Difference Between UPVC and CPVC
Poly (vinyl chloride) is the name for a group of plasters containing macromolecules with recurring -CH2-CHCl units. In its pure form PVC is rigid and fragile, but its features can be easily modified. More than a hundred kinds of vinyl chloride plastomers are known. They are distinguished by the methods of preparation, the type and amount of softening, containing monomers or other polymers. Their physical properties change from flexible, elastomeric to stringy or rigid materials.

What is UPVC?
Unplasticized polyvinyl chloride is a solid, versatile material that is resistant to a large number of chemicals. UPVC is a tough, sinewy, transparent and hard-wearing material, but it is very resistant to the influence of the atmosphere, moisture and chemicals, has excellent electrical properties and low flammability. Tubes and fittings made of UPVC are suitable for installation in and out of the soil. This material is resistant to aggressive environments – caused by natural phenomena or industrial outbreaks. It is also resistant to all kinds of corrosion. The advantage of tubes and fittings made of UPVC is the long life, resulting in a long period of safe installation. UPVC has excellent chemical resistance, which eliminates the formation of limescale and provides good flow characteristics. UPVC is odorless and tasteless, it is suitable for transport of processed water, wastewater, as well as for a large number of chemicals. UPVC is suitable for use at temperatures ranging from 0°C to 65°C at a wide range of operating pressures, depending on the selected system. It is also easy and simple to install – using a bundle for joints and not requiring special tools.

What is CPVC?
Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a thermoplastic made by chlorinating the polyvinyl chloride resin. It is resistant to degradation and provides a long life span of use. In fact, the first pipeline systems used by the CPVC occurred in 1959, and they continue to work without any problems. CPVC is additionally chlorinated PVC. The chlorine bonded to the carbon atoms of the pre-chlorinated PVC contains 65-67% chlorine, which is 7% more than UPVC. Because of the increased chlorine content, it has excellent chemical resistance, primarily to acids, alkalis and salts, and is therefore very suitable as a material in the chemical process industry. The temperature range of application ranges from -40°C to + 95°C. CPVC is an extremely valuable, structurally rigid and solid plastic material used in industrial media transport applications with a maximum operating temperature of up to 100°C. Like other PVC systems, it is characterized by easy handling and simple and fast bonding. It also optimal fore transfer of treated and untreated drinking water, demineralized water and water for spa and medical use. Another advantage is the high value of perimeter strength, which ensures extended life of the device without significant mechanical or physical damage. CPVC is characterized by its optimum temperature stability, and its non-flammability which is an important factor in its use. Thanks to its long life in aggressive and corrosive environments, CPVC is becoming more and more important.
Difference Between UPVC and CPVC
-
Manufacturing of UPVC and CPVC
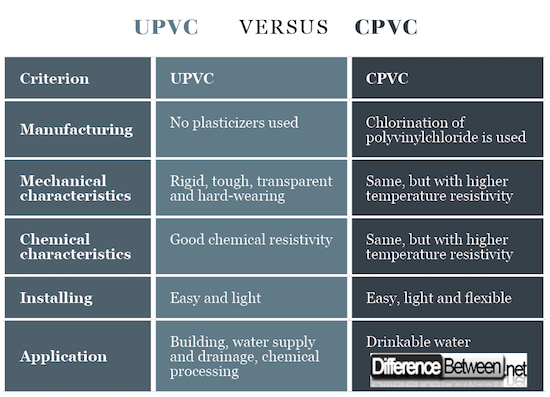
The molecule of poly (vinyl chloride) is produced with petroleum or natural gas and salt processing. The chlorine used for the manufacture of PVC is separated from kitchen salt (50% of the weight of PVC is from salts). The string molecular processes of the molecule (NaCl) are divided and Na + and Cl-ions are obtained. This obtained ions of Cl- react with ethylene or acetylene and vinyl chloride monomer is formed. The vinyl chloride monomer is pressurized and placed in a polymerization reactor containing water and catalysts that help in the heated polymerization reaction – the chemical process in which poly (vinyl chloride) is obtained. UPVC is PVC without plasticizers (they are not used in the manufacturing process). CPVC is a thermoplastic product obtained by chlorination of polyvinylchloride.
-
Mechanical characteristics of UPVC and CPVC
UPVC is a rigid, tough, transparent and hard-wearing material. It has high strength and swiftness. CPVC is more flexible. The mechanical at room temperature of CPVC are very similar to those of UPVC. CPVC is also a material that has high mechanical strength. In case of CPVC these characteristics are preserved during higher temperatures.
-
Chemical characteristics of UPVC and CPVC
UPVC has very good resistance to chemically aggressive and corrosive fluids. It shows good resistance to acids, bases and salts and has excellent weathering resistance. It is not resistant to aromatic or chlorinated solvents, esters and ketones. It is non-conductive and low-combustive. CPVC shares the same characteristics, but even at higher temperatures. UPVC shows good resistance to around 65°C, while CPVC to around 95°C.
-
Installing of UPVC and CPVC
The materials are easy and light to transport and to install. CPVC’s flexibility further ease the process.
-
Application of UPVC and CPVC
UPVC is most commonly used in the building industry, due to its low-maintenance properties. It is also used as supply and drainage water systems (non-drinkable), in the chemical processing industry, shipbuilding etc. CPVC can additionally be used for water-plumbing.
UPVC Vs. CPVC
Summary of UPVC Vs. CPVC
- UPVC does not contain plasticizers as they are added only in flexible PVC. UPVC has almost completely replaced the use of iron for plumbing and drainage, which is used for waste pipes, drainage pipes, ducts and rays. UPVC is known for its strong chemical resistance, mechanical strength and easy handling.
- CPVC is flexible material, having similar properties with UPVC – however, more resistant to temperature. It can be used for drinkable water supply.
- Difference Between Thermodynamics and Kinetics - June 24, 2018
- Difference Between Welding and Soldering - June 24, 2018
- Difference Between Additive Colors and Subtractive Colors - June 20, 2018
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
3 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Calhoun, A., Peacock, A. “Polymer Chemistry – Properties and Applications”, Munich: Hanser Publishers, 2006
[1]Termonia, Y., Smith, P. “High Modulus Polymers”, NY: Marcel Dekker Inc., 1988
[2]Aftalion, F. “A History of the International Chemical Industry”, Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1991
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cpvc_sprinkler_rohr_kanadische_holzkabache.jpg#/media/File:Cpvc_sprinkler_rohr_kanadische_holzkabache.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/146543510@N02/32125531501

Nice i gain the knowledge
Good explanation ….
thank you for given information
upvc windows in hyderabad