Difference Between Security and Privacy
Both security and privacy are interdependent and they are often synonymous with each other. Many of us may believe both are closely related terms and one cannot have one without the other, while some would argue that one can have security without privacy, but not the other way around. Both terms are synonymous with technology and networks.
The impact of technology on our lives continues to rise, with digital businesses moving at a much faster pace than traditional businesses. As large organizations embrace technologies such as big data, Internet of Things, and cloud, security is a necessary evil. In this technology-driven digital era where everything is connected and easily accessible, security must be more than an afterthought. This article explains how the two differ from each other rather than related.

What is Security?
Security refers to personal freedom from external forces. It’s the state of being free from potential threats or dangers. Just like a home security system which protects the integrity of your household, data security protects your valuable data and information from prying eyes by safeguarding your passwords and documents.
Security refers to protective measures put in place to protect digital data from unauthorized users, such as cyber criminals and hackers. Technology has gotten more advanced, so does hackers, and so should data security measures. While security does not guarantee that data or information cannot be compromised, strict security measures and protocols help preventing unauthorized access. So, it’s always recommended to safeguard your online accounts with strong passwords, with different combinations on different websites that require a log in.
The main objectives of security are confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The goal is to strengthen internal control and restrict unauthorized access from both internal and external factors, thereby protecting the confidentiality and integrity of resources and assets.
All security measures try to address at least one of the three goals:
- Protecting the confidentiality
- Preserving the integrity of information assets
- Promoting availability of data and information.
These measures apply to areas such as personnel security, network security, and administrative security. The security protocols and measures define what you wish to protect and from what. To develop strong and legit security policies, you must define you security objectives, which will further help you draw up the security plan for a secure system.

What is Privacy?
Privacy is one’s right to freedom from intrusion and prying eyes. It’s the state of being free from unwanted attention and secret surveillance. Privacy is more like a notion that includes secrecy. It’s one of the core principles of human dignity.
Let’s take the window, the one in your home. A window has various functions. For one, it updates the interiors with a graphical control element. It allows people to enjoy the beautiful outdoors, and at the same time, it also provides access to outsiders or unwanted visitors from getting inside. Just like you look outside, others may look inside. To prevent outsiders from peeking into your windows, you can put a curtain or a drape to cover the window. This is called privacy. Restricting the view protects your privacy as intruders or thieves may not be able to see who or what’s inside. Similarly, information security protects limits access to personal data or information.
Difference between Security and Privacy
-
Definition of Security and Privacy
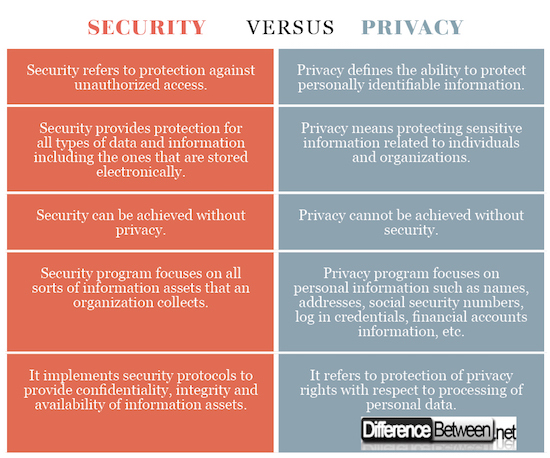
While both are interlinked terms that are often used in conjunction with each other. While one cannot exist without the other, they are often misappropriated. Security is the state of personal freedom or being free from potential threats, whereas privacy refers to the state of being free from unwanted attention.
-
Objectives of Security and Privacy
The three main goals of security are confidentiality, integrity and availability. Security means safeguarding your information assets and confidential data from unauthorized access. It affects both information security and cyber security. All security protocols address at least one of the three goals. Privacy, on the other hand, refers to the rights of individual and organizations with respect to personal information.
-
Programs for Security and Privacy
A security program refers to a set of protocols and regulations set in place to protect all the confidential information assets and resources that an organization collects and owns. It focuses on the data and information rather than personal information of individuals. Privacy program, on the other hand, focuses on protecting only personal information such as log in credentials, passwords, etc.
-
Principles of Security and Privacy
The three core principles of security include protecting confidentiality, preserving integrity of information assets, and promoting availability of data and information. Privacy defines the rights of individual and organizations with respect to personal information. To some extent, privacy can be achieved with security initiatives and security depends on privacy of credentials and access to data.
-
Dependency
Security and privacy go hand-in-hand. One can envision an environment which is secure but doesn’t guarantee privacy. Similarly, one can imagine a home which is private because of the windows, but it doesn’t guarantee security from outsiders. Security can be achieved without privacy, but privacy cannot be achieved without security. It security is weak or vulnerable, it automatically affects privacy.
Security vs. Privacy: Comparison Chart
Summary of Security vs. Privacy
While security and privacy are interdependent, security can be achieved without privacy but privacy cannot be achieved without security. Security protects confidentiality, integrity and availability of information, whereas privacy is more granular about privacy rights with respect to personal information. Privacy prevails when it comes to processing personal data, while security means protecting information assets from unauthorized access. Personal data may refer to any information concerning any individual such as names, addresses, credentials, financial accounts information, social security numbers, etc.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
2 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/data-binary-one-null-privacy-2248219/
[1]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/cyber-security-encryption-security-2537786/
[2]Salomon, David. Data Privacy and Security. Berlin: Springer, 2012. Print
[3]Solove, Daniel J. Nothing to Hide: The False Tradeoff Between Privacy and Security. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2011. Print
[4]Song, Houbing, Glenn A. Fink, and Sabina Jeschke. Security and Privacy in Cyber-Physical Systems. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2017. Print

Hi, in point 1. you write “one cannot exist without the other” and in point 5. “Security can be achieved without privacy”. Which one do you stand for?
Furthermore, in chapter 5. “one can imagine a home which is private because of the windows, but it doesn’t guarantee security from outsiders” and “but privacy cannot be achieved without security”.
Both meaning are to keepsake all your infos and not to be exposed to the public. It is very alarming how the cyber criminals were able to penetrate your details. And having both privacy and security is important.