Difference between Primary Storage and Secondary Storage
Data storage is a common term for archiving data or information in a storage medium for use by a computer. It’s one of the basic yet fundamental functions performed by a computer. It’s like a hierarchy of comprehensive storage solution for fast access to computer resources. A computer stores data or information using several methods, which leads to different levels of data storage. Primary storage is the most common form of data storage which typically refers to the random access memory (RAM). It refers to the main storage of the computer because it holds data and applications that are currently in use by the computer. Then, there is secondary storage which refers to the external storage devices and other external media such as hard drive and optical media.

What is Primary Storage?
Primary storage is commonly referred to as simply “primary memory” which is volatile in nature such as the RAM which is a primary memory and tends to lose data as soon as the computer reboots or loses power. It holds data or information that can be directly accessed by the central processing unit. RAM is stored in integrated circuits for immediate access with minimum or no delay. It’s a high-speed data storage medium which is directly connected to the processing unit via the memory bus, allowing active programs to interact with the processor. Simple speaking, primary storage refers to internal storage devices that provide fast and efficient access to data or information. However, it stores data or applications for a short period of time while the computer is running.
Other examples of primary storage include Read Only Memory (short for ROM), which represents both the primary memory of the computer and a non-volatile storage because it’s able to retain data and applications even if the device loses power; PROM (Programmable read-only memory) which is kind of a memory chip that is programmed after the memory is constructed. PROM is a sophisticated version of ROM that can be programmed once after it has been created; and Cache memory which is also a common example of primary storage that is directly integrated with the CPU chip to provide high-speed data access for future requests. It’s more of a volatile memory of the computer that is placed between the CPU and the main memory.
What is Secondary Storage?
Secondary storage is yet another ideal storage solution in the computer’s memory hierarchy that is used to store data or information on the long term basis, more like permanently. Unlike primary storage, they are non-volatile memory or commonly referred to as external memory that are not directly accessed by the central processing unit. They are also called as auxiliary storage which can be both internal and external, plus beyond the primary storage. Because they are not directly accessed by the I/O channels, they are relatively slower than primary storage devices when it comes to data access. However, it’s one of the most valuable assets of data storage hierarchy that is capable of storing applications and programs permanently. Unlike RAM, it’s a long-term storage solution that expands the data storage capability.
Common example of secondary storage includes hard disk drives (HDD) which is the most common data storage device used to store and retrieve digital information. It’s a high-capacity secondary storage device which also comes in internal storage mediums as internal hard drives. It’s one of the most versatile mediums of data storage that uses magnetic storage to archive applications or data permanently. Other examples of secondary storage include optical media such as CDs and DVDs which are capable of storing any substantial amount of data; magnetic tapes which are conventional methods of data storage used across corporate environments. However, secondary storage devices are quite slower than their primary counterparts, which make them relatively cheaper but equally efficient.

Difference between Primary and Secondary Storage
-
Storage
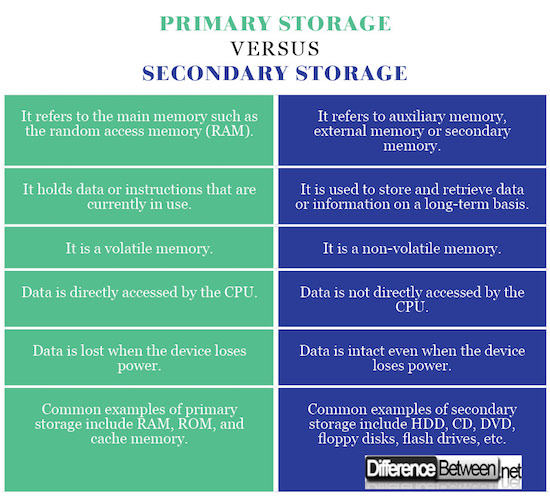
Data storage is the basic functionality of a computer which is divided into primary and secondary storage.
Primary storage refers to the main storage of the computer or main memory which is the random access memory or RAM.
Secondary storage, on the other hand, refers to the external storage devices used to store data on a long-term basis.
-
Access of Primary Vs. Secondary Storage
Primary storage holds data or applications which can be directly accessed by the processing unit with minimum or no delay.
On the contrary, secondary storage is used to store and retrieve data permanently with no delay.
-
Nature of Primary Vs. Secondary Storage
Primary storage is a volatile memory which means data is lost as soon as the device loses power and it cannot be retained. Primary storage is commonly referred to as primary memory such as the RAM.
Secondary storage, commonly known as secondary memory, is a non-volatile memory which is able to retain data even if the device loses power.
-
Device used for Primary Vs. Secondary Storage
RAM is the most common primary storage device which also goes by main memory and is used to store data machine code currently in use. Instructions can be retrieved from the RAM whenever required. It provides fast data access with no delay.
Secondary storage refers to external storage devices such as optical media (CDs and DVDs), hard disk drives (HDD), floppy disks, USB flash drives, etc.
-
Speed of Primary Vs. Secondary Storage
As programs and applications are stored in main memory, primary storage provides fast and efficient access to the CPU.
On the contrary, secondary storage is more of a long-term storage solution with substantial data storage capacity which makes them relatively slower than their primary counterparts.
Primary vs. Secondary Storage: Comparison Chart
While both are integral to data storage hierarchy and provide fast and efficient access to computer resources, they do it very differently. While primary storage offers much faster access than secondary storage devices, it’s only a temporary solution which lacks the ability to store data on a long-term basis. Secondary storage, on the contrary, is an ideal data storage solution which is able to hold millions of files including audio, video, documents, pictures, records, and more. Data stored in secondary storage is usually safe and reliable and is less expensive to maintain than its primary counterpart.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
19 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Blundell, Barry, Nawaz Khan, Aboubaker Lasebae, and Muthana Jabbar. Boston: Cengage, 2007. Print
[1]Patterson, David and John Hennessy. Computer Organization and Design ARM Edition. Burlington: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2016. Print
[2]Worboys, Michael F., and Matt Duckham. GIS: A Computing Perspective (2nd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2004. Print
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Burned_primary_storage.JPG#/media/File:Burned_primary_storage.JPG
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Seagate_Hard_Disk.jpg#/media/File:Seagate_Hard_Disk.jpg

Thanks a bunch really helped with my grades.
Awesome contents…soo helpful
Helpful
Please what i am looking for is not available
Thank you very much this was greatly appreciated, friend. I’ve learned a lot from this and this has assisted me in learning certain terms I was unsure of prior to this. I would love to see more from you!
THIS INFO DOESNE’T HELP ME UNDERSTAND THE RAM AND MEMORY OF A CUMPUTER. THIS SUCKS!!!!!!!!!!!
thanks for the help, I really needed it 🙂
That’s good I appreciate your work
Thank you…I was searching for this. ..it is beneficial specially for students. ..keep it up!
This is a very helpful information Sagar Khillar, you’re the best
This information has really helped me a lot because I couldn’t find any relevant information online THANK YOU FOR YOUR GREAT WORK DONE KEEP IT UP!!!!!!!
I really appreciate for the information..
Wow I really love and appreciate this post
It really helped me to understand both primary and secondary storage
This was good for me , I really understood what is secondary and primary data storage
This is more than awesome
no you are awesome. Mr swag
Thanks for your help really help me
The site is of more use . thank you
In God everything is possible