kim, V., & Criner, G. J. (2013). Chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 187(3), 228-237.
[4]Mossad, S. B. (1998). Fortnightly review: treatment of the common cold. BMJ: British Medical Journal, 317(7150), 33.
[5]Worrall, G. (2008). Acute bronchitis. Canadian Family Physician, 54(2), 238-239.
