Difference Between Private Cloud and On Premise
If you are looking at cloud hosting solutions for your business and how you might go about deploying those solutions, you have two hosting models to choose from – private cloud and public cloud. A private cloud is a dedicated environment reserved solely for a single business entity or organization. The cloud infrastructure may be managed by the organization or a third party cloud service provider and may exist on premise or off premise. In a private cloud, the services and infrastructure are privately managed and maintained. But how do you know which private cloud model is best for your business – hosted private or on premise? We take a look at some key differences between the two.
What is Private Cloud?
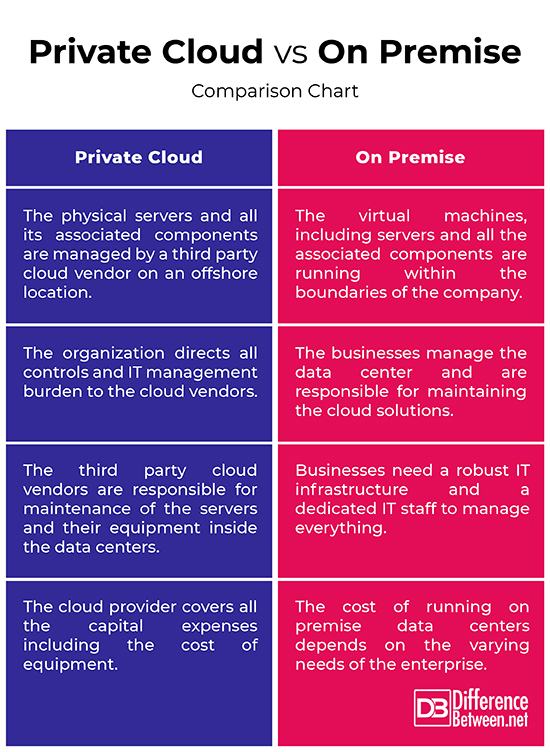
A private cloud, as the name suggests, is a single-tenant environment meaning the cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a single business entity comprising multiple consumers or business units. The IT services are provisioned over private IT infrastructure as a fully-managed service and the services are provided by a third party cloud vendor. These are exclusive cloud offerings dedicated and customized for a single client and the whole infrastructure is labeled as an isolated landscape where you have the entire physical server to yourself. The third part cloud vendor manages everything from maintenance of hardware to software updates, performance monitoring, and security. You have the granular control of server resources such as CPU cores, RAM and storage space. The physical servers that are in physical storage are dedicated to the customer. So, a private cloud is where businesses go to third party cloud vendors who are responsible for maintenance of the servers and their equipment inside the data centers.
What is On Premise Cloud?
The concept of on premise cloud infrastructure is simple – when a business or an organization chooses for on premises, all of its computing resources and the IT infrastructure is located within its premises. It is an in-house private cloud service which allows businesses to collocate all cloud computing equipment on premise, which is either managed by self or some third party cloud vendor. All virtual machines, including servers and the associated components are running within the boundaries of the company. Since the cloud infrastructure is managed on premise, the enterprises are in control of their own destiny because they manage the data center and they are responsible for maintaining the cloud solutions and all its related processes. This offers enterprises more control and security, and they only pay for the resources they use with the flexibility of procuring whatever hardware configuration for their needs.
Difference between Private Cloud and On Premise
Deployment of Private Cloud vs On Premise
– A private cloud is a dedicated environment which may be managed by the organization or a third party cloud service provider. A private cloud can be on premise or hosted in a third party’s data center. In a hosted private cloud, the IT infrastructure is labeled as an isolated landscape where the physical servers and all its associated components are managed by a third party cloud vendor on an offshore location outside the organization’s boundaries. On premise, on the other hand, an in-house private cloud service which allows businesses to collocate all cloud computing equipment on premise.
Cost of Private Cloud and On Premise
When an organization opts for on premise cloud model, all cloud management is performed on premise and they need a robust and sophisticated IT infrastructure of their own. Since the companies manage the data center, they need to invest in the right hardware, servers, and software and storage systems for their business needs. They also need a dedicated IT staff to manage the whole IT infrastructure. So, a hefty sum is required for the procurement of the necessary hardware and the whole setup. With a hosted private cloud, the third party cloud vendors are responsible for maintenance of the servers and their equipment inside the data centers. So, the third party providers bear the cost.
Control of Private Cloud and On Premise
– In an on premise cloud model, the businesses or organizations are in control of their own destiny because they manage the data center and they are responsible for maintaining the cloud solutions and all its related processes. This gives them more control and flexibility to set the terms and customize those terms to meet their business needs. With the hosted private cloud, the business applications and the data are processed and stored outside the boundaries of an enterprise, so the organization directs all controls and management burden over to the cloud service providers.
Private Cloud vs. On Premise: Comparison Chart
Summary
Both hosted private clouds and on premise clouds are a part of managed cloud services where each customer pays only for the resources used. However, hosted cloud is usually provided as hosted service where a third party cloud vendor hosts everything for you either in house or in an offshore location, whereas on premise cloud is a private cloud service where a business or an organization hosts everything on premise. In an on premise environment, the businesses manage the data center and are responsible for maintaining the cloud solutions whereas in a hosted private cloud, the business gives all the controls to the third party cloud vendor.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Bento, Alberto M. and Anil K. Aggarwal. Cloud Computing Service and Deployment Models: Layers and Management. Pennsylvania, United States: IGI Global, 2012. Print
[1]Kavis, Michael J. Architecting the Cloud: Design Decisions for Cloud Computing Service Models (SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS). New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2014. Print
[2]Smoot, Stephen R. and Nam K. Tan. Private Cloud Computing: Consolidation, Virtualization, and Service-Oriented Infrastructure. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2011. Print
[3]Bond, James. The Enterprise Cloud: Best Practices for Transforming Legacy IT. Massachusetts, United States: O'Reilly Media, Inc., 2015. Print
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HybridCloud.png
[5]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/8376/8533881094_167d241e09_b.jpg
