Difference Between 5 Dextrose Saline and Dextrose Saline
What are 5 Dextrose and Dextrose Saline?
Both 5 Dextrose and Dextrose saline are sugar solutions that are dispensed into the vein or veins. That is why they are called intravenous sugar solutions. These intravenous sugar solutions aid in the substitution of body fluids and are source of carbohydrates in the body.
Both 5 Dextrose and Dextrose saline sugar solutions are sterile, nonpyrogenic and composed of dextrose. The major difference between the two is the presence or absence of Sodium Chloride (NaCl).
However, avoid dextrose in case of high blood sugar, low potassium levels in the blood, swelling in the arms, feet, or legs and when fluids build up in the lungs.

What is 5 dextrose?
5 dextrose is 5 percent dextrose which is a mixture of dextrose and water. 5 dextrose is an intravenous sugar solution that is composed of 5 gms of dextrorotatory form of glucose dissolved in 100 ml of H2O. Since it is a solvent in water, so it is called an aqueous solution. Movement of water out of the cell is exactly balanced by movement of water into the cell and that is why it aids as an isotonic solution soon after it is administered into the body. But at a later stage, it acts as a hypotonic solution (In a hypotonic solution, the total molar concentration of all dissolved solute particles is lesser than that of another solution or lesser than that of a cell). The reason for this is the cell metabolization supported by the dextrorotatory glucose molecules. This alleviates the concentration of dextrorotatory form of glucose in the D5W, making it a hypotonic solution. 5 dextrose is not pyrogenic i.e. it does not cause excessive heat in the body.
5 dextrose aids in Parenteral Fluid Therapy. This kind of therapy is administered to patients who are hypovolemic and the Fluid therapy with crystalloid solutions is utilized to resuscitate such patients to correct free water deficits in case of patients suffering from dehydration, to replace ongoing fluid losses, and to meet the fluid requirements of patients who are unable to take fluids orally. 5 dextrose is a source of nutrient enrichment in the form of calories and carbohydrates. It is used to treat low blood sugar or fluid loss (dehydration). Examples of low blood sugar symptoms include fatigue, confusion, heart palpitations and sweating.
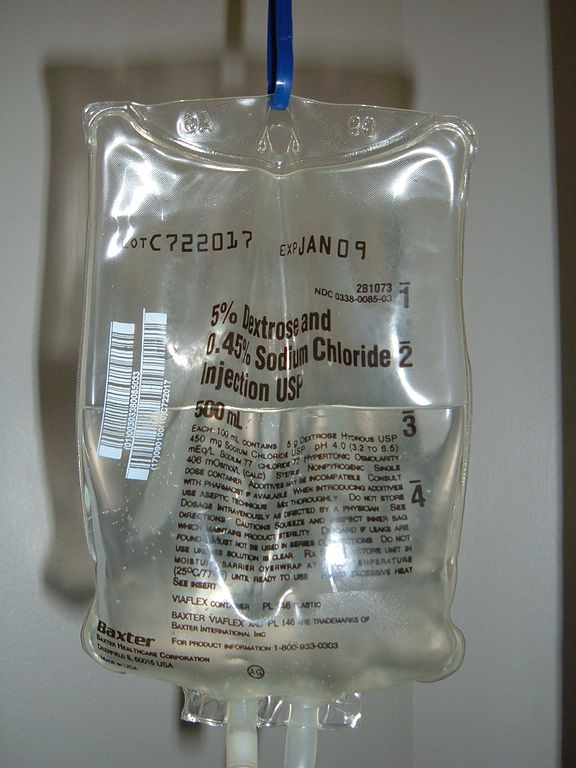
What is Dextrose saline ?
Dextrose saline is a mixture of dextrorotatory form of glucose, NaCl, and H2O. It contains 5% dextrorotatory form of glucose and NaCl dissolved in H2O. The NaCl content varies based on the usage. This saline solution is a sterile solution which enters the body through intravenous administration
Dextrose saline aids in electrolyte nourishment in the body. So, it is also one of the parenteral fluid. It comprises of 100 ml of H2O, 5 percent dextrorotatory form of glucose and 0.45 gms of NaCl. Dextrose saline is hypertonic. That means it has the highest pressure exerted to pass through the semipermeable membrane. Thus, when it is administered to the veins, it enters the body and offers nourishment in the form of carbohydrates, H2O and electrolytes. NaCl is present in the form of Na+ ions and Cl– ions. Na ion is the main cation of the extracellular solution in cells. Cl ions are beneficial for cells in order to maintain the absorbing action. Hence, dextrose saline is very important as a source of these ions.
Difference between 5 Dextrose and Dextrose saline
-
Definition
5 dextrose
It is an intravenous sugar solution which comprises of glucose and water.
Dextrose saline
Dextrose saline is a mixture of 5% dextrose with sodium chloride and water.
-
Chemical composition
5 dextrose
5 Dextrose means 5% dextrose and is also known as D5W. It is composed of water and 50 gms of glucose
Dextrose saline
It is composed of dextrose, Sodium Chloride (NaCl) and water. The NaCl content varies depending on the application.
-
Types
5 dextrose
5% dextrose in H2O is packed as an isotonic solution (A solution is isotonic when it has the same concentration of solutes like the other solution across a semipermeable wall) but becomes hypotonic (A solution is hypotonic when water is less-concentrated than the cell, the water surrounds) once it enters the body because the glucose (solute) that mixes in sterile water exhibits metabolism action by the body cells.
Dextrose saline
Dextrose saline is hypertonic (A hypertonic solution is one in which the concentration of solutes is greater in the exterior of the cell than the interior of it).
-
Importance
5 dextrose
5 dextrose provides carbohydrates and calories (10% of daily requirements)
Dextrose saline
Dextrose saline is a source of electrolytes.
-
Osmolarity
5 dextrose
Osmolarity is about equal to serum, expands intravascular compartment.
Dextrose saline
Osmolarity is greater than the serum, draws fluid into the intravascular compartment through the cells and interstitial compartments.
-
Uses
5 dextrose
It is used to treat low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), insulin shock, or fluid loss (dehydration). It offers nutritional support to patients who are not able to eat because of illness, injury, or any other medical condition.
Dextrose saline
Dextrose saline is an important source of electrolytes like Sodium (Na) and Chloride (Cl) ions. This solution contains no anti-microbial agents.
Summary of 5 Dextrose Vs. Dextrose saline: Comparison Chart
The points of difference between 5 dextrose and Dextrose saline have been summarized below:

- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
3 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/20/Glass_IV.jpg/576px-Glass_IV.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/01/Baxter_dextrose_and_sodium_chloride_injection_USP.JPG/576px-Baxter_dextrose_and_sodium_chloride_injection_USP.JPG
[2]Floss, K., & Borthwick, M. (2018). Intravenous fluid therapy—background and principles. Stroke, 13, 57.
[3]Hoorn, E. J. (2017). Intravenous fluids: balancing solutions. Journal of nephrology, 30(4), 485-492.
[4]Tsui, B. C., Kropelin, B., Ganapathy, S., & Finucane, B. (2005). Dextrose 5% in water: fluid medium for maintaining electrical stimulation of peripheral nerves during stimulating catheter placement. Acta anaesthesiologica scandinavica, 49(10), 1562-1565.

What are the injection used to a diarrhea patient
Benvolent
Your note is excellently pithy
What are medication for piles