Difference Between TENS and EMS
Both TENS and EMS deliver low voltage electric impulses meant for stimulation. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulators (TENS) and Electronic Muscle Stimulators (EMS) are technically the same. They both are basically Electrotherapy devices that work by producing electrical impulses which stimulate nerves in the skin leading the muscles controlled by those nerves to react by contraction action. But there is a difference as well. TENS stimulates nerves and EMS stimulates muscles.
ENS & EMS machines are really effective for avid sports people who suffer a long-term injury. TENS and EMS machines help in muscle and nerve recovery and also help in muscle recovery after the birth so you can get that tummy back in shape.
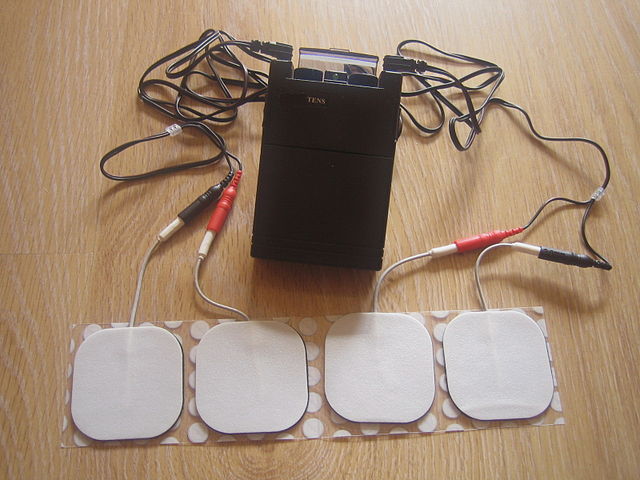

TENS
It is a machine that produces electric current to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic reasons. A TENS unit makes use of a microcurrent to intensify the making of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that is a source of energy to all the cells in the body. However, it is also important that for maximum benefits of TENS units and for lasting pain minimization, frequent and regular microcurrent sessions are required. But at the same time, some individuals are seen to experience maximum pain reduction and lasts longer and also, the time between the frequency of sessions increases. This is because of the increase in the blood circulation action that helps the lymph system to wash off the toxins from the body. The sensations generated by the microcurrents and the conventional TENS treatments are like tingling feeling than the uncomfortable and distressing feeling of a small electric current.
EMS
EMS maximizes the flow of blood by using stimulatory cycles. It contracts and then relaxes the muscles to increase the blood flow which minimizes inflammatory actions and accelerates healing and muscle growth. By stimulatory actions in the muscles, an EMS unit results in muscle contractions that are same as experiences by physical exercises. The EMS units are specifically utilized to block atrophy of muscles or for retraining of muscles, like people who suffer from paralysis. Also, EMS is effective for range of motion improvement, maximize circulatory blood flow and in the prevention of blood clots.
Difference between TENS and EMS
Definition
TENS
TENS stimulates the nerves – the logic is that these stimulatory actions prevents pain signals from reaching the brain.
EMS
EMS accelerates contraction of muscles – by mimicking the action potential that comes from the central nervous system
Signals
TENS
TENS devices offer a wider range of signals with respect to frequency, pulses and intensities.
EMS
EMS devices offer limited signals and thus narrower functions in this regard.
Uses
TENS
TENS therapy, offers short-term pain relief. TENS is not painful and is an efficient and effective therapy to mask pain like diabetic neuropathy. TENS therapy also encourages the production of endorphins, which act as body’s natural painkillers. Electrical stimulation from TENS also improves circulation locally. It can also either minimize or completely put an end to muscle spasms.
It is also used for;
- Arthritis relief
- Relieves acute, chronic, and psychogenic pain
- Bursitis
- Tendonitis
- Osteoarthritis
- Nerve pain
- Shoulder pain
- Migraines and Headaches
- Sciatic pain relief
EMS
In medicine, Electrical muscle stimulation is used for rehabilitation purposes. It should never be utilized as a replacement for training.
Some of the uses of EMS are:
- It aids in muscle strengthening when in pain or injured
- Electrical muscle stimulation can help activate fatigued muscles, with no risk to the athlete.
- Electrical muscle stimulation is an extremely useful tool to assist a healthy or injured athlete, in conjunction with tactical and proven concords.
- EMS also offers the added benefit of pain reduction for patients who are not willing or are not able to take oral pain reduction medications or any anti-inflammatory tablets or liquid drugs.
- EMS benefits also include Muscle Atrophy, Osteoarthritis, Pressure Sore Prevention, muscle re-education, massaging of sore muscles.
Applications
TENS
TENS generates stimulatory actions in nerves to block pain and relax muscles consequence. TENS provides immediate pain relief.
EMS
EMS stimulates muscles cells. An EMS unit is usually appropriate before and after physical exercise or any workout sessions or can also be used on the advice of a physiotherapist in case you are rebuilding your muscles that have suffered atrophy. EMS offers long range treatment for muscle development.
Penetration value
TENS
Low penetration value and temporary benefits
EMS
Deep penetration value and permanent results
Summary of TENS and EMS
The points of difference between TENS and EMS have been summarized below: Comparison Table

- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Azman, M. F., & Azman, A. W. (2017, November). The effect of electrical stimulation in improving muscle tone (clinical). In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 260, No. 1, p. 012020). IOP Publishing.
[1]DeSantana, J. M., Walsh, D. M., Vance, C., Rakel, B. A., & Sluka, K. A. (2008). Effectiveness of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for treatment of hyperalgesia and pain. Current rheumatology reports, 10(6), 492.
[2]Vance, C. G., Dailey, D. L., Rakel, B. A., & Sluka, K. A. (2014). Using TENS for pain control: the state of the evidence. Pain management, 4(3), 197-209.
[3]Zeng, C., Yang, T., Deng, Z. H., Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Lei, G. H. (2015). Electrical stimulation for pain relief in knee osteoarthritis: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 23(2), 189-202.
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/11/Hamstrings_EMS_recovery.jpeg/622px-Hamstrings_EMS_recovery.jpeg
[5]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6b/Tens.jpg/640px-Tens.jpg
