Difference Between the Amygdala and the Prefrontal Cortex
Both the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex are crucial brain parts in facilitating emotions, memories, and actions. For instance, they work together concerning the stress response system; the amygdala signals the presence of stress or threat and the prefrontal cortex assists the amygdala in assessing the situation in a less threatening perspective, which is crucial in feeling calm (Bezdek & Telzer, 2017). The amygdala is generally responsible for emotional responses, memories, and stress detection. On the other hand, the prefrontal cortex is involved in regulating executive functions, emotions, stress responses, and personality development. The following discussions further delve into their distinctions.
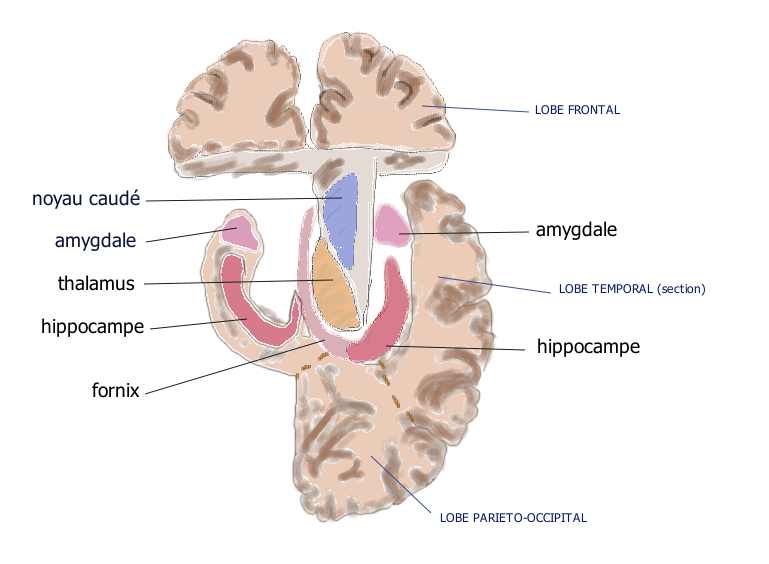
What is the Amygdala?
“Amygdala” came from the Greek word “amugdalē” which means “almond”. It is an almond-like shaped structure situated in the medial temporal lobe; it is the size of a small kidney bean in the middle of the brain. It is a paired structure (one in each brain hemisphere) which is a part of the limbic system.
The amygdala has various functions; some of them include the following:
Detects Stress
The amygdala can detect both emotional stressors (stimuli that can cause anxiety, sadness, etc.) and biological stressors (stimuli causing illness or injury). It alerts us if something is scary or dangerous. It drives our flight or fight response. Hence, this function is crucial for survival (Bezdek & Telzer, 2017). However, if the amygdala is overstimulated, it can lead to “amygdala hijack”; this happens when people have “lost it” or have lost control of their emotions and actions, which usually causes regrettable behavior.
Help Regulates Emotion
The amygdala plays a key role in various emotions; its different parts are involved in triggering fear, aggression, and peacefulness (Open Learn, 2020).
Encodes memories
A research implies that direct stimulation of the amygdala enhances image recognition. In addition, it is the storehouse of emotional memories; it seems to tag an emotive experience so that it is better recalled. From an evolutionary point of view, emotionally heightened events are the ones that are often linked with survival (Sukel, 2018).
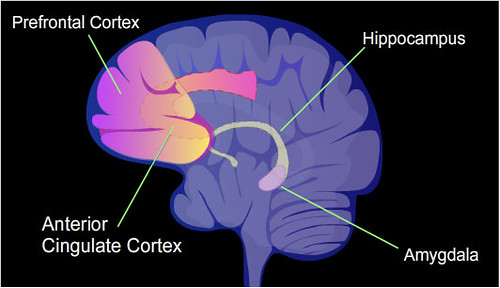
What is the Prefrontal Cortex?
The prefrontal cortex, as its name suggests, is the anterior part of the frontal lobe. This big region in front of the brain has various functions; several of them include the following:
Control Center/ Executive function
The prefrontal cortex controls actions and thoughts; it is involved in planning complex cognitive behavior, working memory, expressing one’s characteristics, making choices, and facilitating social behavior. It is responsible for the moderation of emotions, conflicting goals, attention, delay of gratification, and the reflection of future consequences.
Regulates Stress and Emotions
The prefrontal cortex regulates stress responses; it helps the amygdala to perceive tense situations as less frustrating or dangerous. It has a significant role in making people feel calm during stressful events.
Personality Development
The prefrontal cortex plays a role in how we make conscious decisions based on our motivations. Overtime, such tendencies lead to the manifestation of traits such as being sociable, hardworking, or fearful; indeed, this brain part contributes to the development of complex attitudes. Most neurologists would agree that our prefrontal cortices do not fully mature until around the age of 25; this is one of the physiological explanations why younger individuals tend to make rash decisions or display more aggressive behavior than their older counterparts (Good Therapy, 2021).
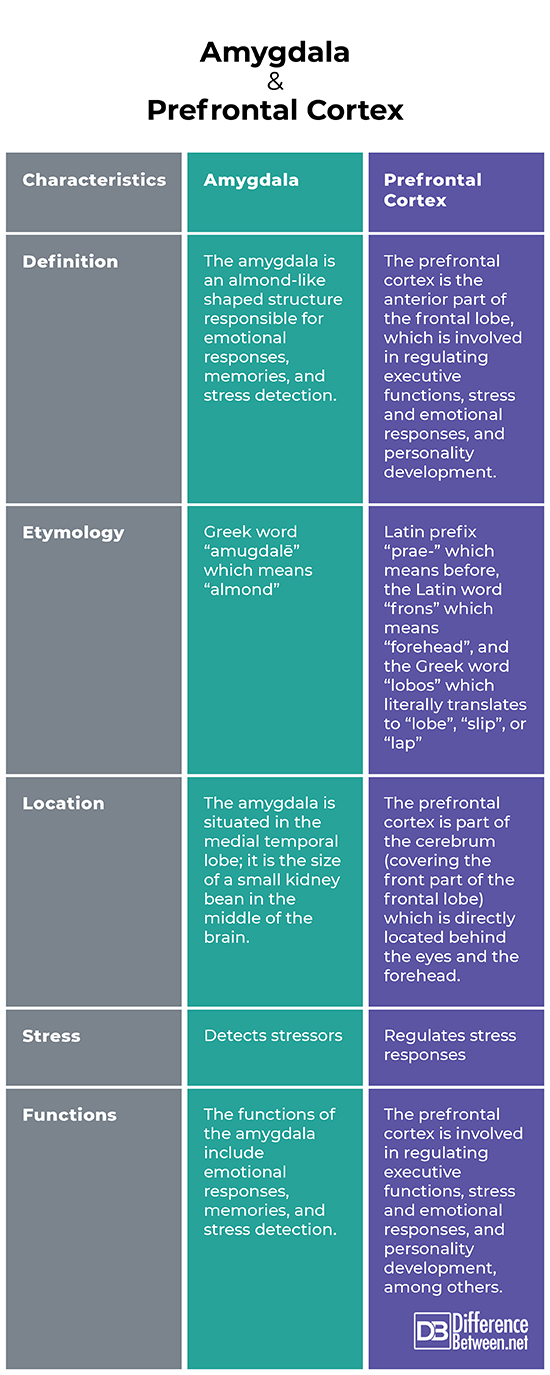
Difference between Amygdala and the Prefrontal Cortex
Definition
The amygdala is an almond-like shaped structure responsible for emotional responses, memories, and stress detection. On the other hand, the prefrontal cortex is the anterior part of the frontal lobe, which is involved in regulating executive functions, stress responses, and personality development.
Etymology
“Amygdala” came from the Greek word “amugdalē” which means “almond”. In comparison, “prefrontal cortex” came from the Latin prefix “prae-” which means before, the Latin word “frons” which means “forehead”, and the Greek word “lobos” which literally translates to “lobe”, “slip”, or “lap”.
Location
The amygdala is situated in the medial temporal lobe; it is the size of a small kidney bean in the middle of the brain. A paired structure (one in each brain hemisphere) is a part of the limbic system. On the other hand, the prefrontal cortex, as its name suggests is covering the front part of the frontal lobe. This part of the cerebrum is directly located behind the eyes and the forehead.
Stress
Regarding stress, the amygdala can detect both emotional (stimuli that can cause anxiety, sadness, etc.) and biological (stimuli causing illness or injury) stressors. It alerts us if something is scary or dangerous. As for the prefrontal cortex, it regulates stress responses; it helps the amygdala to perceive tense situations as less frustrating or dangerous. It has a significant role in making people feel calm during stressful events.
Functions
The amygdala has several functions, some of them include the initiation of emotional responses (i.e., triggering fear, aggression, etc.), recalling information (tags emotional experiences so that they are better recalled), and stress detection (It drives our flight or fight response). On the other hand, the prefrontal cortex is involved in a number of processes such as regulating executive functions (controls actions and thoughts), moderating emotions, stress responses (it helps the amygdala to perceive tense situations as less frustrating or dangerous) and personality development (i.e., the manifestation of traits such as being sociable, hardworking, or fearful).
Amygdala vs Prefrontal Cortex
Summary
- Both the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex are crucial brain parts in facilitating emotions, memories, and actions.
- The amygdala is an almond-like shaped structure responsible for emotional responses, memories, and stress detection.
- The prefrontal cortex is the anterior part of the frontal lobe, which is involved in regulating executive functions, stress and emotional responses, and personality development.
- The amygdala is situated in the medial temporal lobe; it is the size of a small kidney bean in the middle of the brain.
- This prefrontal cortex is directly located behind the eyes and the forehead.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Bezdek, K. & Telzer, E. (2017). Have no fear, the brain is here! How your brain responds to stress. Frontiers for Young Minds. https://kids.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/frym.2017.00071#:~:text=Amygdala%3A%20%E2%86%91%20The%20brain%20structure,stress%20by%20regulating%20the%20amygdala.
[1]Good Therapy. (2021). Prefrontal cortex. https://www.goodtherapy.org/blog/psychpedia/prefrontal-cortex
[2]Open Learn (2020). The amygdala and emotion. https://www.open.edu/openlearn/health-sports-psychology/health/emotions-and-emotional-disorders/content-section-2.4
[3]Sukel, K. (2018). Beyond emotion: Understanding the amygdala’s role in memory. Dana Foundation. https://www.dana.org/article/beyond-emotion-understanding-the-amygdalas-role-in-memory/#:~:text=The%20amygdala%20may%20be%20best,a%20pivotal%20role%20in%20memory.
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Amygdala_hippocampus.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/1452/24024310606_215e426a02.jpg
