Difference Between Text Mining and Data Mining
We live in a digital era where massive amounts of data are collected daily. Terabytes or petabytes of data are generated every day. But, the data in its raw form is of no use, so analyzing such data is important. Data mining helps analyze such massive volumes of data by providing tools to discover knowledge from data. Text mining is a sub-type of data mining that turns untapped text data into valuable resources.
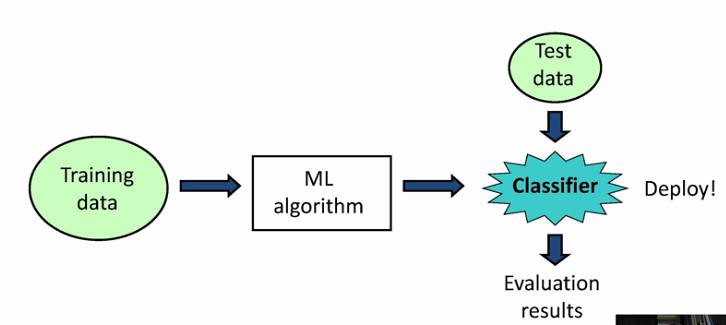
What is Data Mining?
Similar to how gold ore is extracted from the earth in its pure form through mining, data mining is the sorting and extraction of meaningful information or data from large datasets. Data mining typically involves identifying trends or patterns in data that usually go beyond simple analysis procedures using software algorithms and statistical methods. Also known as knowledge discovery in data (KDD), data mining seeks to obtain valuable information from data in order to help answer business questions and predict future trends and behavior.
It can be viewed as a result of the natural evolution of information technology. Simply put, data mining is knowledge mining from data. The data sources can include databases, data warehouses, the World Wide Web, or other information repositories. It can be applied to basically all forms of data including spatial data, graph or networked data, data streams, ordered/sequence data, and text data.
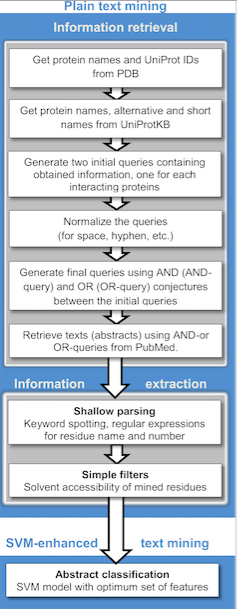
What is Text Mining?
Text mining, also called text data mining, is the process of extracting meaningful insights or information from unstructured text data. It is a sub-type of data mining that involves text – one of the most common data types within databases. Similar to data mining, it seeks to extract useful information from data sources by identifying and exploring patterns in data. In text mining, however, the data sources are restricted to text. It filters large amounts of text data and extracts the relevant you need.
Text mining requires structuring the input text followed by identifying patterns within the structured data, and evaluation and interpretation of the output. A key element of text mining is document collection, which involves grouping of text-based documents. Typically, text mining involves keyword extraction, classification and clustering, document summarization, anomaly and trend detection, and text streams.
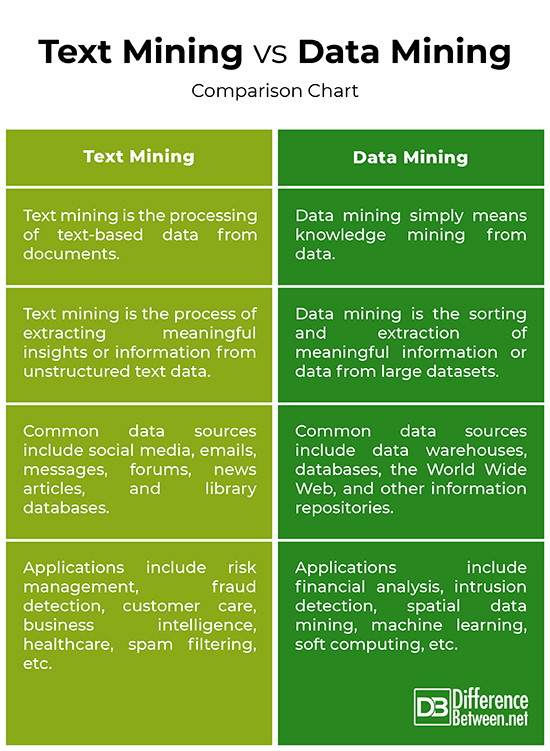
Difference between Text Mining and Data Mining
Meaning
– Data mining is the automated processing of collecting and analyzing large amounts of data sources in order to find meaningful insights or discover hidden patterns from data in a way that provide some valuable information. Data mining simply means knowledge mining from data. Text mining is a part of data mining that seeks to extract useful information from data sources by identifying and exploring patterns in text-based data. Text mining is the processing of text data from documents.
Data Sources
– The different sources of data used in the process of data mining include data warehouses, the World Wide Web, transactional databases, multimedia databases, spatial databases, flat files, and other information repositories. The widely used data sources for text mining include data from sources like social media, emails, messages, product reviews, forums, news articles, library databases, web scraping, and so on.
Mining Methods
– The most important data mining techniques are data collection and cleaning, data preparation, tracking patterns, classification, association, anomaly detection, clustering analysis, regression analysis, and prediction. Some of the most common text mining techniques are information retrieval, text categorization, classification and clustering, document summarization, sentiment analysis, anomaly and trend detection, and text streams.
Text Mining vs. Data Mining: Comparison Chart
Summary
Data mining means sorting and extraction of meaningful information or data from large datasets for the purpose of knowledge discovery. There are many terms with a similar meaning, for example, knowledge mining from data, knowledge discovery, knowledge extraction, data/pattern analysis, and so on. It involves identifying trends or patterns in data that usually go beyond simple analysis procedures using software algorithms and statistical methods. Text mining, on the other hand, is built on various data mining approaches to identify trends in data, except in text mining, data analysis relies on document collection. It makes use of background knowledge to a much greater extent than data mining.
What is text mining with examples?
Text mining is identifying hidden patterns in untapped text data and turning those data sources into actionable insights. Examples of text mining include customer surveys, online reviews, risk management, business intelligence, fraud detection, etc.
What is the difference between text mining and NLP?
While both hold the key to unlocking the business value within the large datasets, NLP is focused on making computers understand human behavior through text, speech, sentiment, and actions. Text mining is simply extracting meaningful insights or information from unstructured text data.
Is NLP a data mining?
NLP is a component of text mining that helps computers to process and analyze large amounts of natural text data. It seeks to extract information from text, like text mining. NLP and data mining are both essential elements in data science.
What are the comparison between data mining text mining and web mining?
Data mining is a collective term for both text mining and web mining. Data mining simply means knowledge mining from data; text mining is extracting meaningful insights or information from unstructured text data; and web mining is to use data mining techniques to discover hidden patterns from the World Wide Web.
- Difference Between El Nino and La Nina - April 13, 2024
- Difference Between an Arbitrator and a Mediator - April 11, 2024
- Difference Between Wire Transfer and EFT - March 21, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Han, Jiawei, et al. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2011. Print
[1]Sanger, James and Ronen Feldman. The Text Mining Handbook: Advanced Approaches in Analyzing Unstructured Data. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 2007. Print
[2]Berry, Michael W. and Jacob Kogan. Text Mining: Applications and Theory. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2010. Print
[3]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/5492/9867971713_ac3c2a1269_c.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Text_mining_protocol.png
