Difference Between Land Breeze and Sea Breeze
Land breeze and sea breezes take place near large bodies of water. The key difference between the two is caused by the property of water to retain and warm up longer. The differences in the temperature of land and water causes respective changes to the densities of the air above them. The resulting low pressures then cause alternating air movements which are manifested as breezes. Individuals situated near coastlines (within 50 kilometers from the oceanfront) experience cool sea breezes during the day and warm land breezes at night. Furthermore, these winds are instrumental in humidity and temperature levels, and precipitation rates.

What is a Land Breeze?
As it name suggests, the local wind system which occurs from land to water is called land breeze and some refer to it as an offshore wind. It arises at night and early morning when the land has a lower heat capacity as compared to the adjacent water. Particularly, land breezes last longer during the last weeks of summer as this is when the sea temperature will gradually increase to the land’s daily temperature variations.
The following occurrences outline how land breeze is formed:
- Late at night, the loss of heat source causes land to quickly cool down which causes the heat to be released towards the surrounding air.
- As compared to land, water retains heat longer which causes the air above it to have lesser density and rise.
- Low pressure is formed above the water while high pressure is formed above the land.
- The denser air above the land moves to the space over the water.
- As winds typically blow from high to low pressure areas, the cooler breeze then comes from the shore and is now called as “land breeze”.
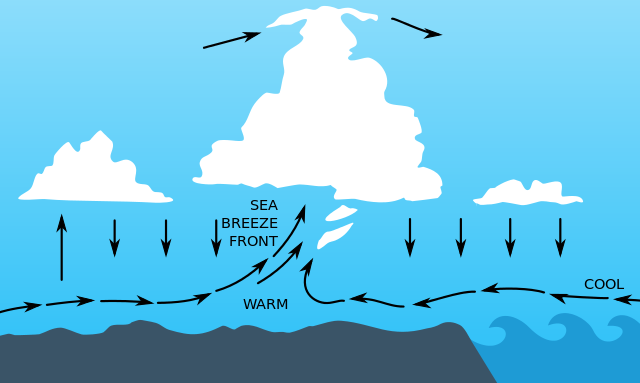
What Is a Sea Breeze?
Winds that blow from large bodies of water specifically seas and oceans are called sea breezes and some refer to them as onshore winds. Generally, they occur more frequently during the spring and summer seasons due to the more apparent temperature differences between the water and adjacent land. This is most often observed in the afternoons when the nearby land has been heated at its maximum level. Notably, sea breezes are stronger during summer months as compared to winter season. This is again attributed to the huge temperature difference between land and sea which may even prompt thunderstorms which are essential in bringing rain. Hence, sea breezes are not that apparent during autumn and winter months because the temperature differentials are smaller.
The following occurrences outline how sea breeze is formed:
- During day time, the sun often quickly heats up land.
- The air above the land gets warmer than the air above water.
- As the air above land is warmer, it gets less dense and it begins to rise.
- Low pressure is formed.
- The denser air above the water moves to the space above the land. This cooler air is now what is termed as a “sea breeze”.
Difference between Land and Sea Breeze
-
Time
Land breeze: is formed at nighttime
Sea breeze: is formed at daytime.
-
Source
As their names suggest, land breeze comes from land while sea breeze comes from water.
-
Depth
Since the cooling of the air over land typically occurs within a shallower layer at night, the land breeze is likewise shallower as compared to the sea breeze.
-
Season
Sea breezes are more often experienced during spring and summer because of the significant temperature differences between land and water. On the other hand, land breezes are most common in autumn and winter due to the cooler nights.
-
Strength
Generally, sea breezes are stronger than land breezes due to the bigger temperature differences.
-
Speed
Sea breezes’ speed usually ranges from 10 to 20 knots while that of land breezes’ only range from 5 to 8 knots.
-
Moisture
Sea breezes have more moisture due to the absorbed particles from the bodies of water. On the other hand, land breezes are often dry winds.
-
Occurrence during Winter Months
Unlike land breezes, sea breezes are not often observed during winter season. During such cold months, land breezes are predominant in influencing weather; particularly when a strong change of wind direction occurs at night.
-
Benefit to glider pilots
Glider pilots particularly take significant advantage of the sea breeze to steer in higher altitudes. Unlike land breezes, sea breezes are strong enough to influence such aircraft operations.
-
Decrease in Air Temperature
A decrease in air temperature is most likely due to sea breezes whereas land breezes do not essentially cause temperature changes.
Land Breeze vs Sea Breeze: Comparison table

Summary of Land Breeze vs Sea Breeze
- Both breezes occur near coastal areas.
- Land and Sea breezes affect precipitation rates, humidity levels, and atmospheric temperature.
- Land breezes come from land while sea breezes come from the ocean or other large bodies of water.
- The key difference is due to the property of water to retain heat and warm up longer as compared to land.
- Land breezes are also known as off-shore winds while sea breezes are also called on-shore winds.
- While a land breeze is formed at night, a sea breeze is formed at daytime.
- Land breezes are more often experienced during autumn and winter while sea breezes often occur during spring and summer months.
- Land breezes are generally weaker than sea breezes. This makes sea breezes quite significant to glider pilots and other related aircraft operators.
- Typically, land breezes are slower than sea breezes.
- Land breezes are generally dry winds while sea breezes have more moisture.
- Unlike sea breezes, land breezes are predominant during winter months.
- Unlike land breezes, sea breezes can significantly lower air temperature.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
3 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/98/SeaBreeze.svg/640px-SeaBreeze.svg.png
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Land_and_Sea_Breezes.gif#/media/File:Land_and_Sea_Breezes.gif
[2]Durstewitz, Michael and Lange, Bernhard. Sea-Wind-Power. Berlin: Springer, 2016. Print.
[3]Gipe, Paul. Wind Energy Basics. Vermont: Chelsea Green Publishing, 2009. Print.
[4]Simpson, John. Sea Breeze and Local Winds. England: Cambridge University Press, 1994. Print.

Important of sea breeze
GOOD INFORMATION
THANKS FOR THE GOOD INFORMATION