Difference Between NB-IoT and LoRa
Both NB-IoT and LoRa are low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technologies designed for low power devices, but they serve different commercial and technical requirements in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. Narrowband IoT, commonly goes by NB-IoT is an LTE-based cellular radio access technology that provides low-power wide area (LPWA) connectivity in licensed spectrum. But there are other short-range technologies available in unlicensed spectrum, including LoRa, which has been developed to address vertically different use cases of industrial IoT. Let’s take a look at the technical differences between the two LPWAN technologies.

What is NB-IoT?
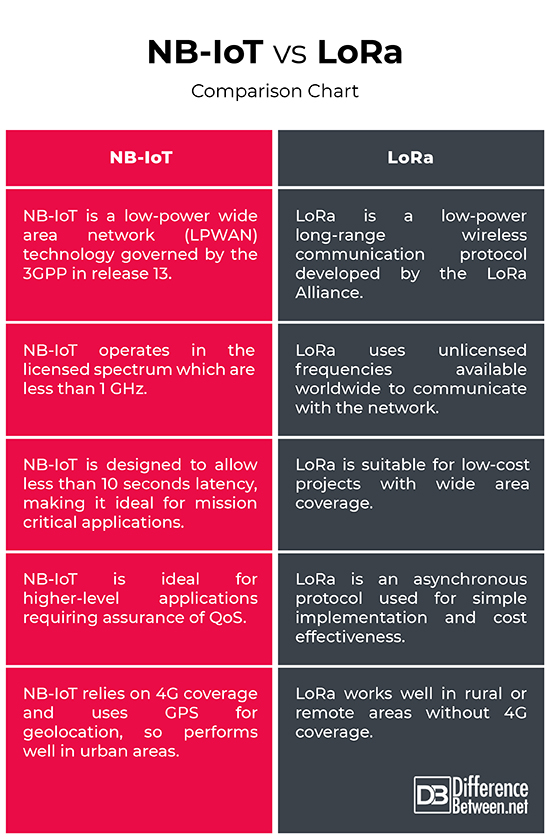
Cat-NB, also known as NB-IoT, or Narrow Band IoT, is a low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technology governed by the 3GPP in release 13 to address the requirements of the Internet of Things (IoT). Like Cat-M1, Cat-NB operates in the licensed spectrum with a goal to provide improved indoor coverage, support for massive number of low throughput devices, low delay sensitivity, low power consumption, low device cost and optimized network architecture. It is based on the Evolved Packet System (EPS) and optimizations to the Cellular Internet of Things (CIoT). Because the channels are narrower than even the 1.4 MHz Cat-M1, cost and power can be further reduced with much simpler designs of the analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters. It operates in half-duplex frequency division duplexing (FDD) with maximum data rate uplink of 60 kbps and downlink of 30 kbps.

What is LoRa?
LoRa, short for long range, is a low-power, long-range wireless communication protocol developed by the LoRa Alliance – a non-profit organization dedicated to the standardization of low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technologies – as a secure, energy-efficient IoT standard. LoRa is a modulation technology for LoRaWAN. LoRaWAN is a LPWAN specification intended for long range communications from base stations with a maximum range of 15-30 km. Bandwidth provided may range from 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps, as dictated by environmental factors. Initially, LoRa was a physical layer modulation developed by a French company named Cycleo. The company was later acquired by another company Semtech and the technology further evolved into a much broader scope, courtesy of the LoRa Alliance. To differentiate from the physical layer modulation called LoRa, the LoRa Alliance uses the term LoRaWAN to refer to its architecture and a LPWAN protocol standard.
Difference between NB-IoT and LoRa
Ecosystem
– While both NB-IoT and LoRa are low-power, wide area network (LPWAN) technologies designed for low-power devices, they boast a different ecosystem. NB-IoT, or Narrow Band IoT, is a low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technology governed by the 3GPP in release 13 to address the requirements of the Internet of Things (IoT). LoRa, on the other hand, is a low-power, long-range wireless communication protocol developed by the LoRa Alliance – a non-profit organization dedicated to the standardization of low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technologies. LoRa is a modulation technology for LoRaWAN – a LPWAN specification intended for long range communications.
Spectrum
– Like Cat-M1, the Narrowband IOT operates in the licensed spectrum but can be deployed in-band within a normal LTE carrier, or standalone for deployments in dedicated spectrum. Since the channel width is so small, it allows the Cat-NB signal to bury inside a larger LTE channel, or replace a GSM channel, or it can even exist in the guard channel of regular LTE signals. LoRaWAN, on the other hand, is a spread spectrum modulation technique designed to facilitate communication between low-power devices and IoT applications. LoRa wireless system uses unlicensed frequencies available worldwide to communicate with the network.
Latency
– One of the key differences between the two LPWAN technologies is their latency. Mission critical IoT applications involve exchange of small and infrequent data packets to/from numerous standalone devices. So, such devices must be implemented with low power consumption without stringent latency requirement. For latency critical applications, NB-IoT is a better choice while LoRa is suitable for low-cost projects with wide area coverage. This is because NB-IoT is designed to allow less than 10 seconds latency and aims to support long battery life, while LoRa can have latency of 10 s of seconds.
Quality of Service
– While both NB-IoT and LoRa are low-power wide area network technologies designed for low-power devices, the NB-IoT has a lower latency compared to LoRa due to the higher device output power, which can provide higher data rates. This means it uses battery faster than LoRa, so it is able to provide cellular-level QoS. The higher-level applications which really need the assurance of QoS, go for NB-IoT, while the low-end business solutions prefer LoRa. LoRa is an asynchronous protocol used for simple implementation and cost effectiveness but cannot offer a better QoS.
NB-IoT vs. LoRa: Comparison Chart
Summary
While both NB-IoT and LoRa are low-power wide area network technologies designed for low-power devices, they serve different commercial and technical requirements and are used exclusively for different applications. While the Narrowband IoT uses licensed bands which are less than 1 GHz, LoRa works with unlicensed spectrum below 1 GHz which procures no cost for the applications using it. NB-IoT can be deployed within existing LTE bands, leveraging the spectrum between two “standard” adjacent LTE frequency carriers. Also, it can be used standalone, providing easy migration path for the GSM/GPRS/EDGE spectrum. The higher-level applications which really need the assurance of QoS, go for NB-IoT, while the low-end business solutions prefer LoRa.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:WhisperNode_LoRa.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://ca.wikipedia.org/wiki/NB-IoT#/media/Fitxer:The_structure_of_cell_mobile_station.JPG
[2]Mahmood, Zaigham. Connected Environments for the Internet of Things: Challenges and Solutions. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2018. Print
[3]Gravina, Raffaele, et al. Integration, Interconnection, and Interoperability of IoT Systems. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2017. Print
[4]Ahmadi, Sassan. 5G NR: Architecture, Technology, Implementation, and Operation of 3GPP New Radio Standards. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Academic Press, 2019. Print
[5]Hanes, David, et al. IoT Fundamentals: Networking Technologies, Protocols, and Use Cases for the Internet of Things. Indianapolis, Indiana: Cisco Press, 2017. Print
