Difference Between Acute and Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
What is Acute and Chronic Asthma Exacerbation?
Asthma is defined as a serious inflammatory disorder of the airways associated with the airways hyperresponsiveness and airflow obstruction that is often reversible either spontaneously or with treatment.
Asthma Exacerbations are of two types – Acute Asthma Exacerbations and Chronic Asthma Exacerbations. Acute Asthma Exacerbations are sudden in onset and Chronic Asthma Exacerbations are a long-term syndrome.
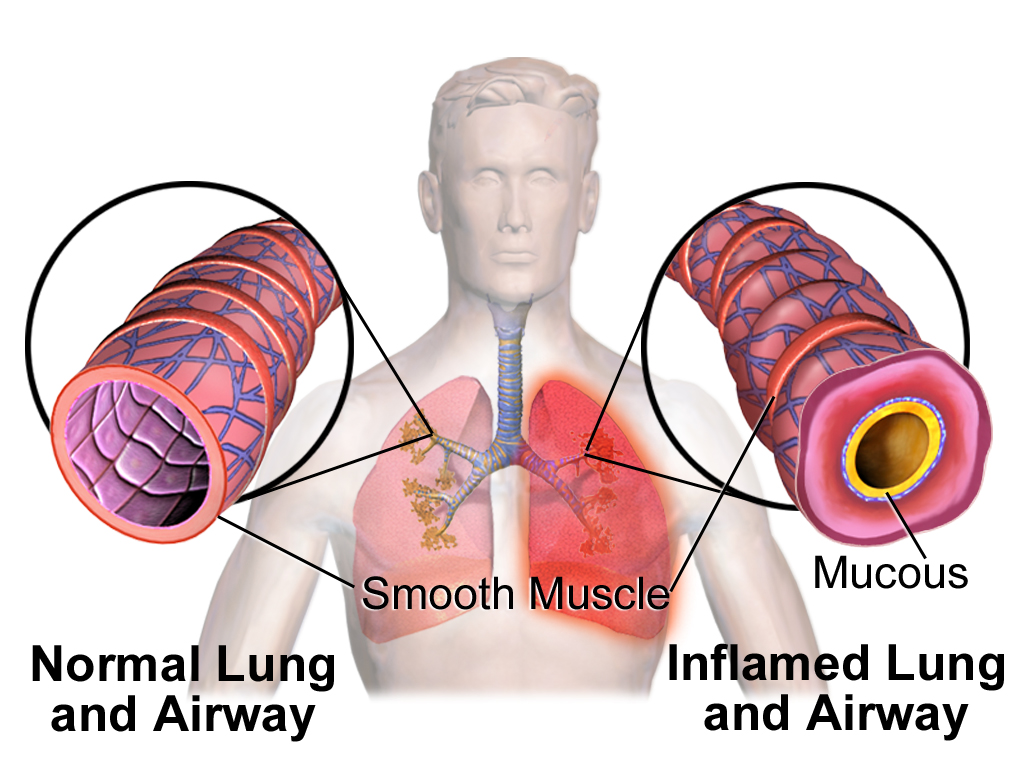
Acute Asthma Exacerbation
Acute Asthma Exacerbation happens when there is a sudden episode of progressive worsening of symptoms of asthma, like wheezing, chest tightness, cough, and shortness of breath. Triggers include
Acute exacerbations can be triggered by a variety of things. Some of the more common triggers are:
- Colds, dry and cold air
- Upper respiratory infections
- Allergens such as mold, dust mites, and pollen
- Smoke of tobacco
- Exercise
- Cats and Dogs
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
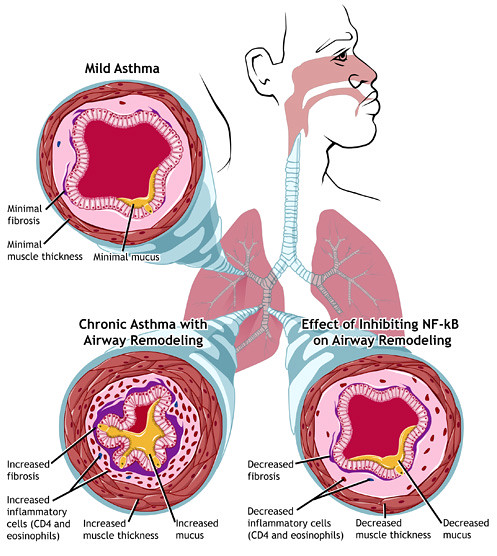
Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
Chronic Asthma Exacerbation happens when the asthma symptoms are intense and there is chronic inflammation and narrowing of the airways in the lungs. In chronic asthma, an asthma attack, is called a flareup or exacerbation. Triggers include:
- Respiratory viral infection, mainly rhinovirus
- Sensitizing agents
- Allergens like pollen, cockroach droppings, weeds, animals, mold, grass, and dust mite
- Air pollution, chemical fumes, household cleaners, strong alcoholic perfumes or other substances in the air
- Stress and anxiety
- Some medications like aspirin and other NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as naproxen and ibuprofen. Some beta-blockers – which treat glaucoma, high blood pressure, heart disease, and migraine
- Illness like severe sinusitis (inflammation of sinuses), flu, heartburn and acid reflux
Difference between Acute and Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
Definition
Acute Asthma Exacerbation
Sudden in onset
Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
Long – developing syndrome
Key features
Acute Asthma Exacerbation
Key Features of Acute Asthma are
- IgE production
- Mucus Hypersecretion
- Airway Hyperactivity
- Eosinophilic inflammation in the pun g
Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
Key features of Chronic Asthma are
- Smooth muscle hypertrophy
- Fibrosis and remodelling
- Epithelial cell changes
- Goblet cell metaplasia
Symptoms
Acute Asthma Exacerbation
- Agitation
- Increase in heart rate
- Reduced lung function
- Hyperventilation
- Difficulty in difficulty speaking or breathing
Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
- Tightened neck and chest muscles, called retractions
- Chest tightness or pressure
- Constant coughing
- Feelings of anxiety or panic
- Feel confused, lost, agitated and unable to focus
- Very rapid breathing
- Severe wheezing when breathing both in and out
- Difficulty and discomfort in talking
- Pale, sweaty face
- Bluish tint to your lips
- Hunched shoulders, and strained muscles in the neck and stomach
Causes
Acute Asthma Exacerbation
- An overly sensitive immune system that makes the bronchial tubes become inflamed and swollen when you’re exposed to certain triggers. Asthma triggers vary from person to person.
- Common acute asthma attack triggers include: Mold, pollen, pets, and dust mites.
Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
- Lung infections, such as a cold or the flu
- Strong emotions and stress
- Smoke inhalation
- Preservatives added to some types of foods and beverages
- Certain medications, including aspirin, beta-blockers, naproxen, and ibuprofen
- Menstrual cycle in some women
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Subset – Life threatening
Acute Asthma Exacerbation
Dyspnea interferes with or limits usual activity
Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
Too dyspneic to speak, perspiration
Clinical Course
Acute Asthma Exacerbation
- Usually needs frequent visits to emergency department and even hospitalization
- Oral systemic corticosteroids; some symptoms last for greater than 3 days after the start of treatment
- Partial relief and comfort from frequently inhaled Short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs) like albuterol and levalbuterol
- Adjunctive therapies are beneficial
Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
Hospitalization, emergency visits and even intensive care unit (ICU)
- Very less or no relief and comfort from frequently inhaled Short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs) like albuterol and levalbuterol
- Intravenous corticosteroids – Fluticasone (Flovent HFA), Budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler), Mometasone (Asmanex Twisthaler), Beclomethasone (Qvar RediHaler), Ciclesonide (Alvesco)
- Adjunctive therapies are sometimes helpful
Summary of Difference between Acute vs Chronic Asthma Exacerbation
The points of difference between Acute Asthma exacerbation and Chronic Asthma exacerbation have been summarized as below:

- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Camargo Jr, C. A., Rachelefsky, G., & Schatz, M. (2009). Managing asthma exacerbations in the emergency department: summary of the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert Panel Report 3 guidelines for the management of asthma exacerbations. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society, 6(4), 357-366.
[1]Dougherty, R. H., & Fahy, J. V. (2009). Acute exacerbations of asthma: epidemiology, biology and the exacerbation‐prone phenotype. Clinical & Experimental Allergy, 39(2), 193-202.
[2]Pollart, S. M., Compton, R. M., & Elward, K. S. (2011). Management of acute asthma exacerbations. American family physician, 84(1).
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/92/Blausen_0620_Lungs_NormalvsInflamedAirway.png
[4]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4011/5081431722_12ebc9227b_z.jpg
