Difference Between Scleroderma and CREST
Scleroderma is an autoimmune disorder which affects the skin of the whole body causing it to harden. CREST syndrome is the name given to limited form of scleroderma in which lesser body parts are affected. The two conditions are differentiated on the basis of the severity and extent of the condition.
CREST syndrome:
This is a type of limited scleroderma. The name of the condition is an acronym in which each letter indicates the symptom of the condition.
C- Calcinosis
R- Raynaud’s phenomenon
E- Esophagial motility disorder
S – Sclerodactyly
T- Telangiactesis
It is a connective tissue disorder which affects all the organs of the body. On the cellular level the condition is characterised by three main features that include – Increased collagen production and deposition, mononuclear cell infiltration in tissues near the vascular structures and abnormalities of the blood vessels.
The condition is relatively more common in the Caucasian population. Women are more affected than men and the common age of onset of the condition is between 30-65 years.
CREST is a subtype of the autoimmune disorder scleroderma. It is a hereditary condition. Exposure to benzene, poly vinyl chloride, silica etc. may trigger the symptoms in people who are genetically predisposed to the condition. The disease process affects the lower arms, legs, face and throat. It may affect the digestive tract. In majority of the cases the symptoms are mild. In very rare cases the heart and lung can get affected causing serious complications.
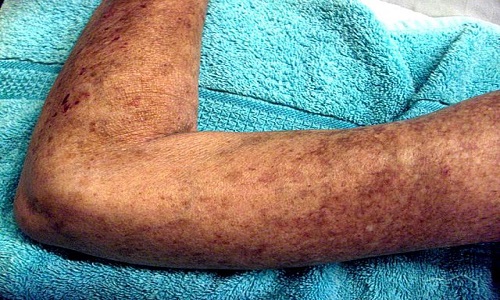
The symptoms appear gradually. The skin over the elbow and knees gets hardened, tight and shiny. The tightened skin makes bending of fingers, toes, elbows and knees very difficult. The small sized blood vessels of the arms and legs are also affected. They become spasmodic which narrows their lumen. This affects the blood supply to the hands and legs, turning them blue. Once the spasm gets relieved there is increased blood supply to the extremities making them very red. This is known as Raynaud’s phenomenon. There is also a throbbing and tingling sensation in the hands and legs. Telangiectasia refers to red streaks on the skin due to swelling of tiny blood vessels situated near the skin especially in the hands and face. There are calcium deposits under the skin surface especially over the fingers, elbows and knees. They become a little tender if infected. Peristaltic movement of the oesophagus is affected which may cause heart burn. The lining of the oesophagus gets inflamed and scarred.
Scleroderma
It is the hardening of the skin of the whole body as a result of autoimmune changes. It has been attributed to mutative changes in the HLA gene. The condition also affects the internal organs. It is diffuse and more severe than the limited scleroderma. The condition spreads very fast and affects one more of the internal organs like kidneys, heart or lungs.
It affects almost all parts of the body and is very disabling. The patient usually dies of heart or lung complications. The patient of scleroderma presents with red and thickened skin over most parts of the body, Raynaud’s phenomenon, Telangiectasia, ulcer or gangrene in the hands and legs, stiff and painful joints, hypertension, cardiac failure, lung congestion. The patient may also have bloating of the abdomen, indigestion, loss of appetite, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, chest pain, lung congestion, kidney failure etc.
Treatment of Scleroderma and CREST
There is no cure for this condition. The main focus of treatment therefore is to managing the severity of symptoms and preventing any complications. Calcium channel blockers are usually prescribed for Raynaud’s phenomenon. Patients are advised to keep their extremities warm by wearing socks and gloves. Topical antibiotics can be applied over the skin ulcers. In case they are ineffective, oral antibiotics are begun. Medications to control blood pressure are also prescribed. Surgical removal of calcium deposits is possible if they become too painful. Amputation is the only option for gangrenous limbs to avoid spread of the cellular damage. For those people who have swallowing difficulties, consuming semisolid food and fluids is preferred as compared to solid food. Antacids can also be taken in case of heart burn. Keep the skin moisturised. Perform stretching of all joints of the body to prevent joint stiffness.
- Difference Between Flu and Fever - September 2, 2015
- Difference Between Haemoglobin and Iron - July 10, 2015
- Difference between Purpura and Ecchymosis - July 2, 2015
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]http://www.hopkinsscleroderma.org/scleroderma/types-scleroderma/
[1]http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/crest-syndrome/basics/alternative-medicine/con-20031524
[2]http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1064663-overview
[3]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CREST_syndrome
[4]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scleroderma
[5]http://www.scleroderma.org/site/PageNavigator/patients_whatis.html#.VWw3P-kcT4g
[6]http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/scleroderma

This data is out of date. Crest is now systemic sclerosis. It is not necessarily hereditary, the genes that make you susceptible are hereditary, but the environmental trigger is not, i.e. silica exposure, infection, etc. This needs an update. I have the RET of CREST, the telangiectasia can be in other locations besides the nailbeds, you don’t have to have all 5 letters active. Treatment for Raynauds may include 5mg of nifedipine daily and an autoimmune suppressant. (cite: Dr Shahid Malick, MBBS, FRACGP and Dr Martin Devereaux, Rheumatologist.)