Difference Between Infectious Colitis and Gastroenteritis
What are Infectious Colitis and Gastroenteritis?
Both are conditions of the abdomen caused by the bacteria, viruses.
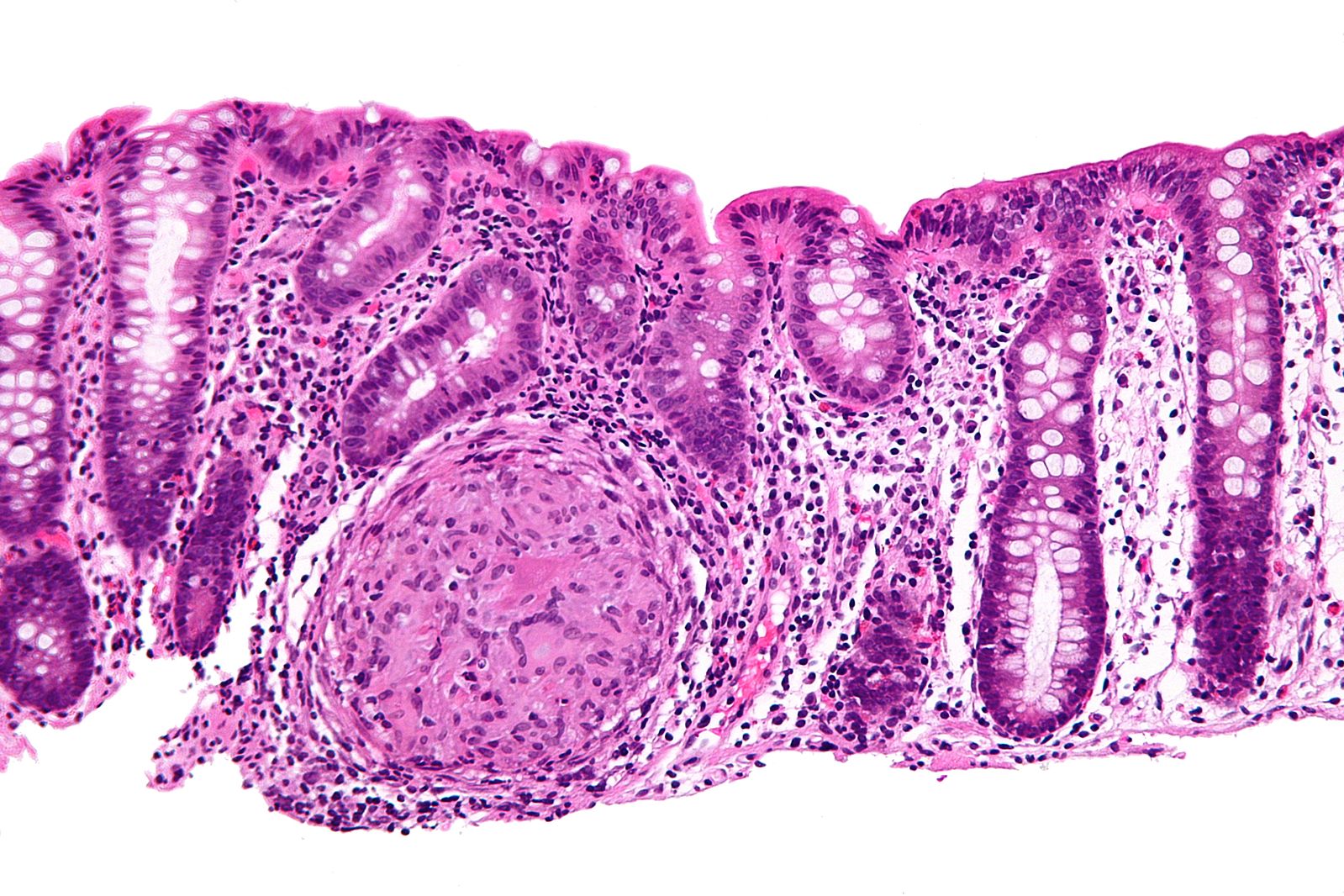
Infectious colitis is basically the irritation and swelling of the colon (large intestines). Primary symptoms include diarrhea with or without dysentery and chronic inflammation of the colon as can be seen using colonoscopy.
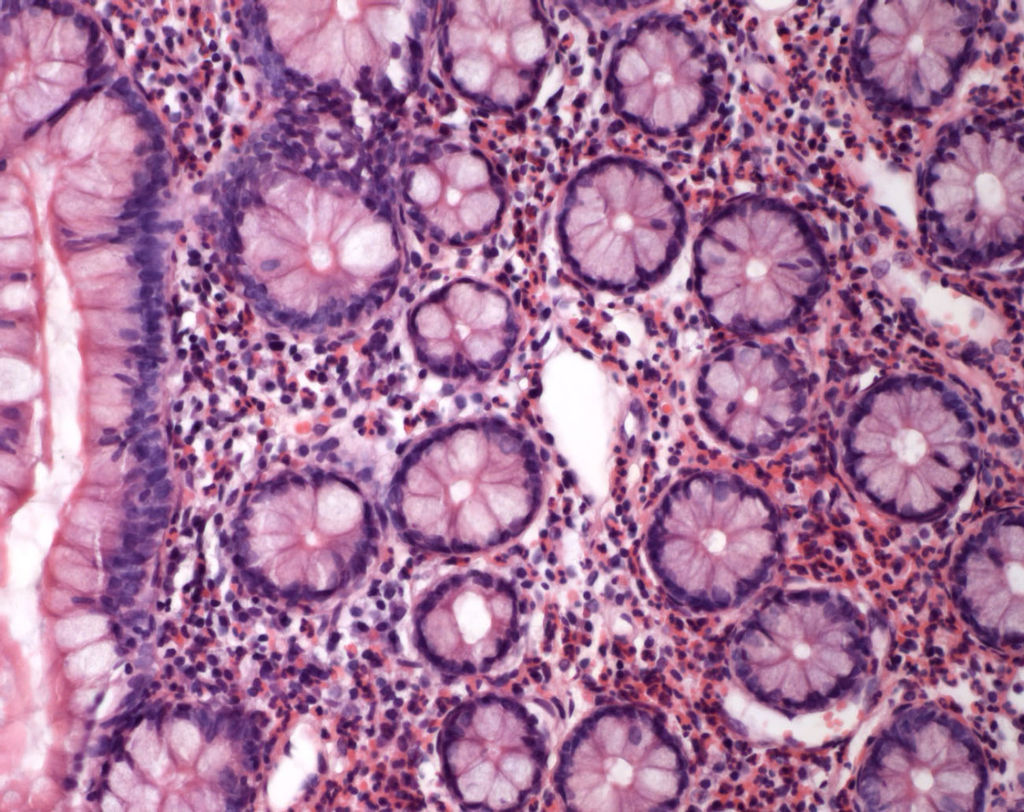
Gastroenteritis is also called stomach flu and is caused mostly by food poisoning, viral enteritis or traveler’s diarrhea. Symptoms include cramps, nausea, vomiting.
Similarity
Both conditions can occur in the abdomen and are mostly triggered by bacterial and viral infections
Infectious colitis
Infectious Colitis is a medical condition in which the large intestines (also called as colon) becomes inflamed.
Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis – also termed as stomach flu is a medical condition that refers to the infection of the gut and inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract (the intestines and the stomach). Several symptoms include – food poisoning, tummy bug, traveler’s diarrhea, viral enteritis or intestinal flu.
Difference between Infectious colitis and gastroenteritis (stomach flu)
Description
Infectious colitis
Infection, irritation and inflammation of colon is referred to as infectious colitis.
Gastroenteritis
Infection, irritation and inflammation of the gastrointestinal gut is referred to as Gastroenteritis.
Signs and symptoms
Infectious colitis
- Diarrhea (accompanied by pus and blood)
- Rectal pain and bleeding
- Loss of weight
- Eye inflammation
- Fatigue
- Inability to defecate despite urgency
- Weight loss
- Canker sores
Gastroenteritis (stomach flu)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain in stomach and cramping
- Appetite loss
- Chills and high temperature (fever)
- Poor appetite and feeding in children
- Muscle pains and headache
- Fatigue and general body weakness
- Loss of control over bowel motions (Incontinence)
- Dehydration, (dry skin and a dry mouth)
Causes
Infectious colitis
Colitis (col=colon + itis=inflammation) is basically the colon infection. Causes of this medical condition include;
Common bacteria causing bacterial colitis include Shigella, Yersinia enterocolitica, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Common causes of viral colitis include Norovirus, Rotavirus, Adenovirus, and.
- Bacterial infection caused by bacteria like Clostridium difficile, Escherichia coli, Campylobacter Jejuni and Salmonella. Viral colitis is triggered by Cytomegalovirus, Norovirus, Adenovirus and Rotavirus. Some parasitic agents also can cause the infection;
- People suffering from Crohn’s disease inflammatory bowel disease) and ulcerative colitis;
- Reduced supply of blood which results in ischemic colitis;
- Allergic reactions;
- Microscopic colitis (collagenous/lymphocytic colitis);
Gastroenteritis
The primary cause of gastroenteritis (stomach flu) is a bacterial or viral infection, and rarely (less common) is parasitic infection.
The viruses responsible for viral infection include rotavirus and norovirus (both children and adults are affected by noroviruses). The bacterial agents which cause bacterial gastroenteritis include – Escherichia coli, Salmonella (mostly affects the intestinal tract) and Campylobacter. Giardia (microscopic parasite) is responsible for causing parasitic gastroenteritis.
People most at risk
Infectious colitis
The people most at risk of infectious colitis are:
- People who smoke
- People suffering from stress and depression
- People taking hormonal medications
- Identical twins
- Children growing up in relatively sterile environments
- Occur in individuals who:
- In their childhood live with pets
- Are brought up in a rural area
- Have a big family
- Consume unpasteurized milk
- Women who take oral contraceptives and suffer from Crohn’s disease
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) such as ibuprofen and aspirin, may also trigger Colitis.
- A lack of vitamin D from decreased sunlight exposure may elevate the risk of colitis.
- Air pollution exposure in kids and young adults as it damages the intestinal microbiome.
Gastroenteritis
The people most at risk of gastroenteritis are:
- Small babies and young kids who have a weak immune system
- The senior citizens, whose immune system does not work with efficiency, and older people especially who reside in rest homes.
- School going children who live in dormitories
- Children in afterhours or day care,
- People with HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)/AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) or receiving chemotherapy
- Traveler’s
Foods that cause these conditions
Infectious colitis
Foods that trigger inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s Disease) include whole grain foods (quinoa, oats, wild rice, buckwheat), fried foods, high fiber foods (corn, seeds, nuts), red meat. Alcohol, Sulphur-rich foods,
Gastroenteritis
- Escherichia coli (E- Coli) present in salads and ground beef
- Yersinia (causes acute stomach illness) found in pork
- Staphylococcus (type of bacteria that live on the skin and mucous membranes) found in dairy products, eggs and meat
- Shigella (very contagious and causes diarrhea (sometimes bloody) found in water (often swimming pools)
- Salmonella (a type of food poisoning), found in meat, dairy products, and eggs.
- Campylobacter (the most common bacterial cause of diarrheal illness), present in meat and poultry.
Summary
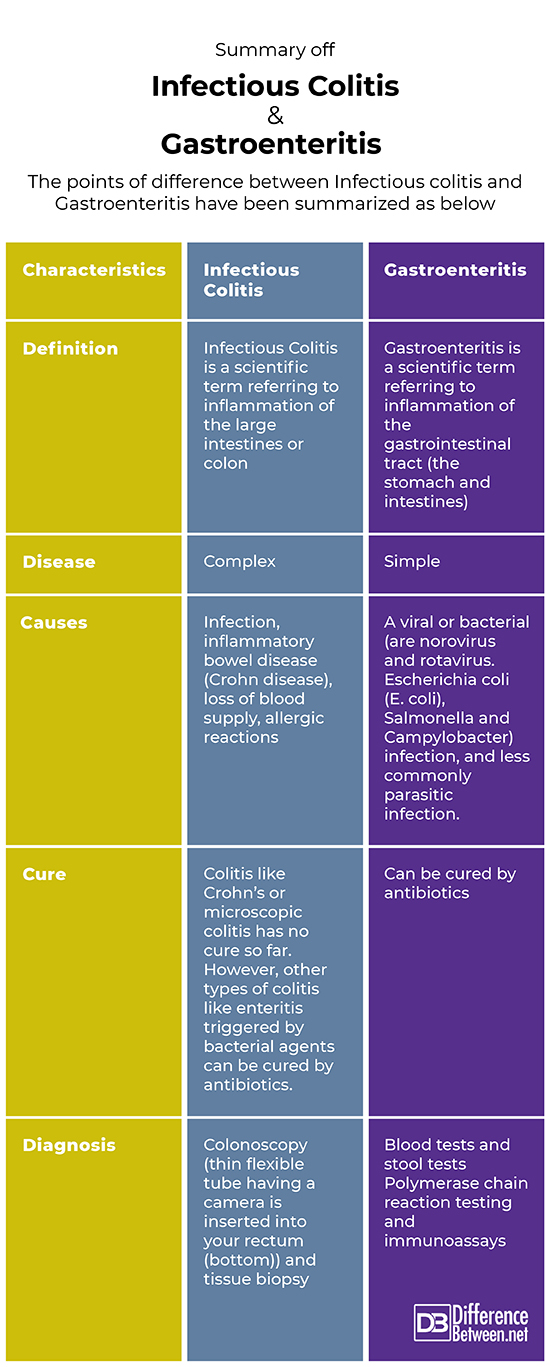
The points of difference between Infectious colitis and Gastroenteritis have been summarized as below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Ji, J., Huang, Y., Wang, X. F., Ma, Z., Wu, H. G., Im, H., ... & Li, J. (2016). Review of clinical studies of the treatment of ulcerative colitis using acupuncture and moxibustion. Gastroenterology research and practice, 2016.
[1]Rodríguez, L. A. G., Ruigómez, A., & Panés, J. (2006). Acute gastroenteritis is followed by an increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology, 130(6), 1588-1594.
[2]Sattar, S. B. A., & Singh, S. (2019). Bacterial Gastroenteritis. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
[3]Sninsky, C. A. (2010). New Research in Ulcerative Colitis: Optimizing 5-ASA Administration for Efficacy and Adherence. Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 6(1 Suppl 1), 4.
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gastroenteritis_virica.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Crohn%27s_disease_-_colon_-_high_mag.jpg
